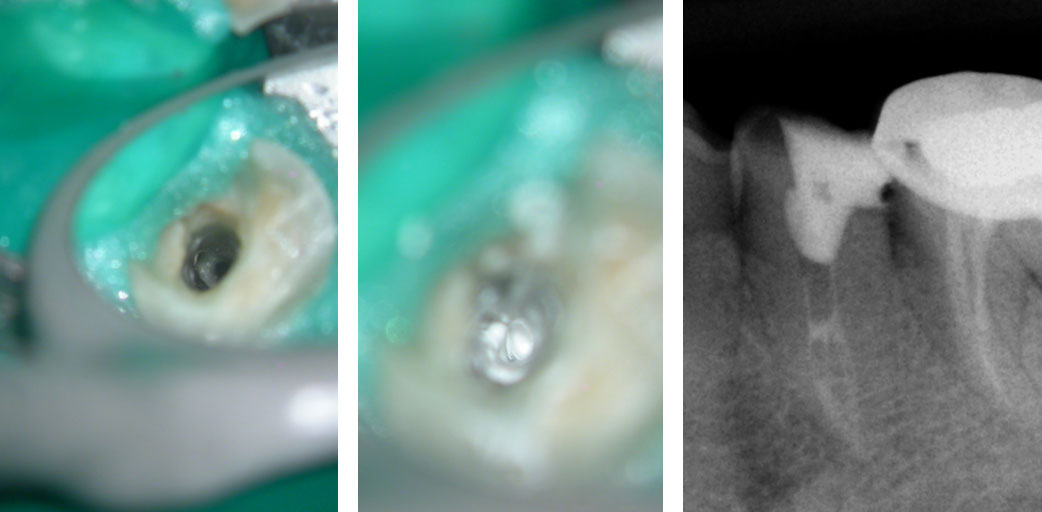

Clinical Case
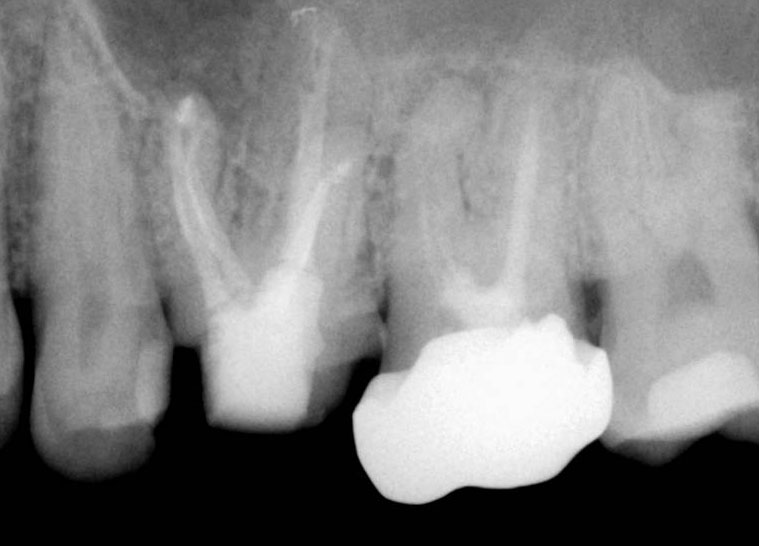
Pre-op
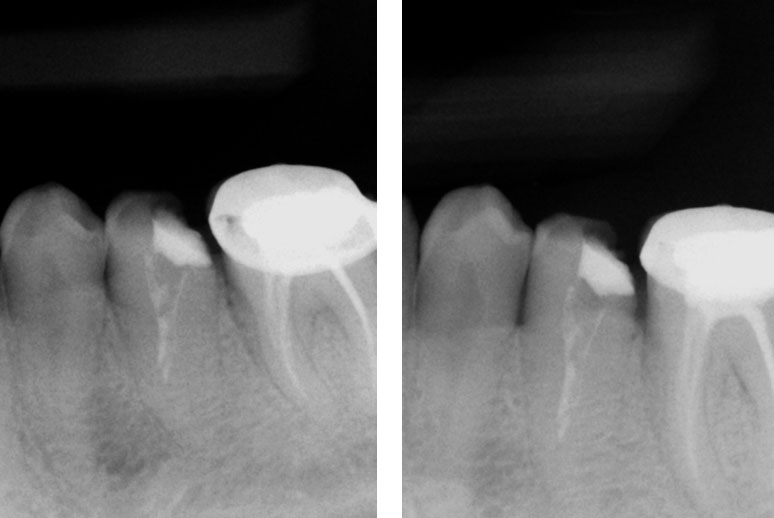
History of persistent swelling in the maxillay first molar despit repeated calcium hydroxide dressings. Patient has undergone multiple “open” and “closed dressings”.
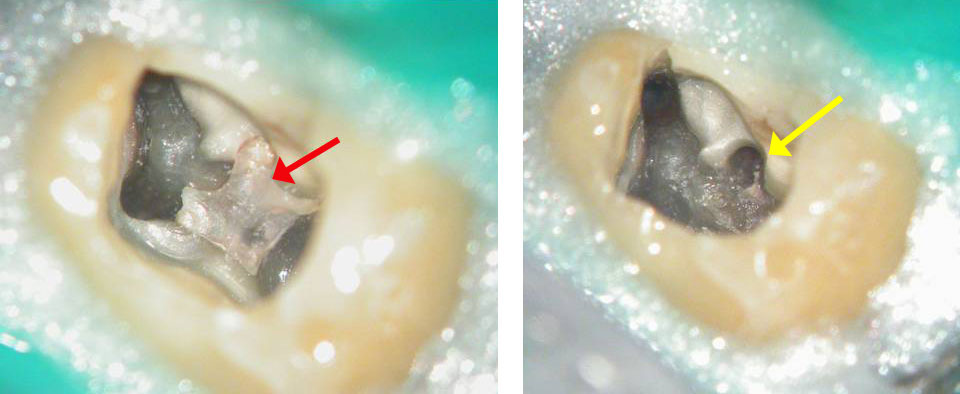
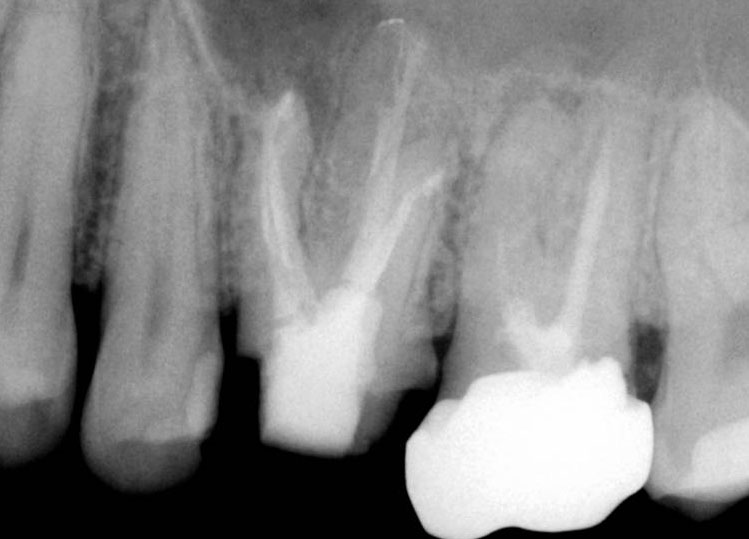
Red arrow shows calcification covering the MB2. Removal of this calcification with ultrasonics reveals the missed MB2(yellow arrow)
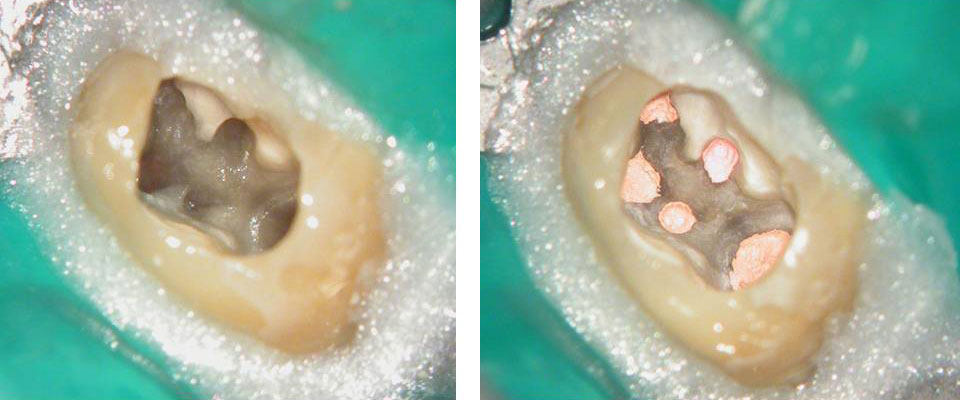
5 canals cleaned, shaped and obturated after 10 days of calcium hydroxide. MB1 and MB2 had seperate portals of exit. DB2 merged intoDB1. Palatal two portals of exit.
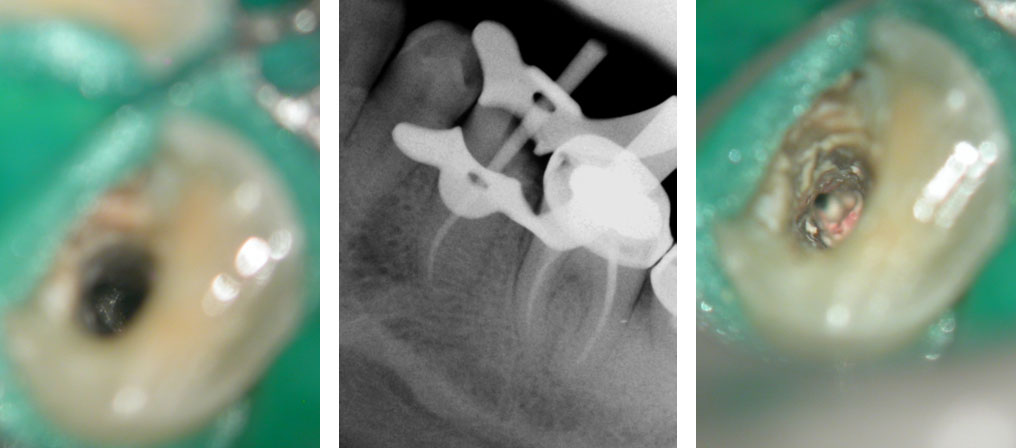
Clinical Case
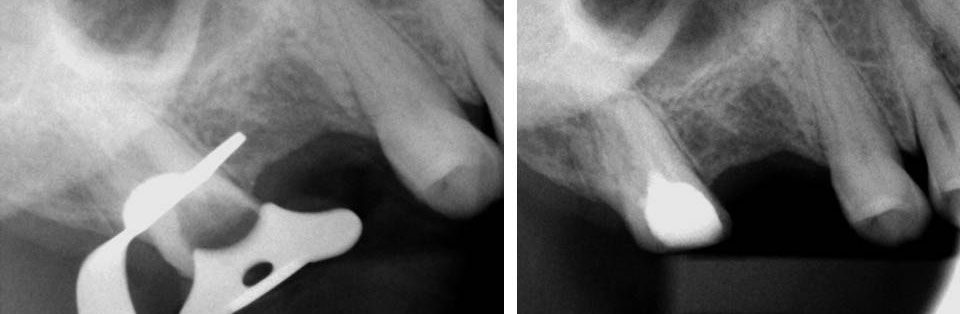
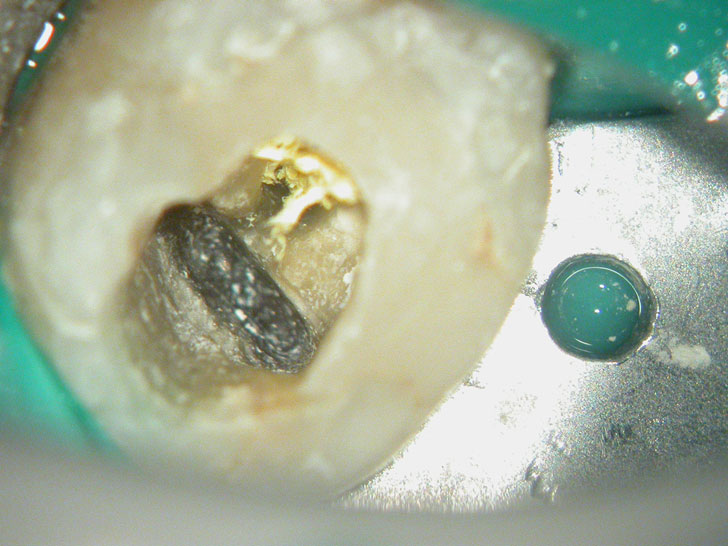
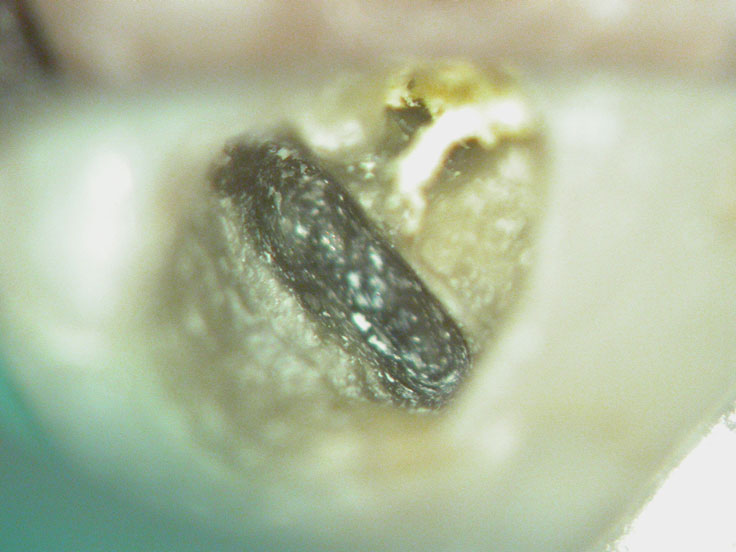
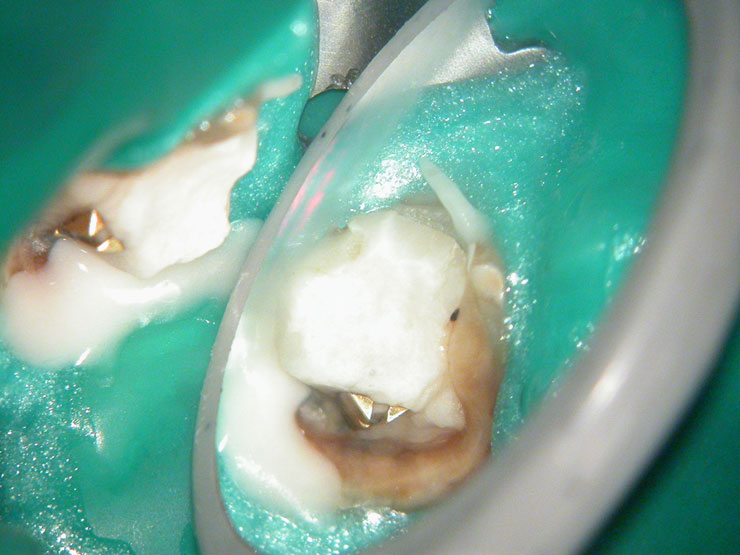
Broken instrument in the mesio-buccal root of the maxillary second molar.
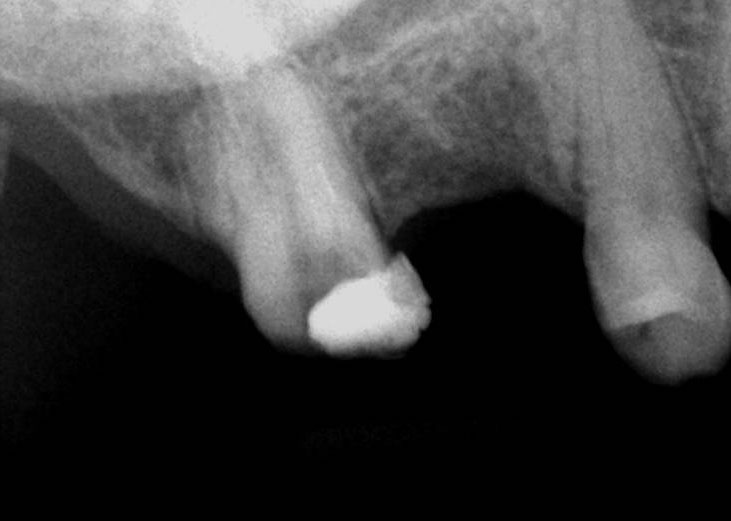
Pre-op
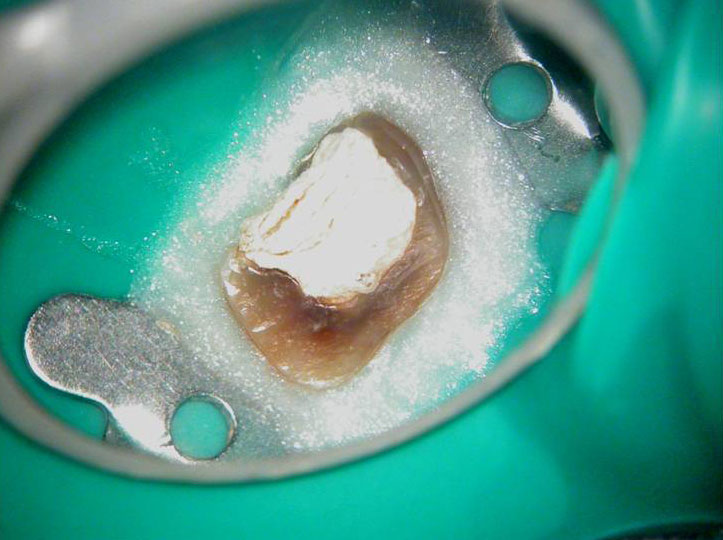
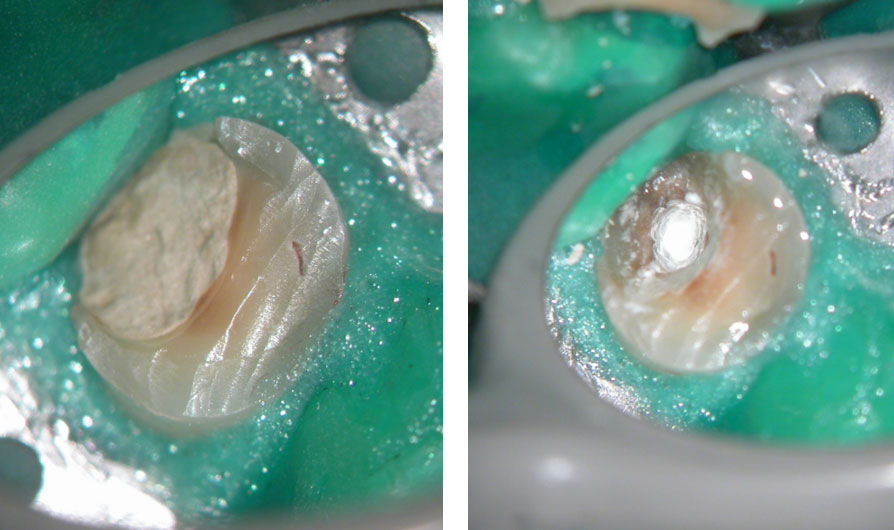
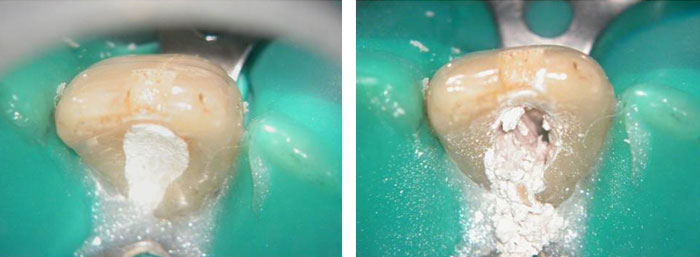
Residual caries seen after temp removal.
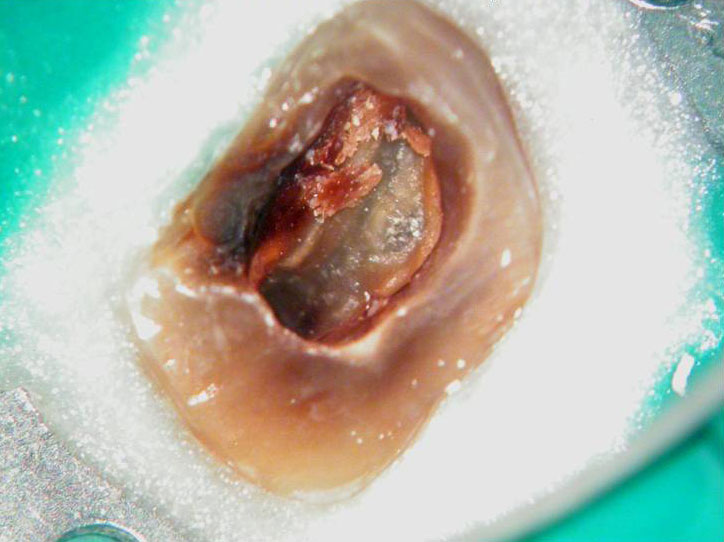
After caries removal
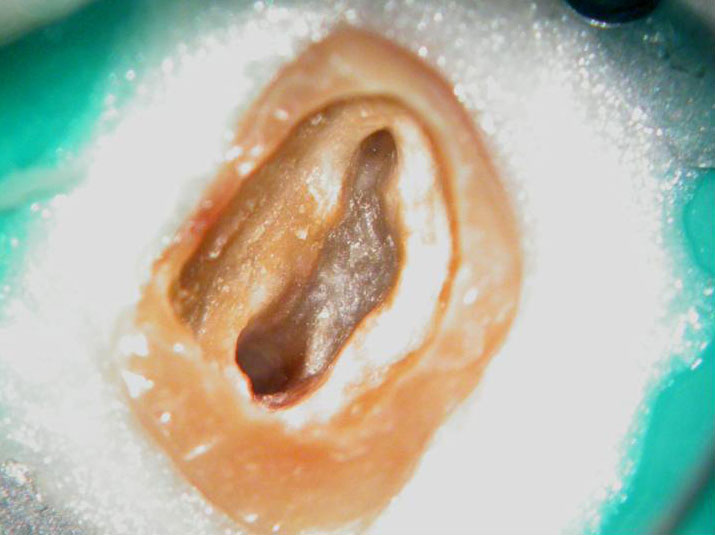
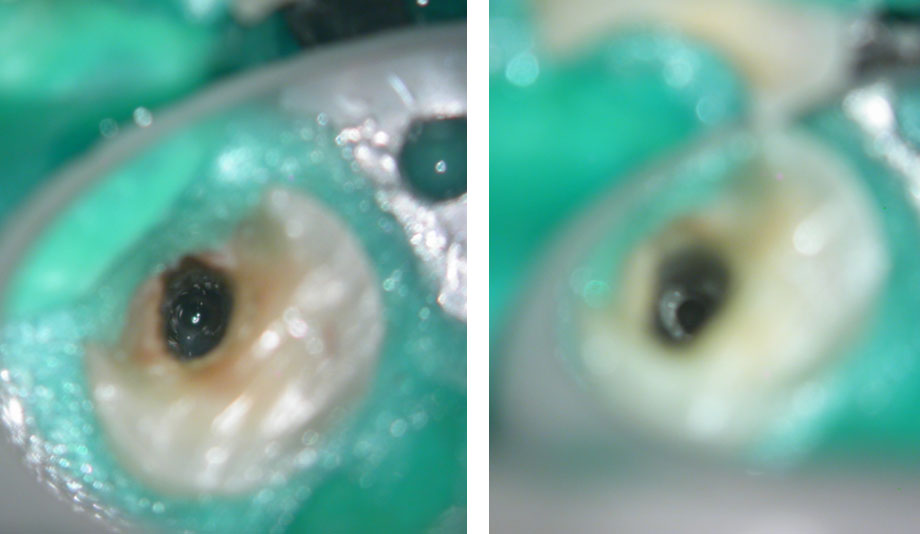
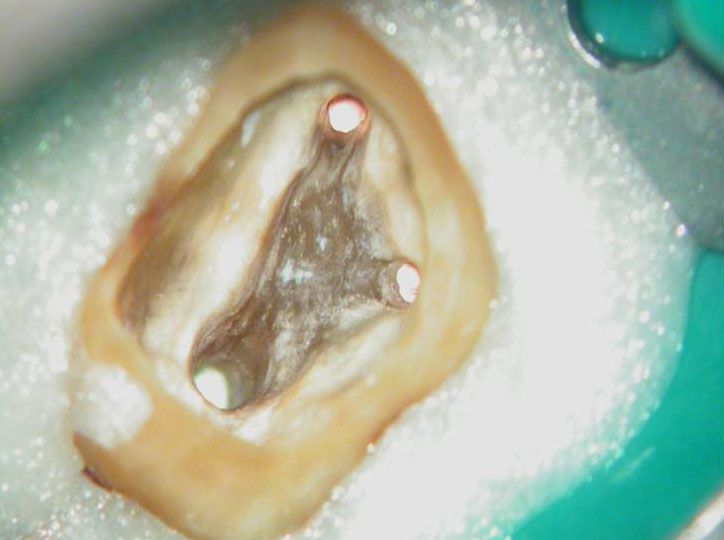
Cotton pellets placed over the palatal and Disto-buccal orifices to prevent the instrument from slipping into those canals.
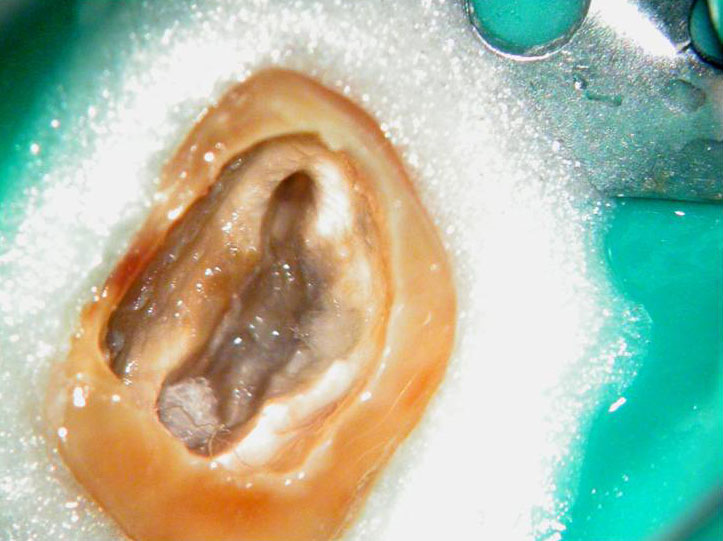
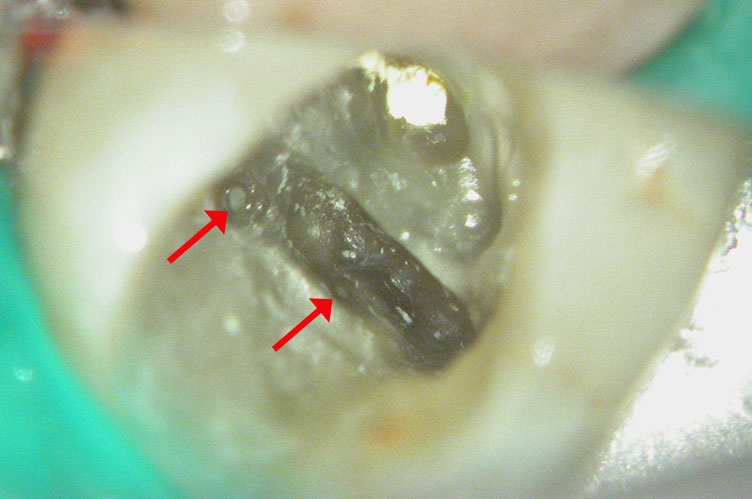
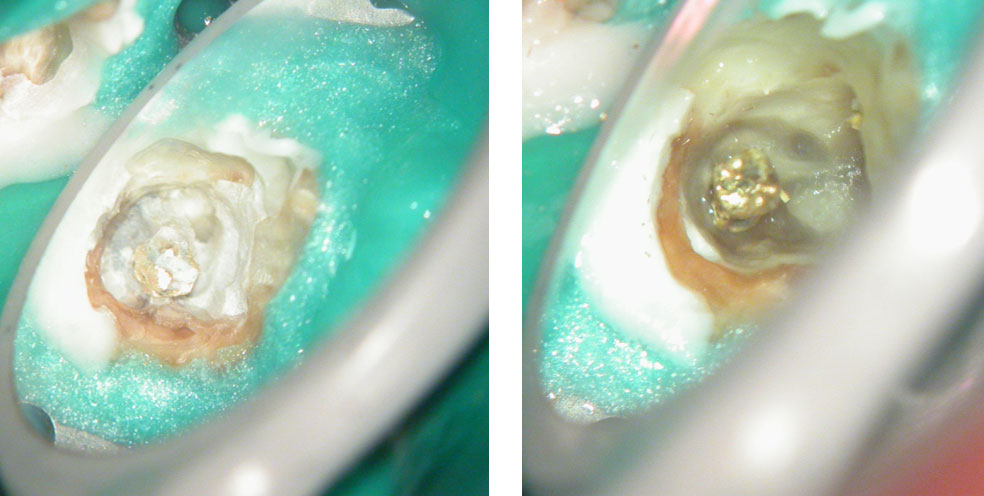
Fractured instrument in mesio-buccal canal
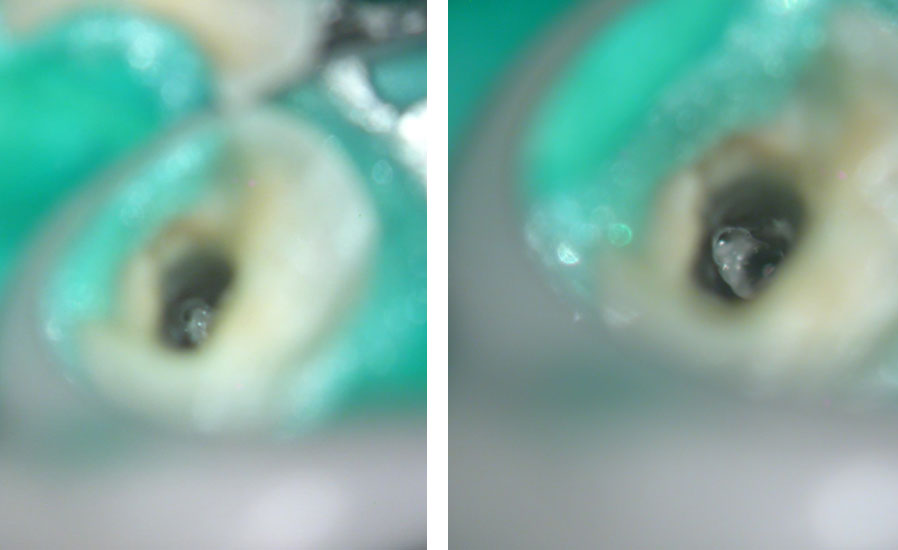
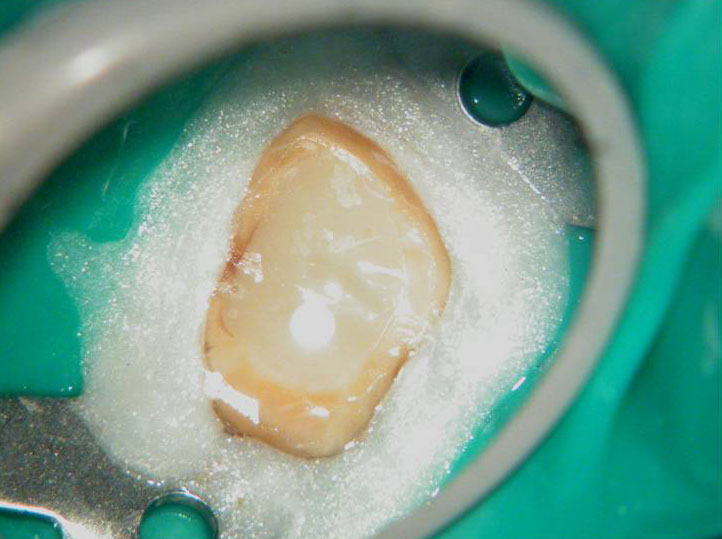
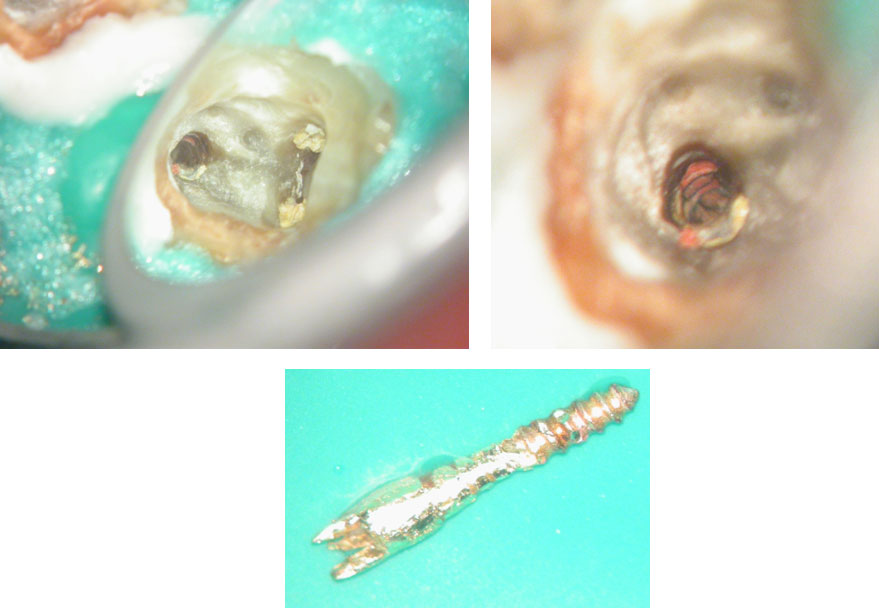
Fractured instrument removed with ultrasonics
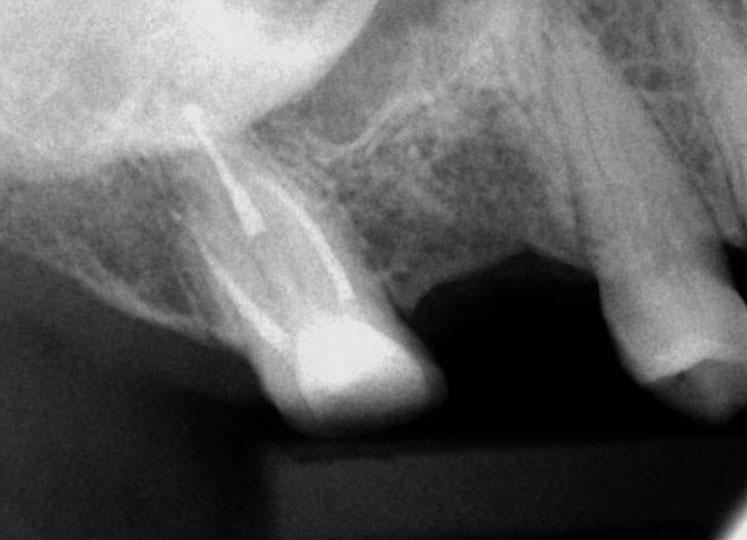
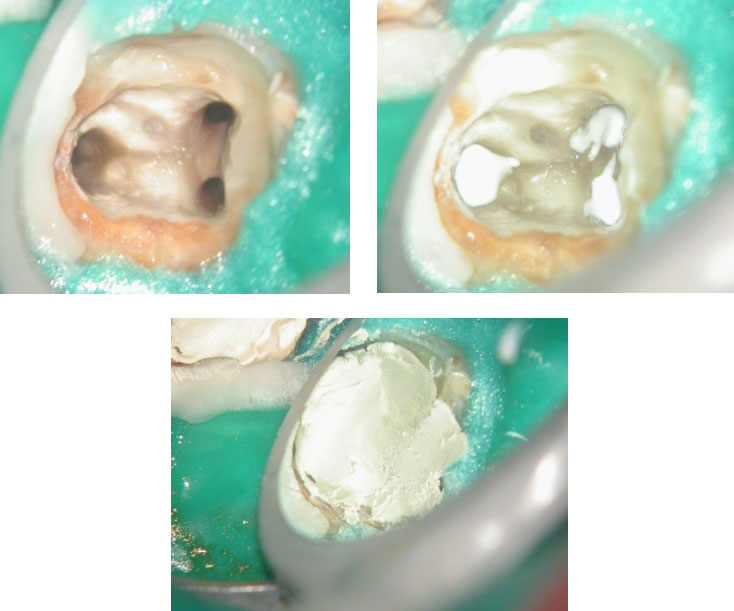
Canals cleaned, shaped and obturated
Fiberglass-post and composite core placed
Post-op
Pre-op & Post-op
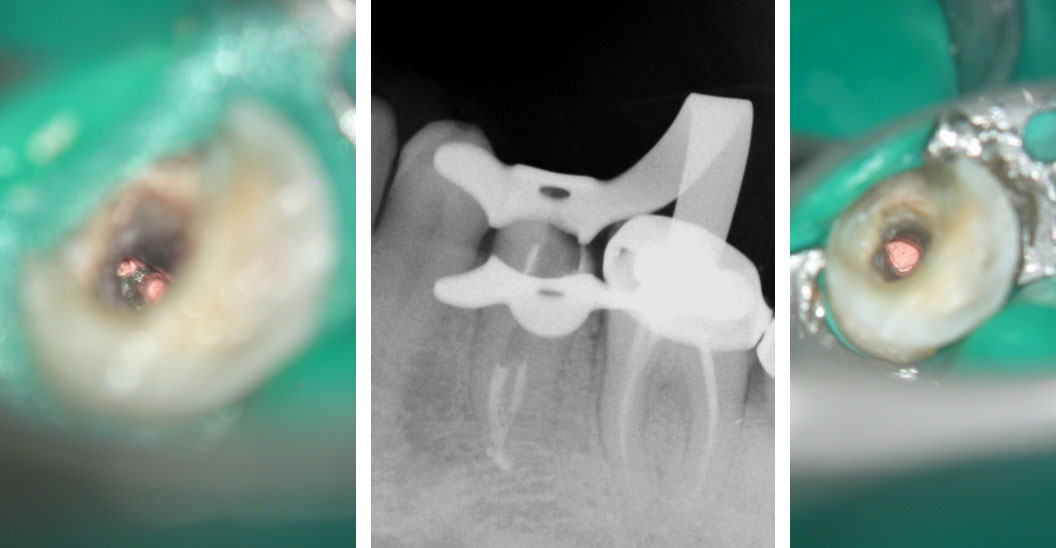
Clinical Case
Pre-op:
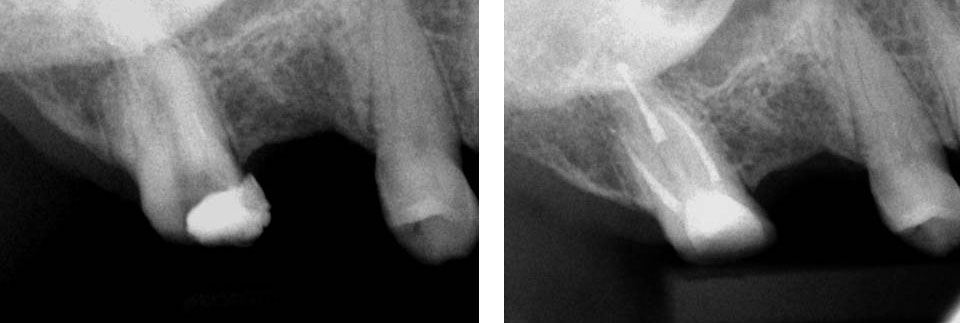
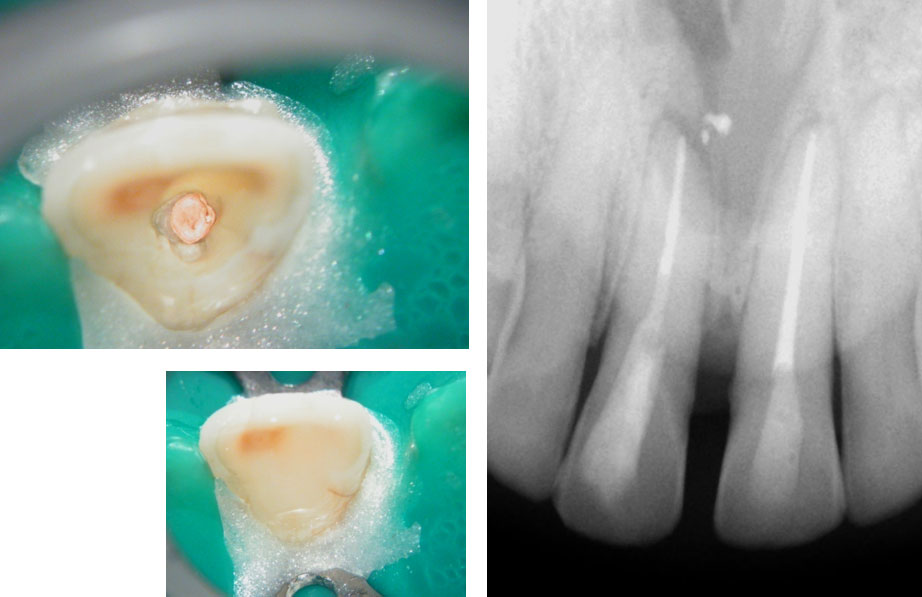
Central incisor referred after previous clinician had accessed the tooth and was unable to locate the calcified canal.
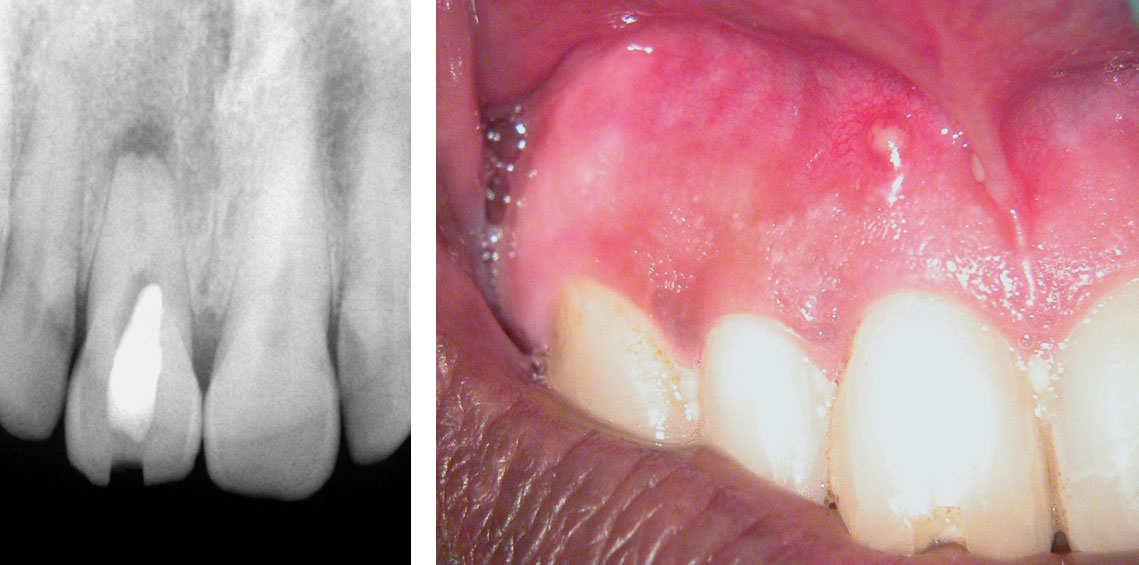
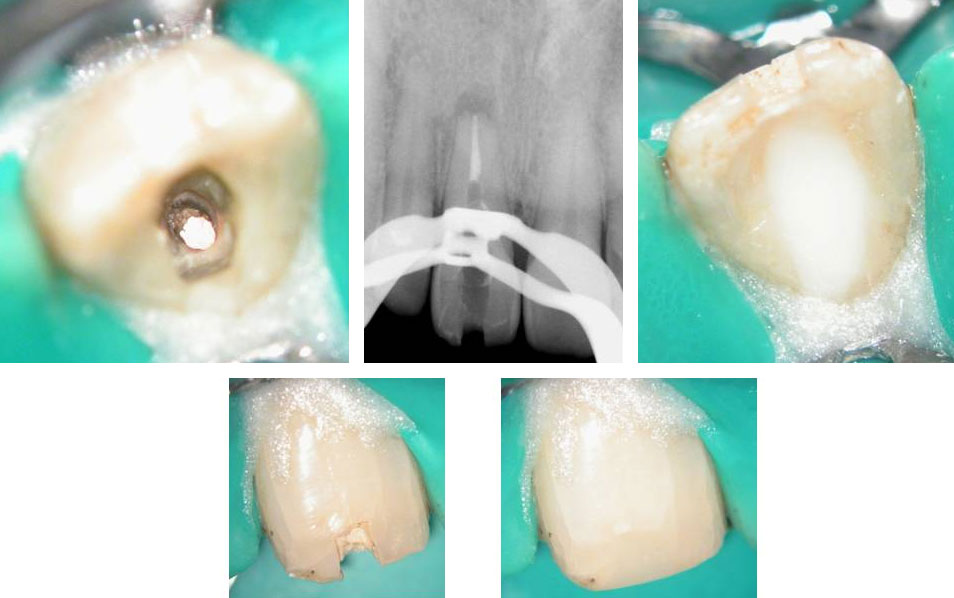
Removal of temporary restoration shows palatal perforation (red arrow) and a calcified canal in the middle (yellow arrow) 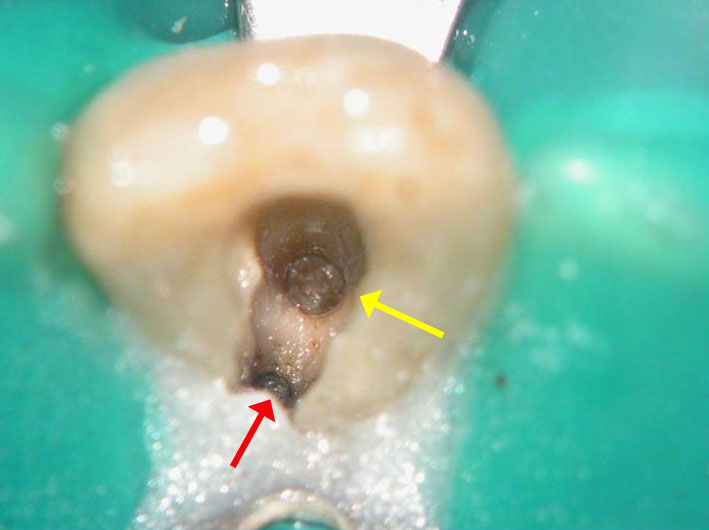
Palatal perforation was supra-crestal and was repaired with GIC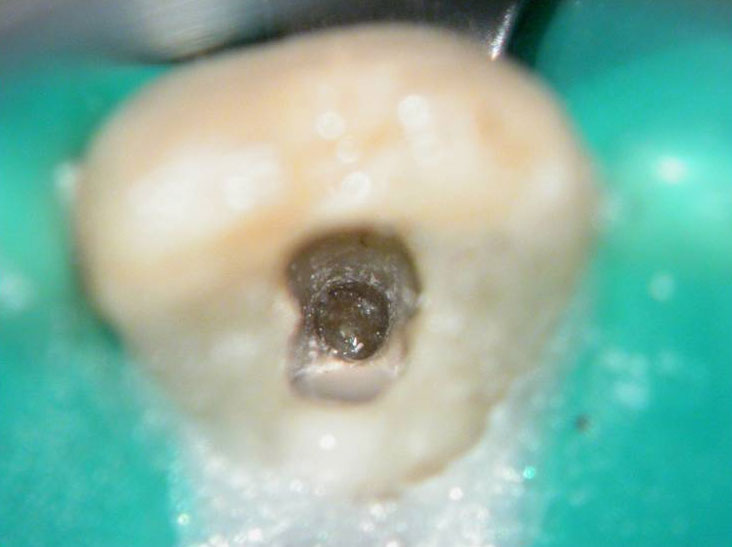
Calcified canal located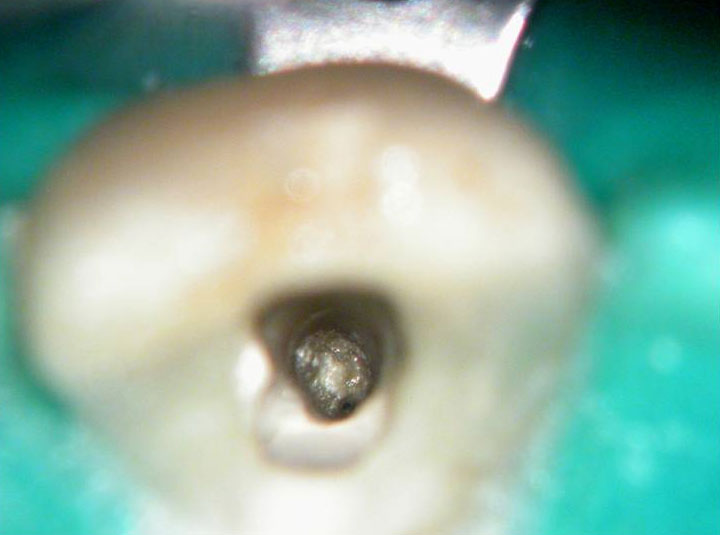
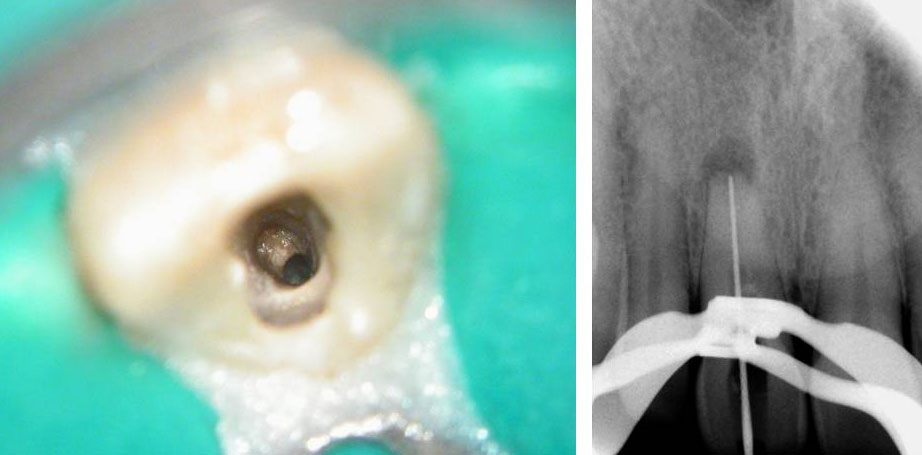
Calcium hydroxide placed 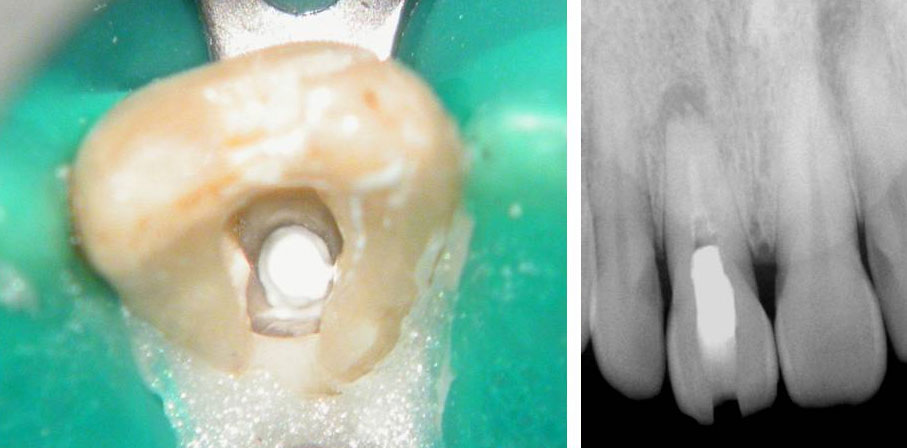
Recall after 10 days. Sinus tract healed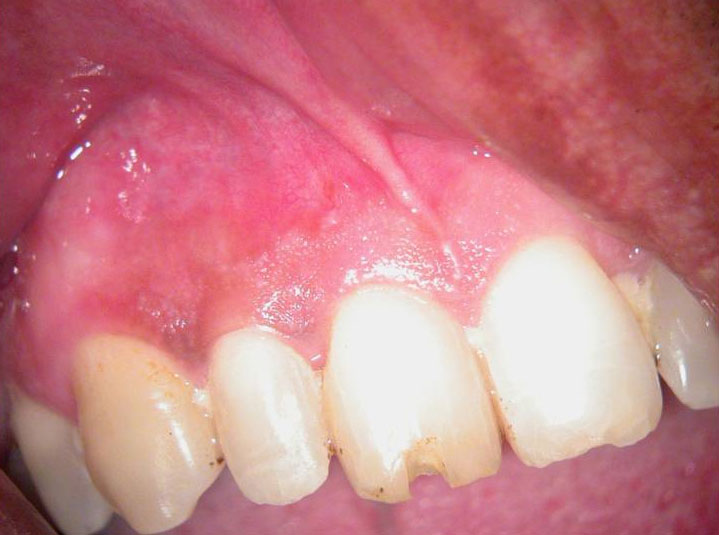
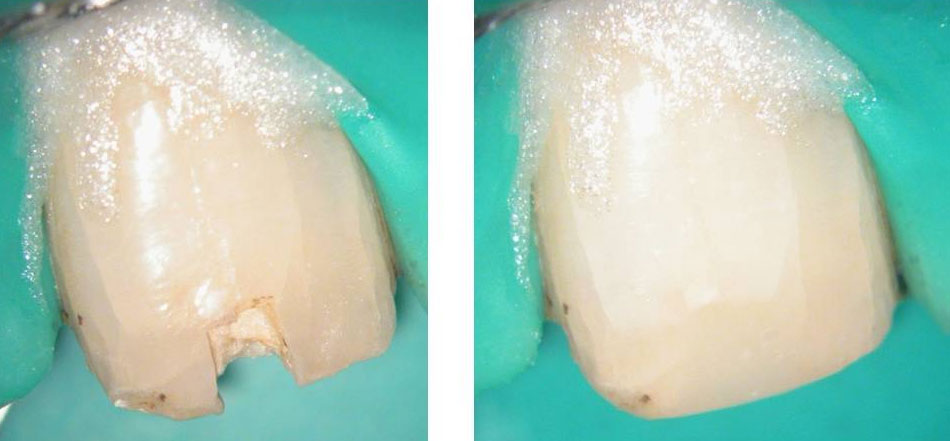
Post-op & 1 year recall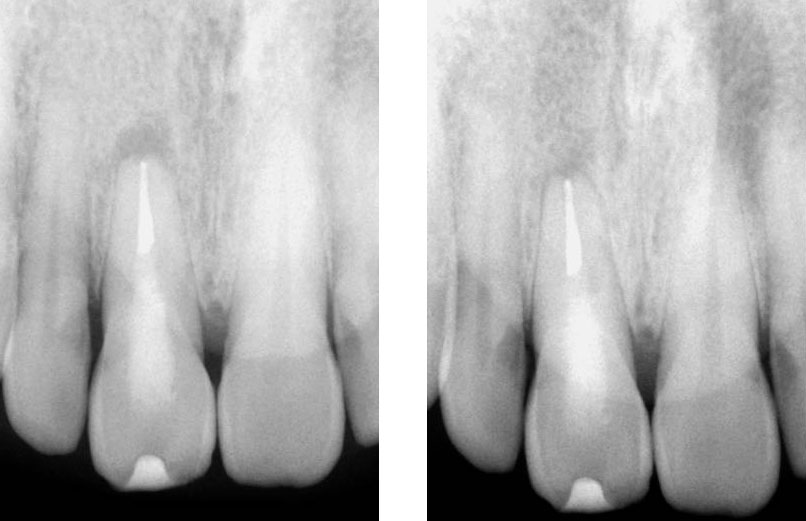
Pre-op, Post-op & 1 year recall
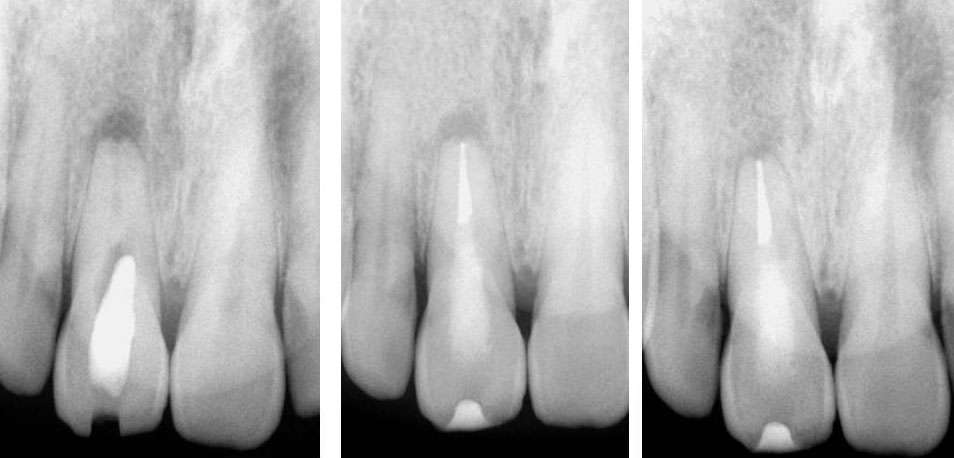
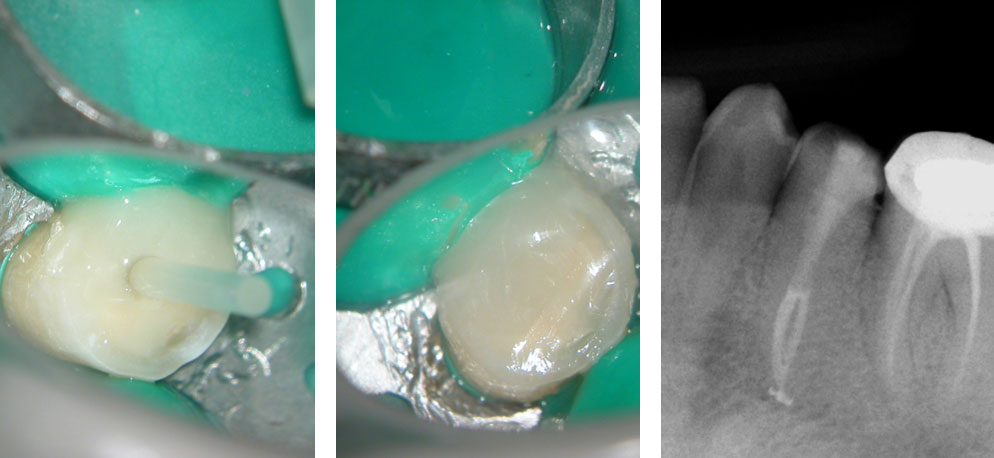
Clinical Case
Naso-Palatine Cyst misdiagnosed + Calcified Canal + Broken Instrument
• This was a Naso-palatine cyst mis-diagnosed as a lesion of endodontic origin
• Treatment was started by the previous clinician and referred to our clinic.
• Referred for:
a) removal of broken instrument in the left maxillary central incisor
b) Location of calcified canal in the right maxillary central incisor
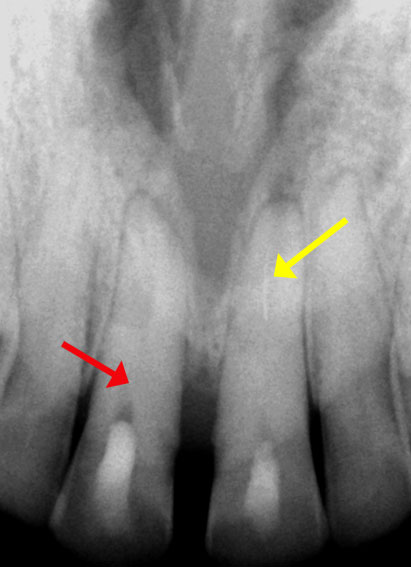
Pre-op
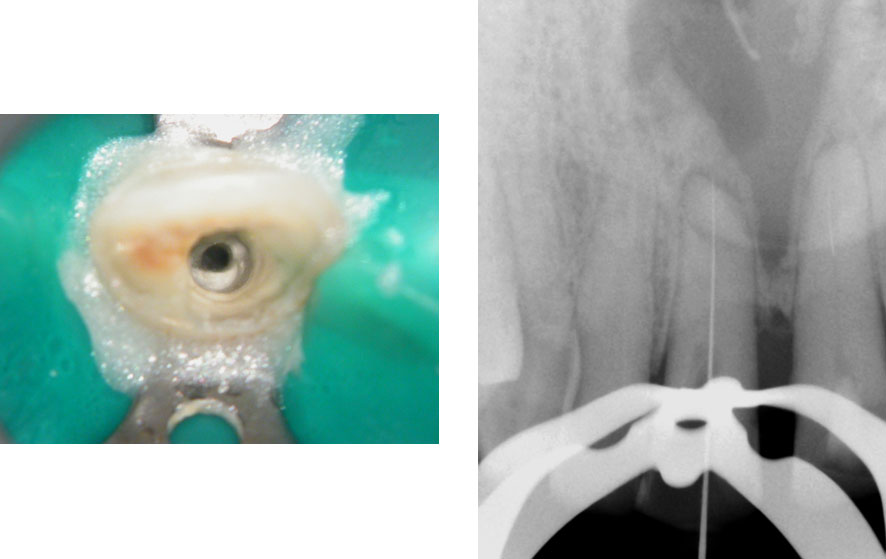
Calcified canal (Red arrow), Broken instrument (Yellow arrow)
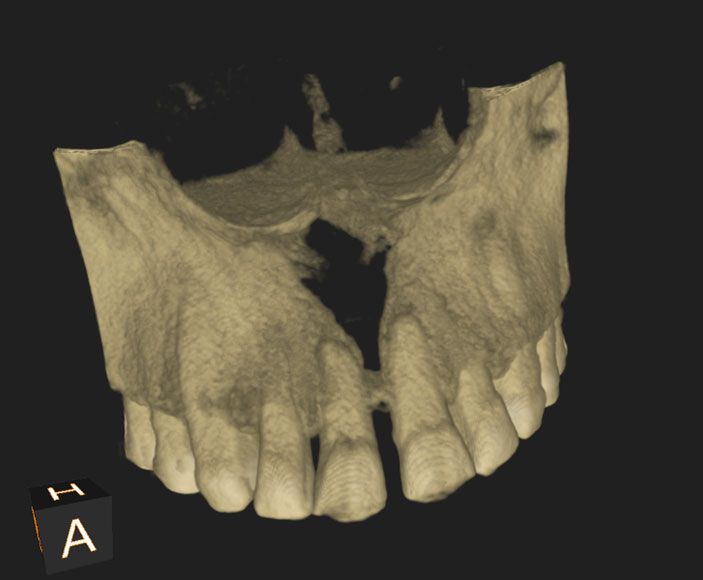
Right Maxillary incisor: CBCT shows that canal is under the palatal wall of the access cavity.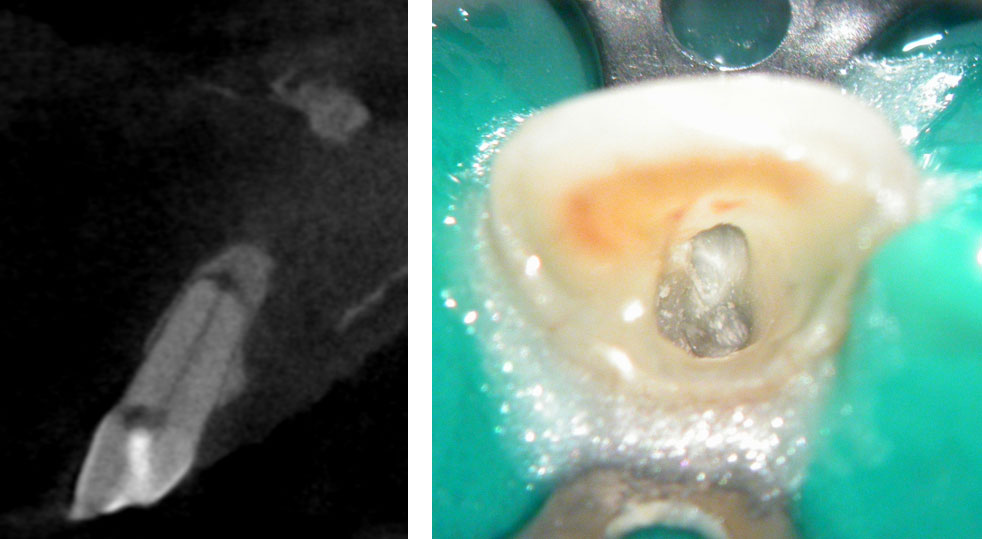
Canal located
Right maxillary incisor cleaned, shaped and obturated.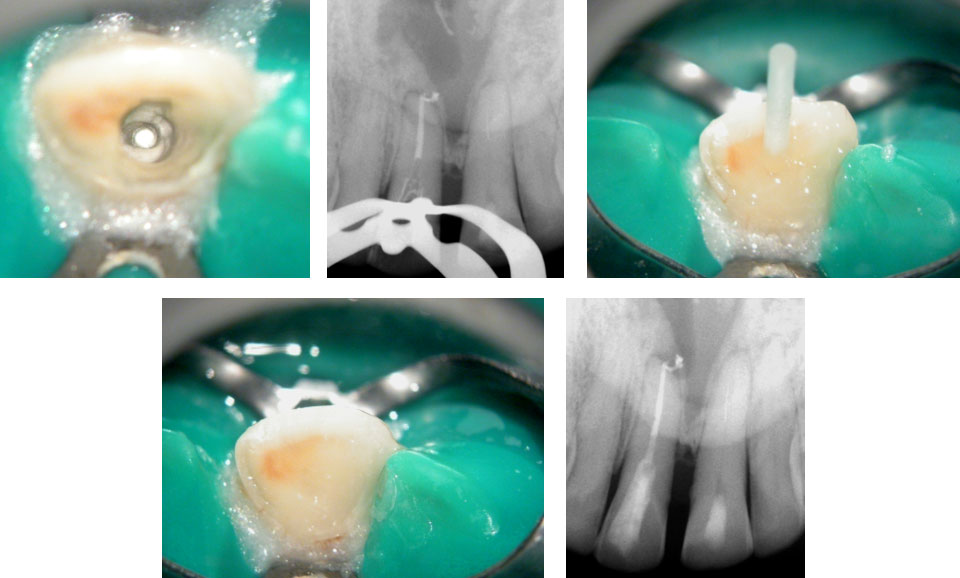
Fractured instrument in the left maxillary incisor.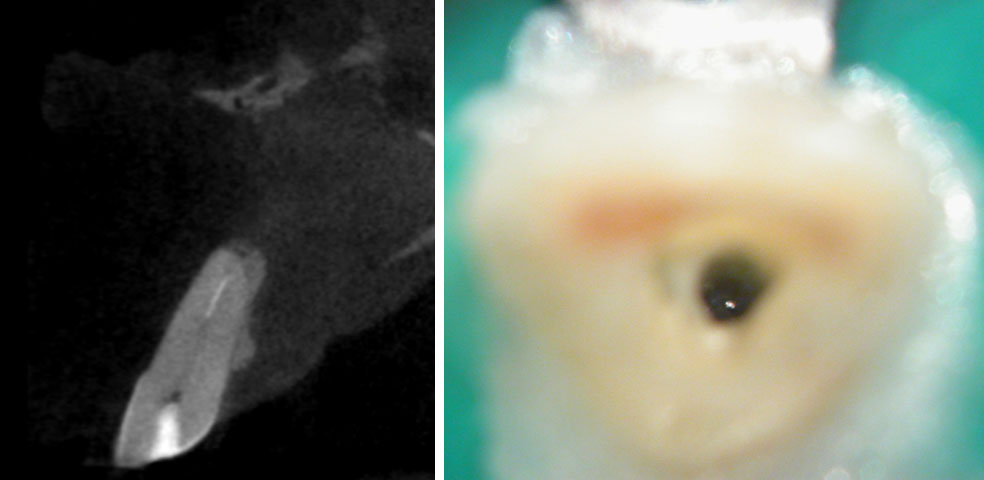
Fractured instrument by-passed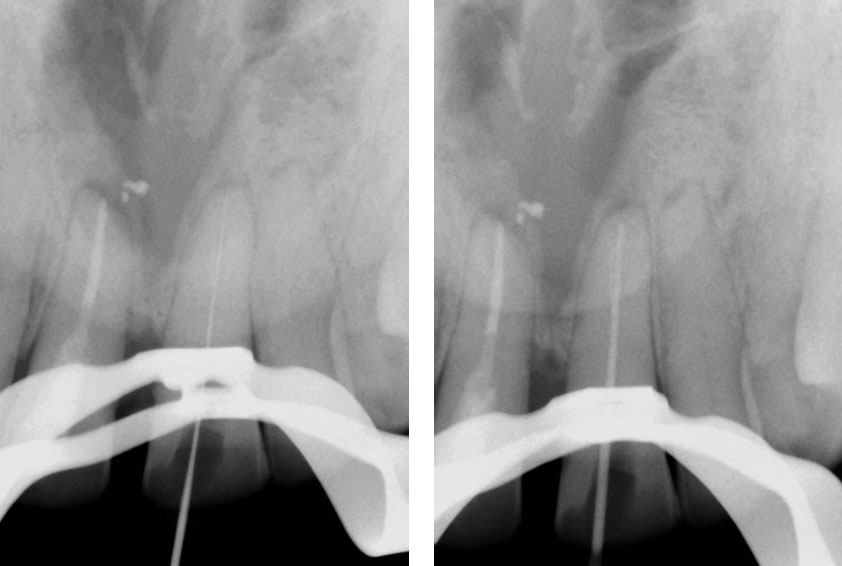
Pre-op & Post-op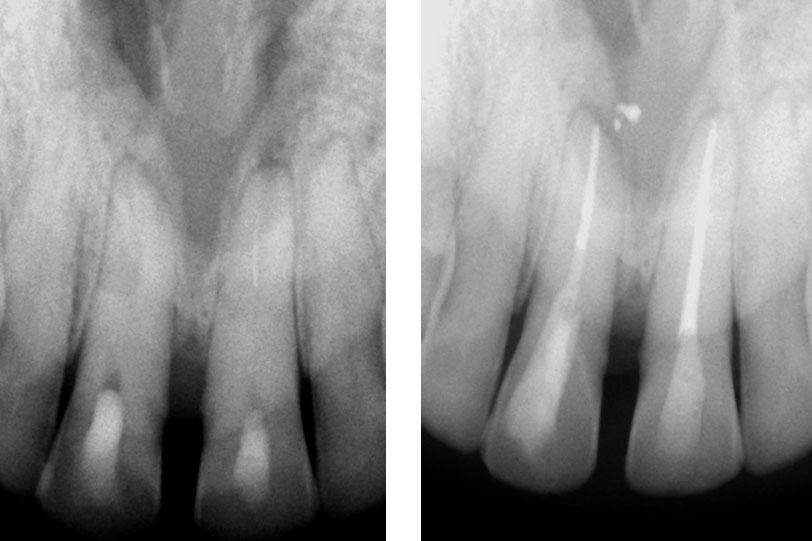
Courtesy: Dr. Anjan Shah, Oral surgeon
Clinical Case
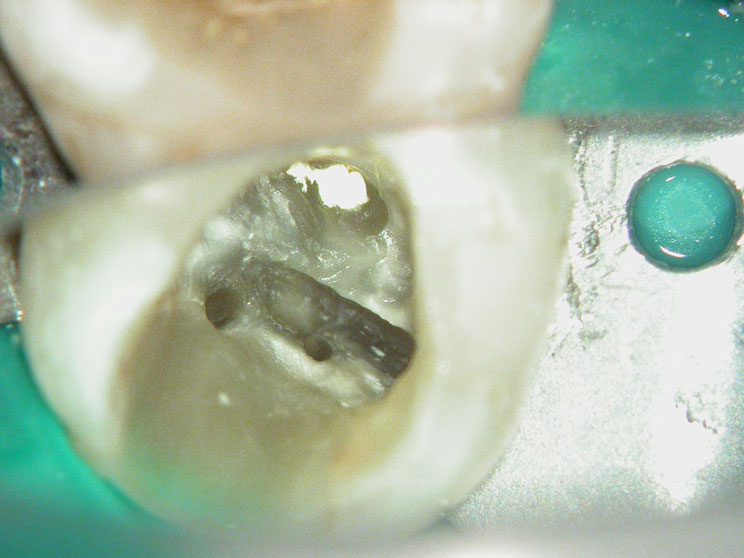
Pre-op
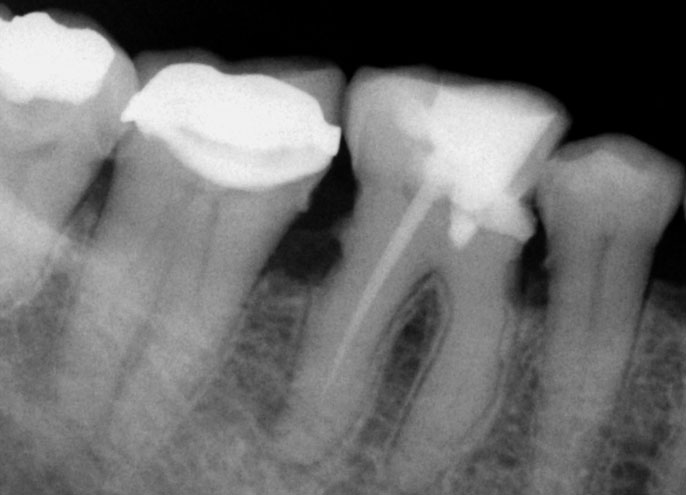
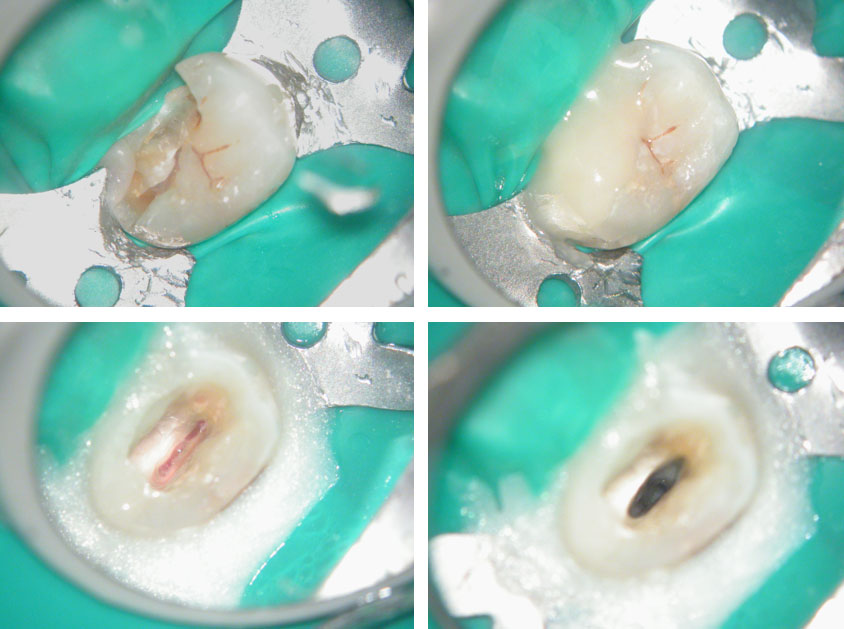
Pain in mandibular first molar after endo. Previous dentist unable to locate mesial canals. Obturated only the distal canal. Patient has generalized periodontal problems as well.
Pre-op, EDTA for 1 minute, After 1 minute EDTA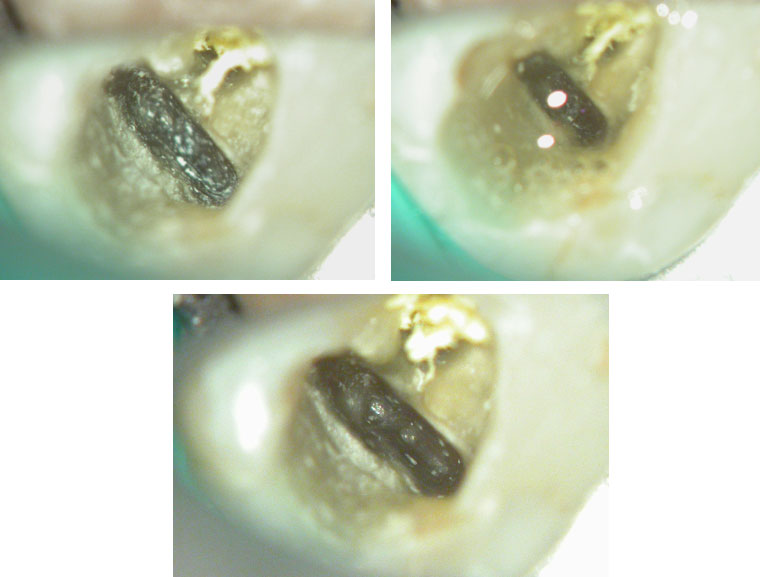
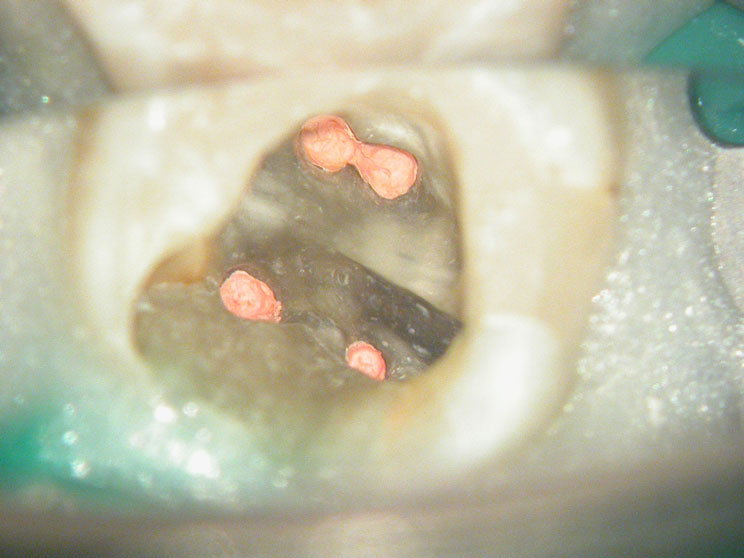
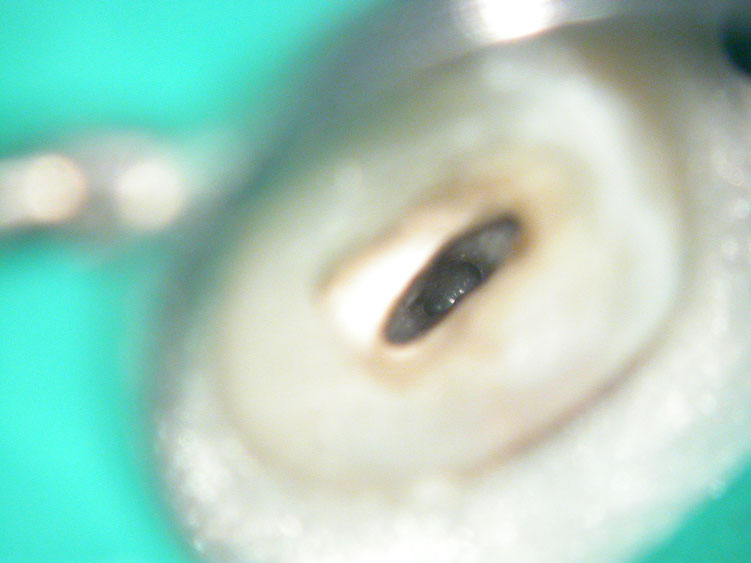
Red arrows show the two “white spots” indicating the calcified mesial canals.
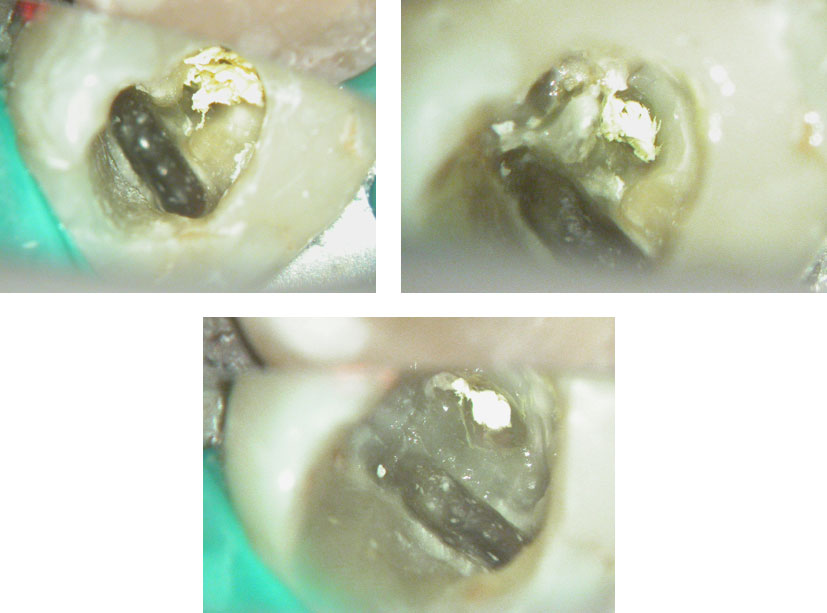
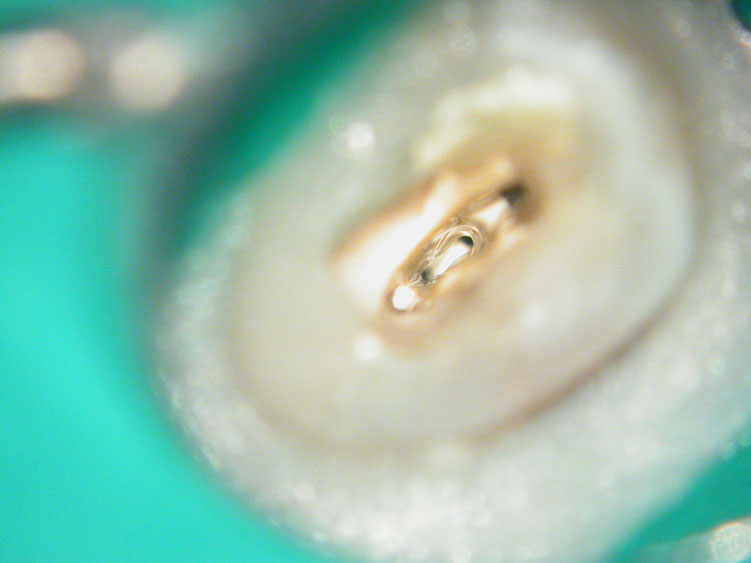
Missed second distal canal (red arrow)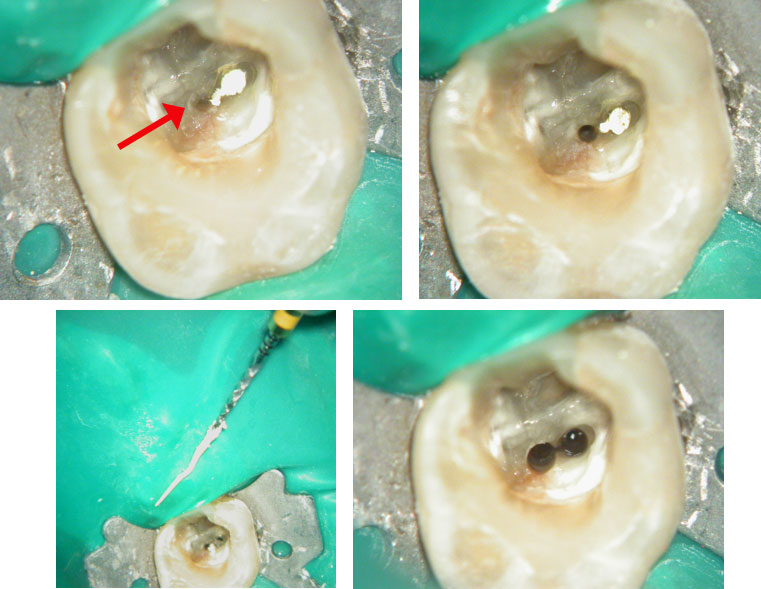
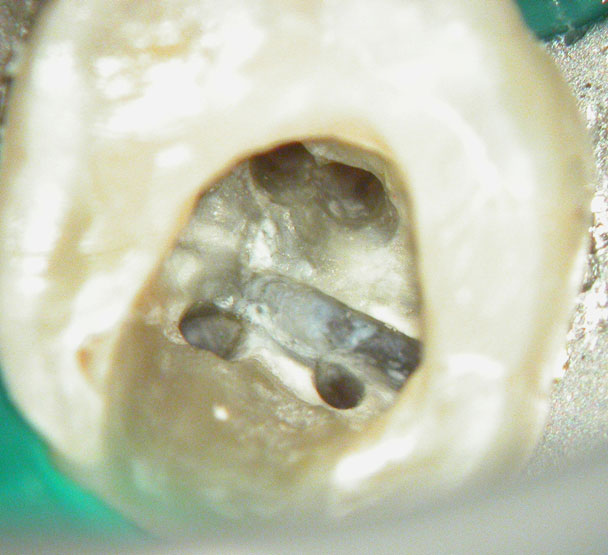
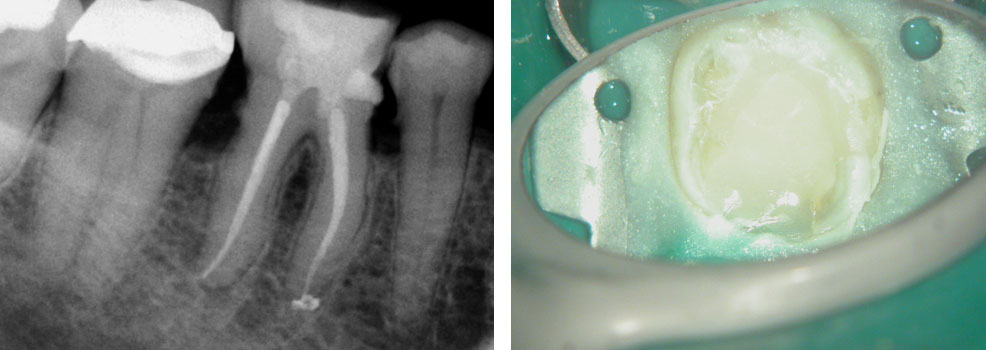
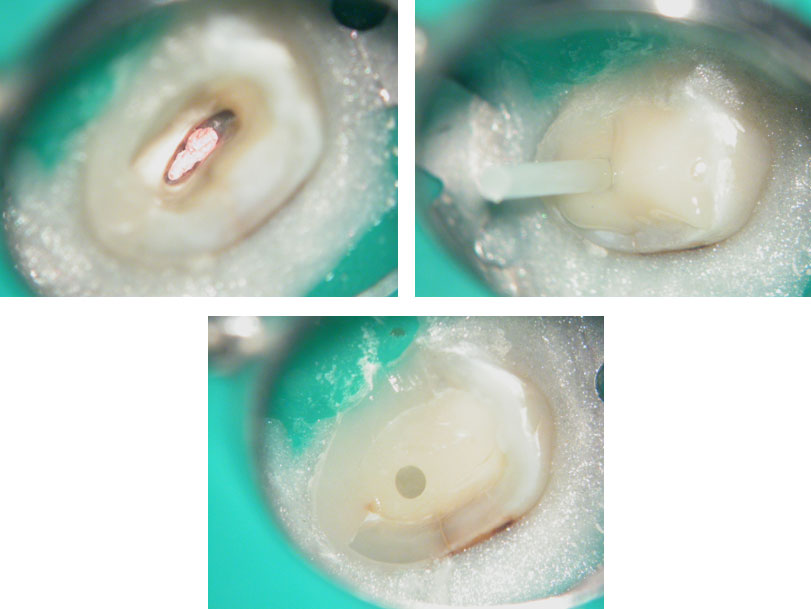
Pre-op & Post-op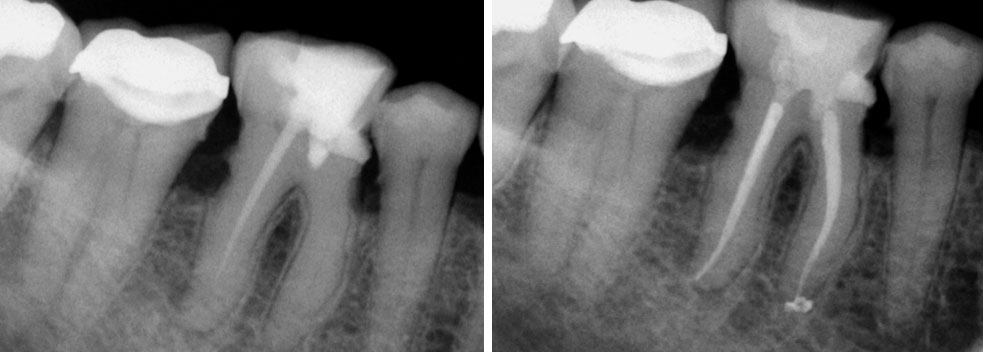
Clinical Case
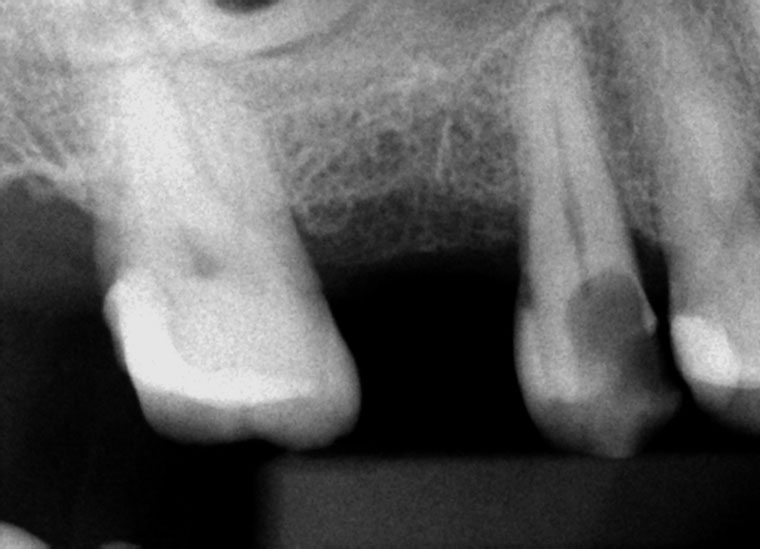
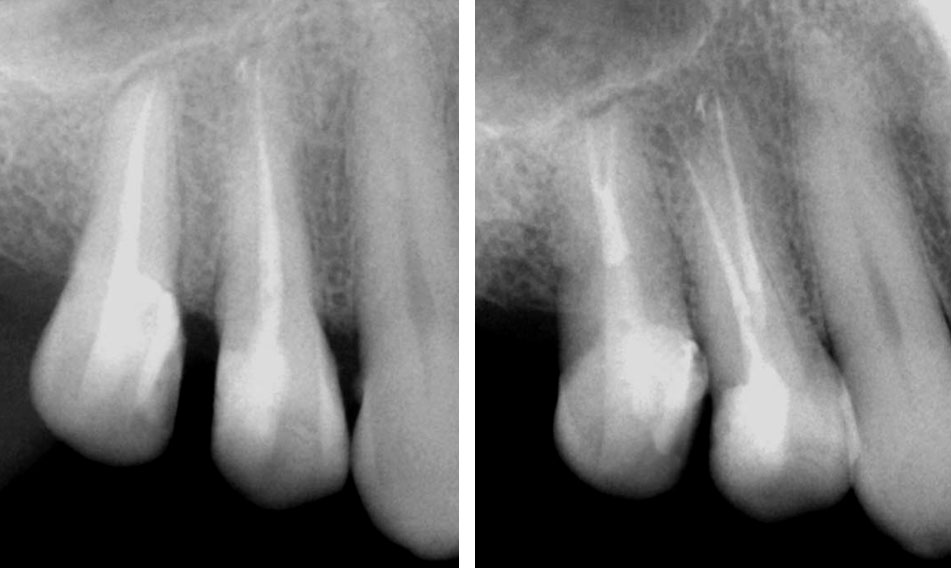
Clinical Case
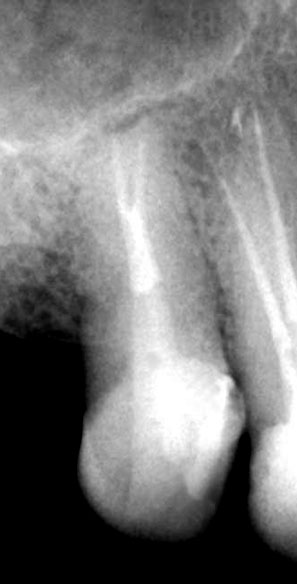
Pre-op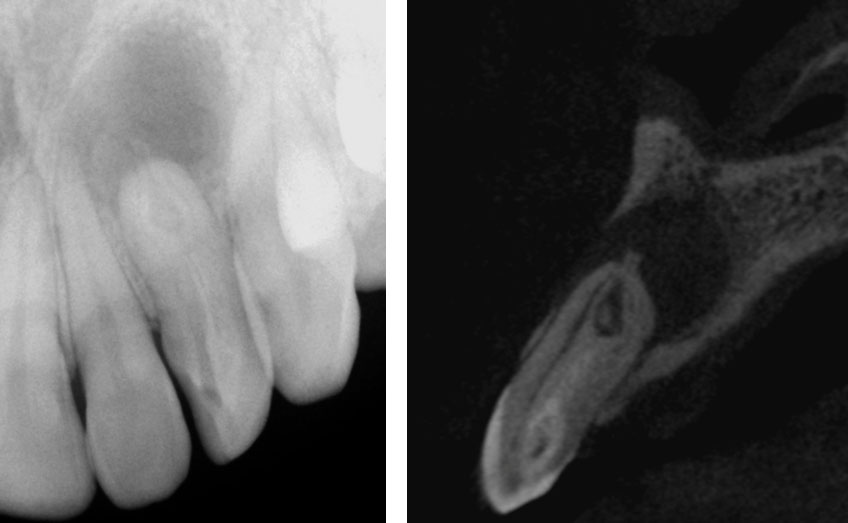
Canal Cleaned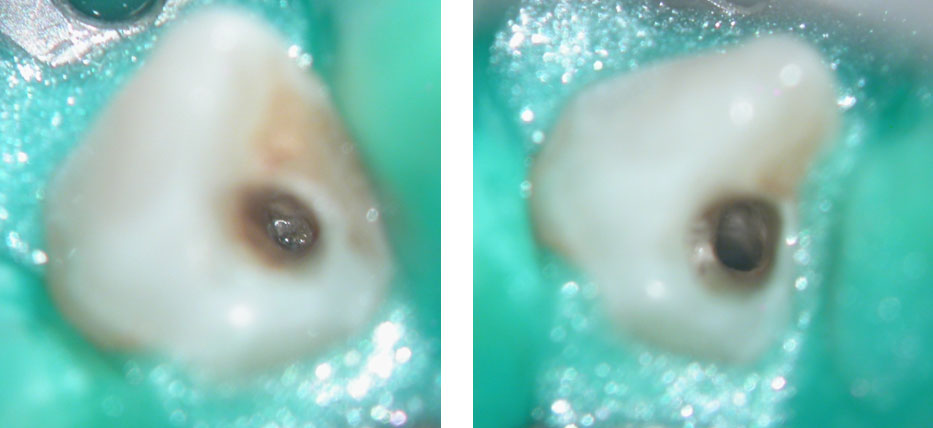
Dens Tract Cleaned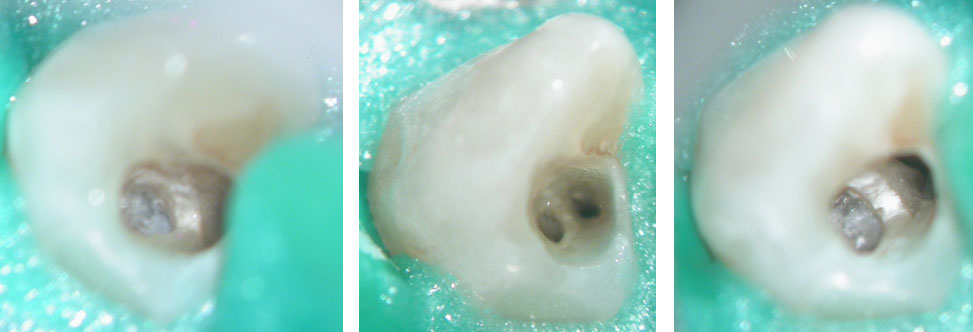
Obturation + Fiber post + Composite core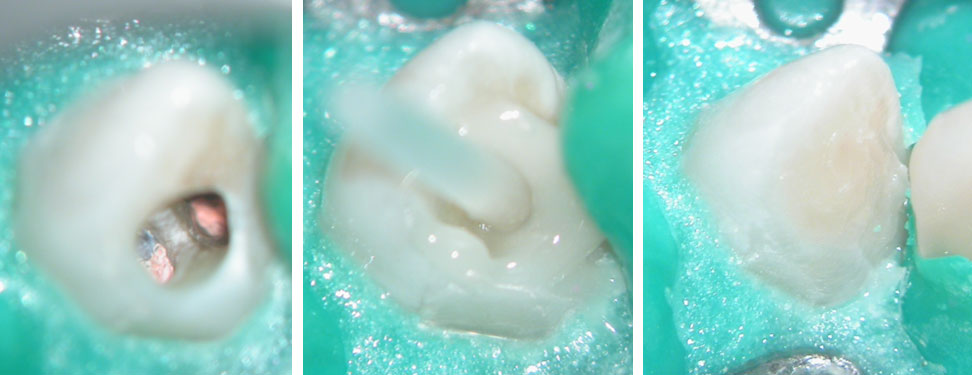
Post-Obturation (Pre-Surgery)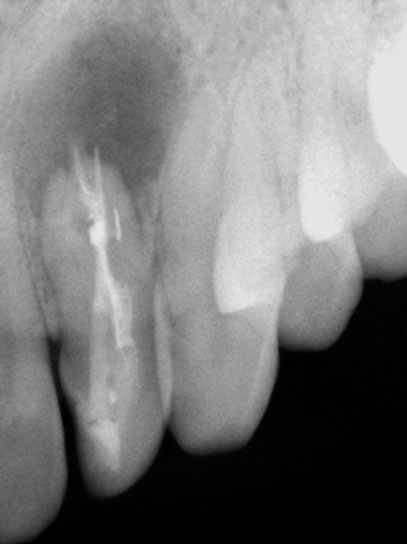
Before root-end resection
After initial root-end resection. Apical “Pouch” still unexposed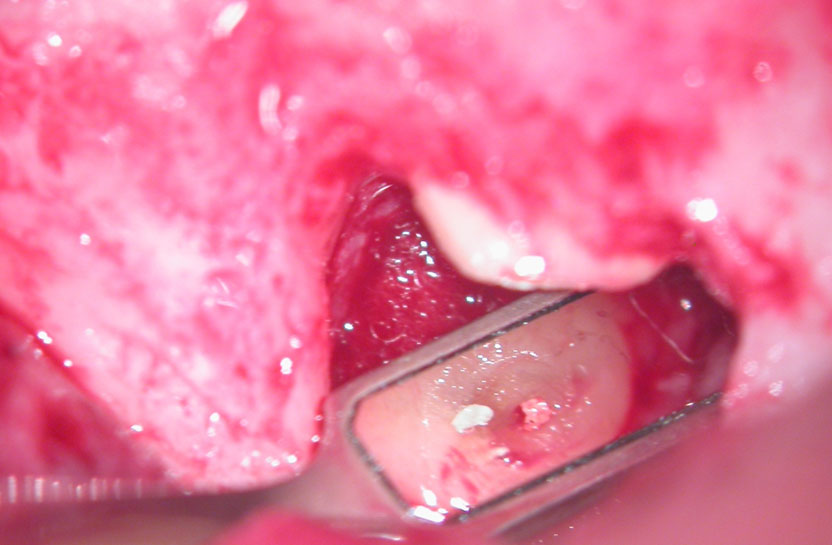
Further root resection and cleaning of the “Pouch”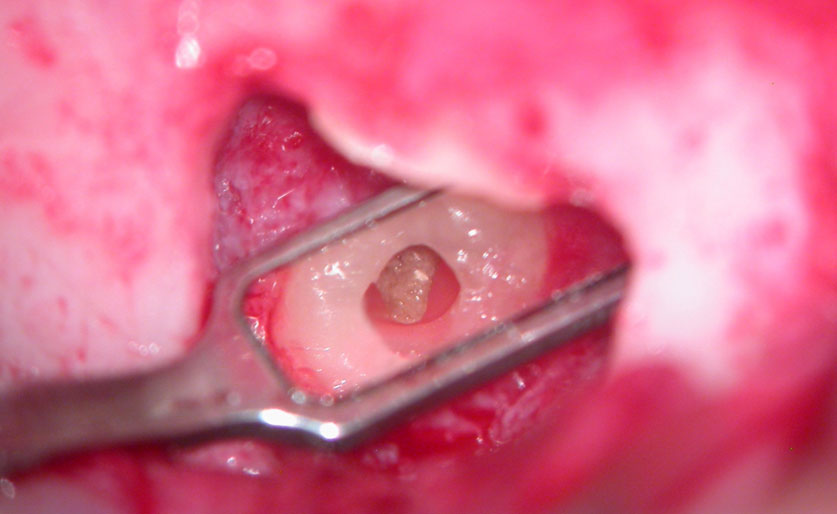
Apical pouch filled with MTA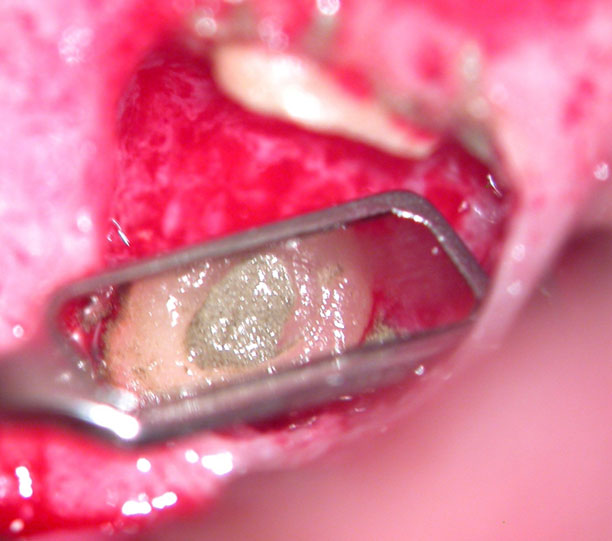
Post-Op 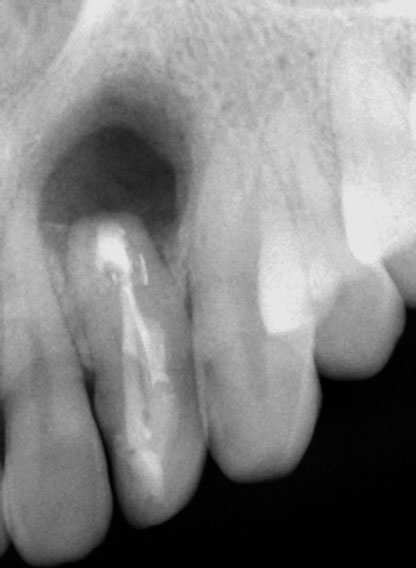
Pre-op & Post-op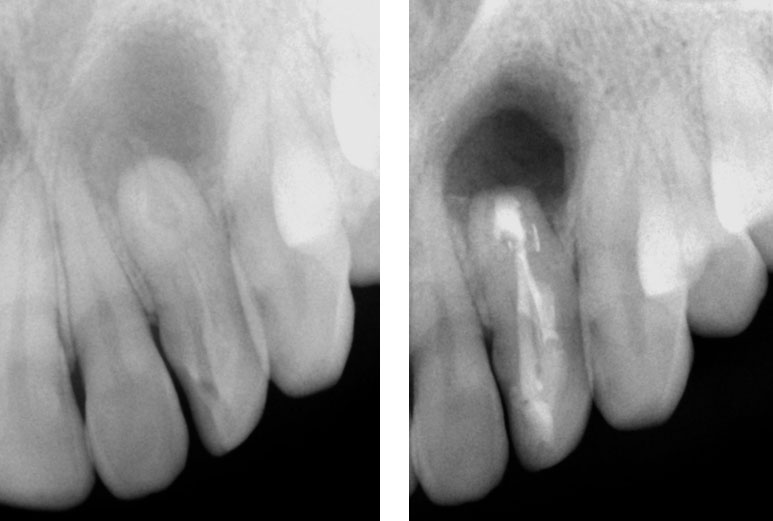
Clinical Case
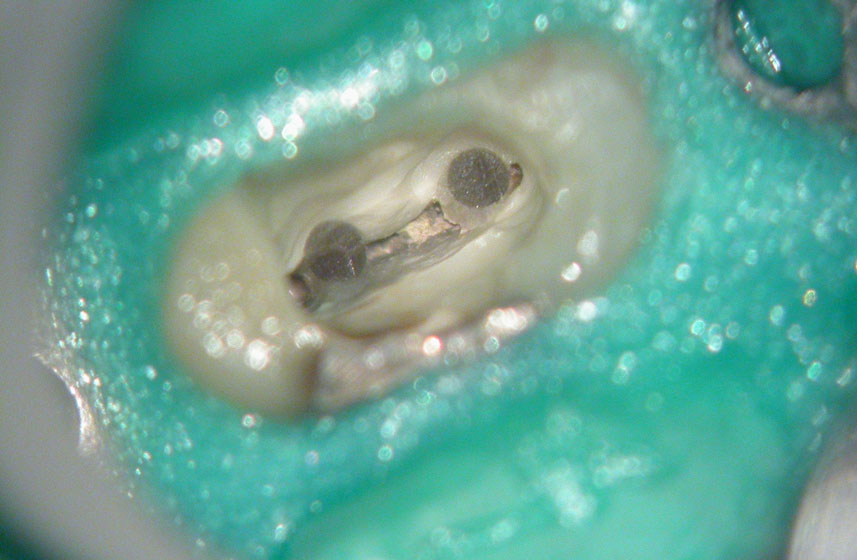
Pre-op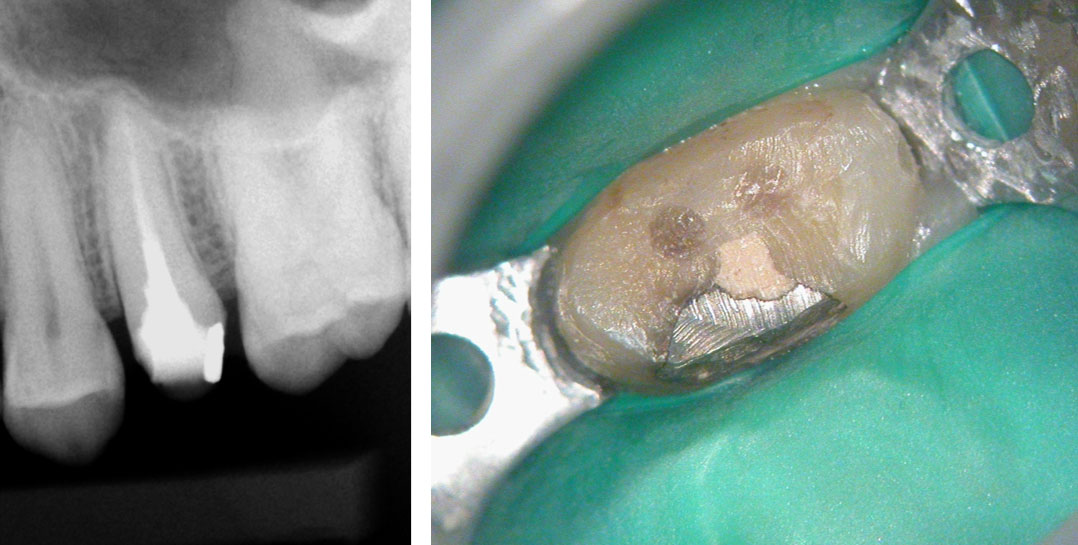
Core is a mix of Fiber Post Composite, Temp and Amalgam!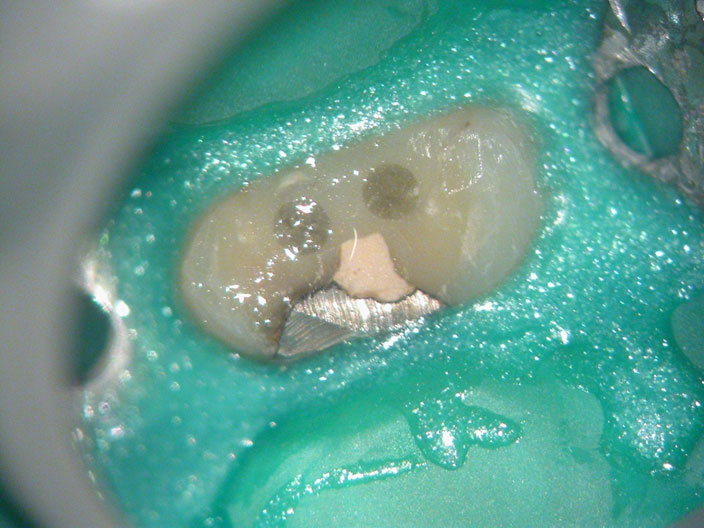
Composite core removed with bur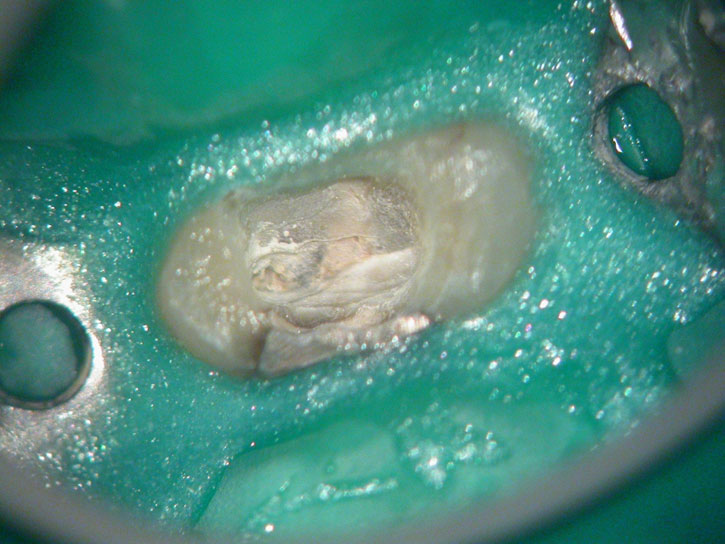
Space between the fiber post and canal walls. Gutta percha in between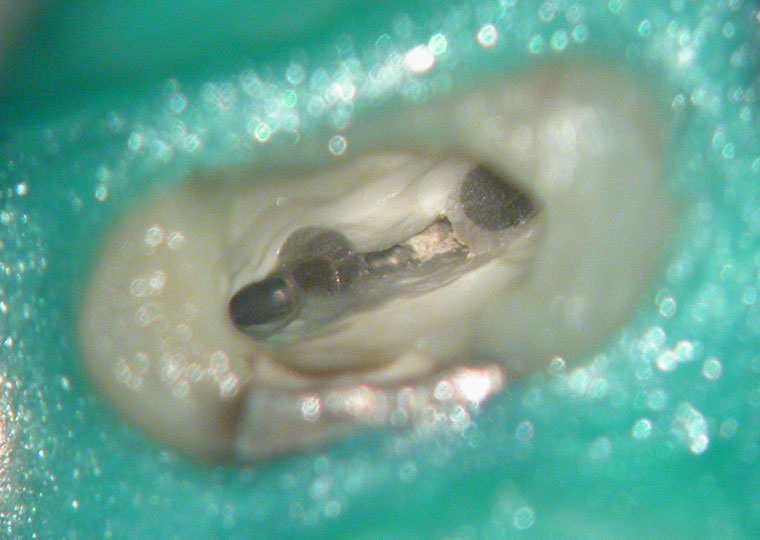
“Munce bur” used to drill out fiber post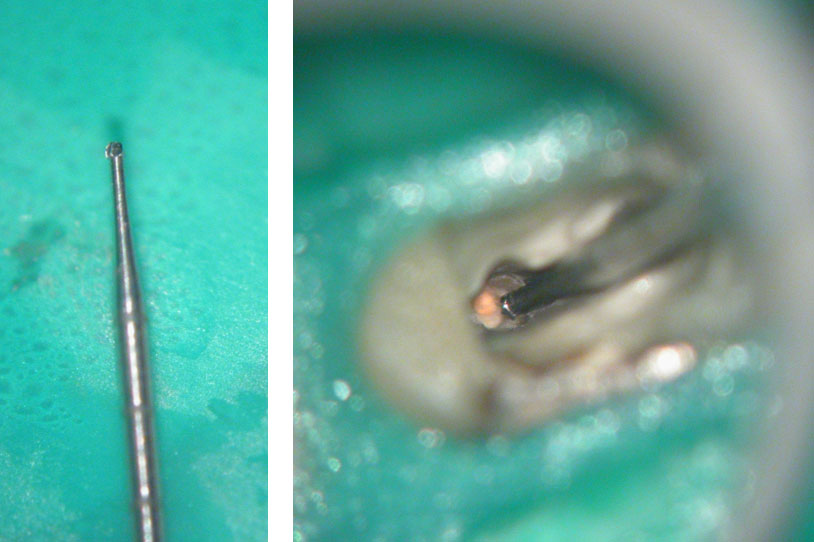
Fiber posts removed to reveal gutta percha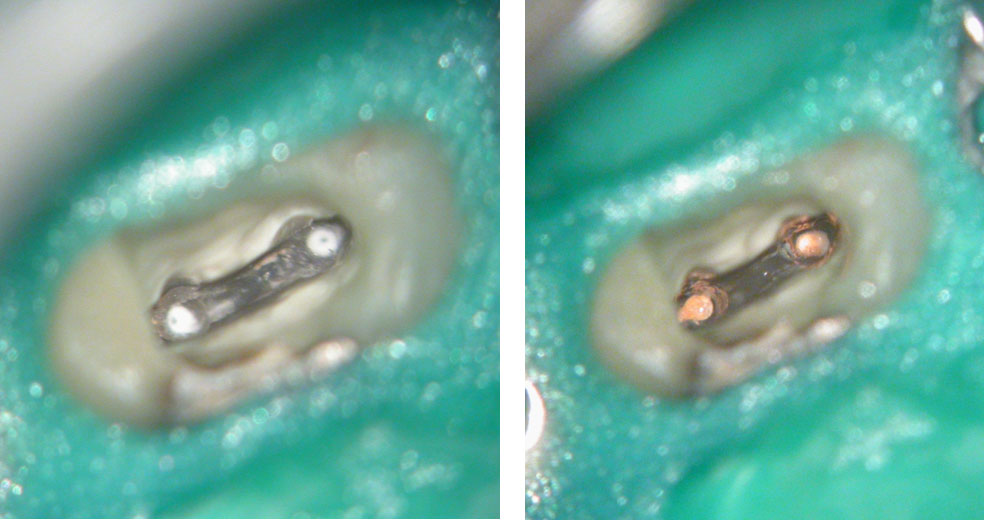
Canals cleaned, shaped and packed with calcium hydroxide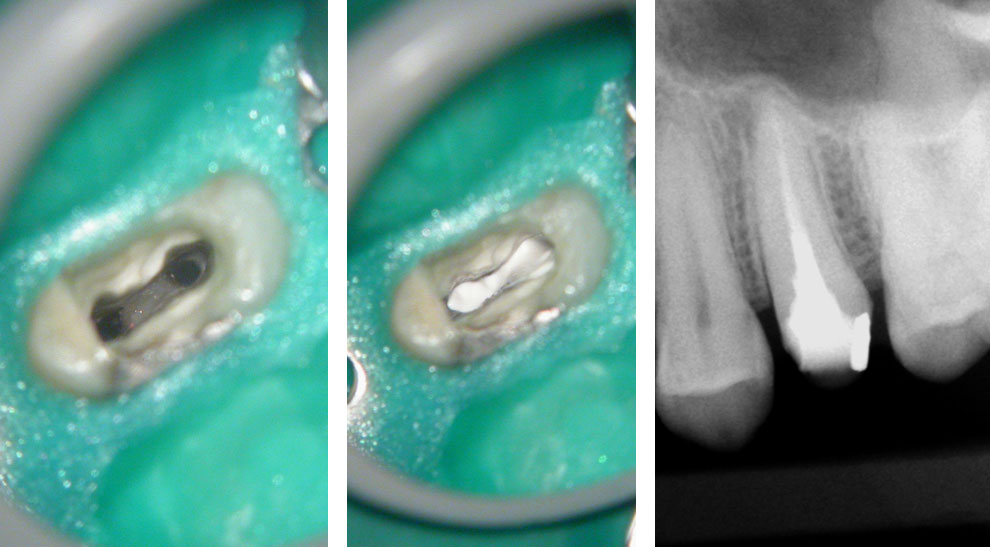
Obturation, posts and composite core 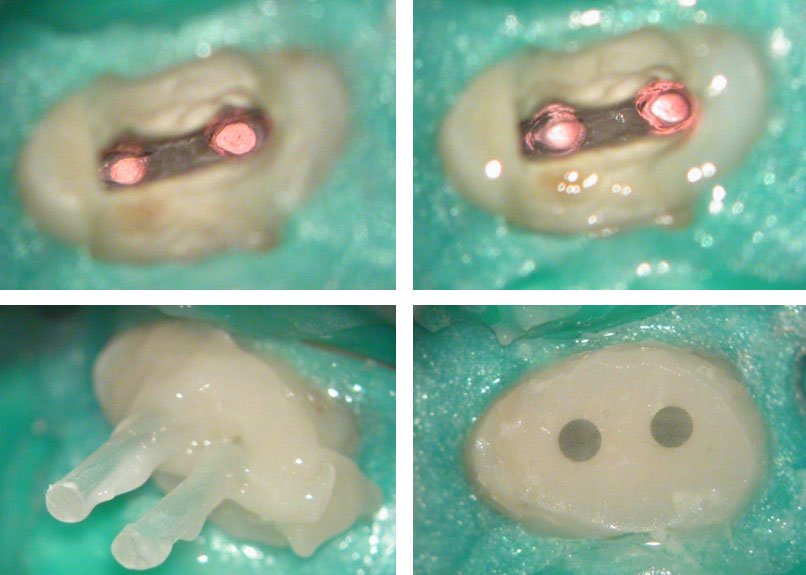
Pre-op & Post-op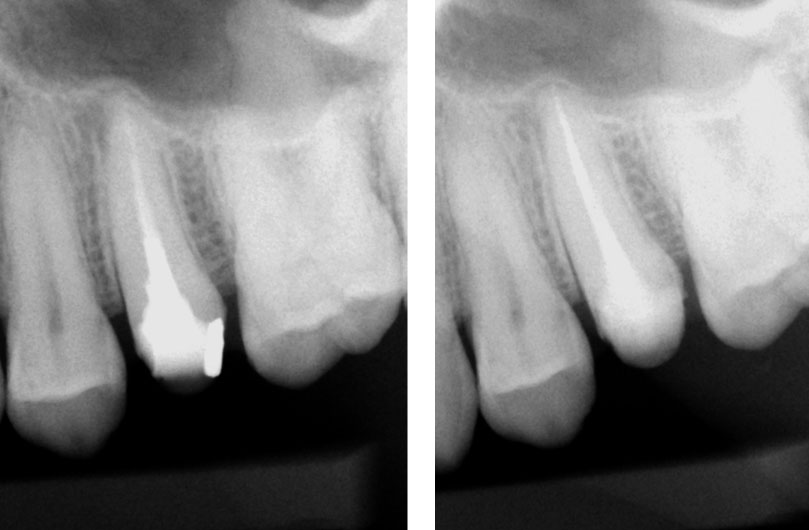
Clinical Case
Age of patient: 15 years
Tooth: left mandibular first molar. Poor restorative prognosis. Very large lesion.
Work done: Obturation done after multiple calcium hydroxide dressings over 5 months and seeing lesion decrease in size. Fiber-post placed in distal canal. Core build-up done with Luxacore composite. Adv crown.
Notes: This is endo done for a “holding period” for implants later on. Healing of bone ensures a more favorable environment for implant placement.
Pre-op
Pre-op CBCT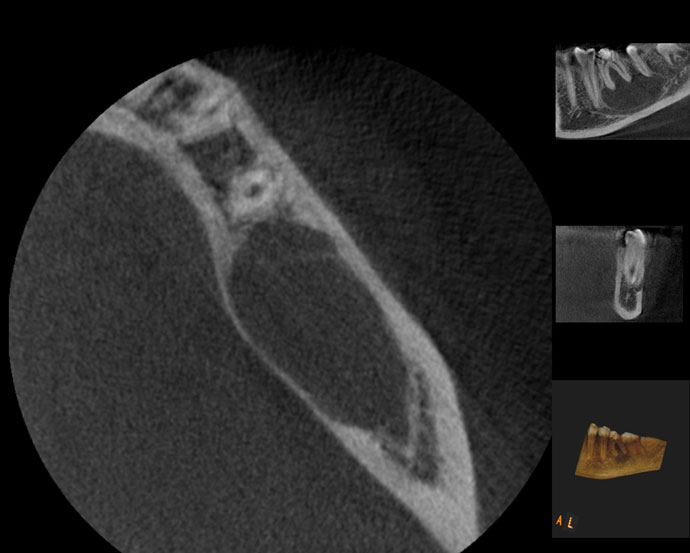
Pre-op CBCT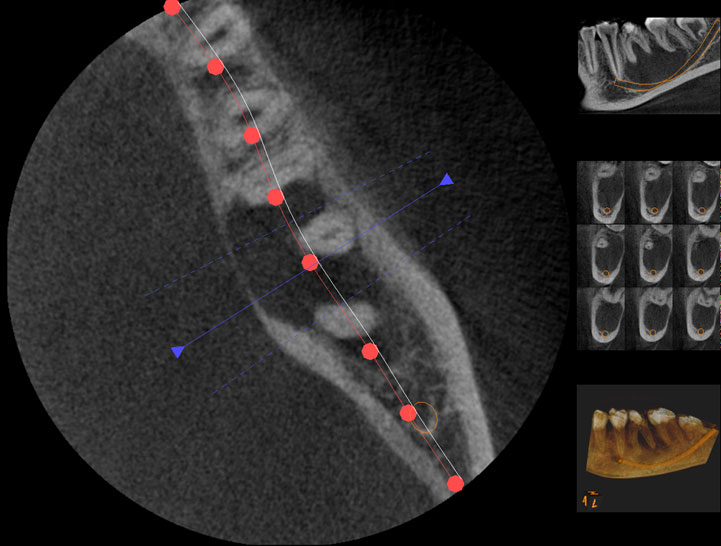
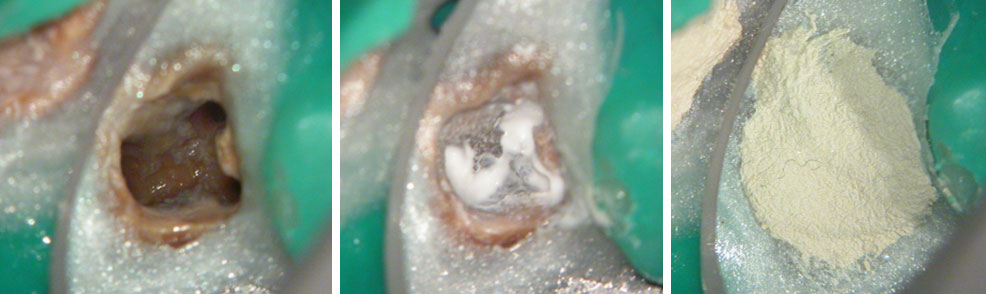
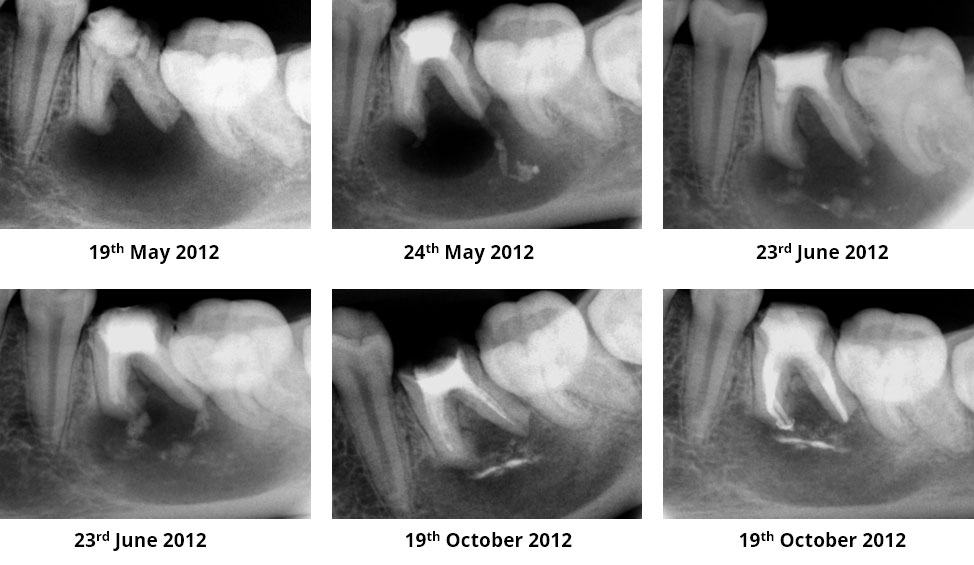
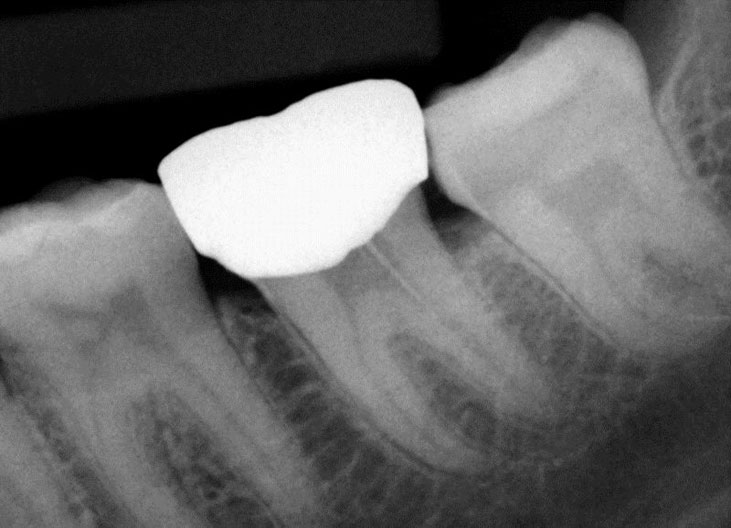
Obturation done after 5 months of calcium hydroxide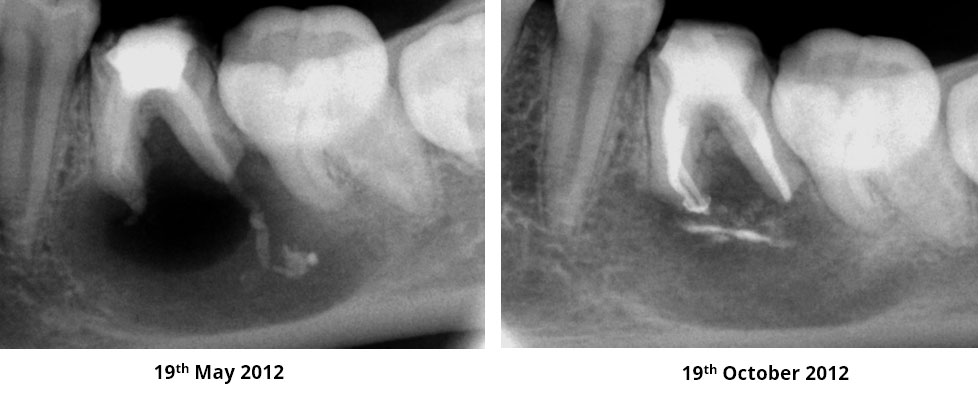
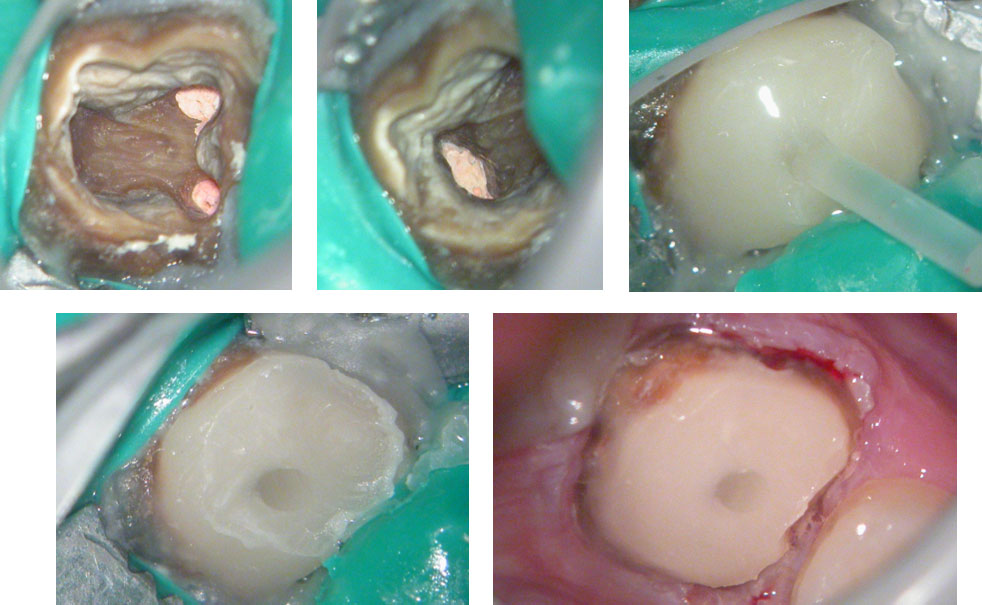
May 2015 – 3 year recall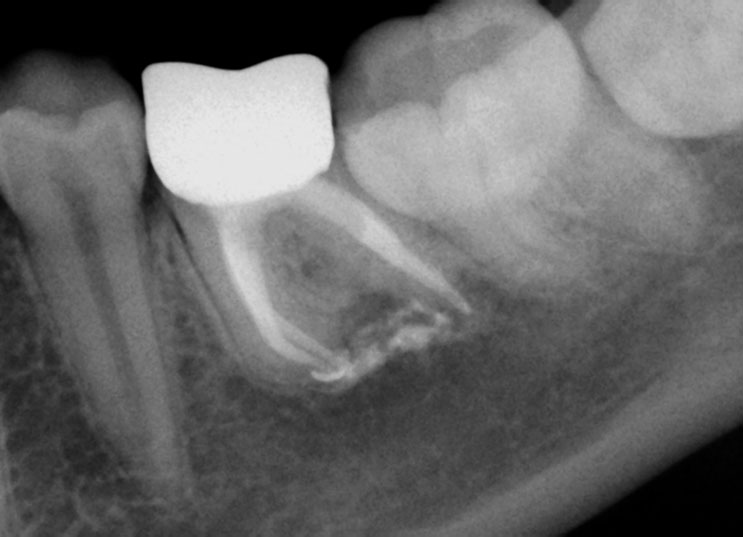
3 year recall CBCT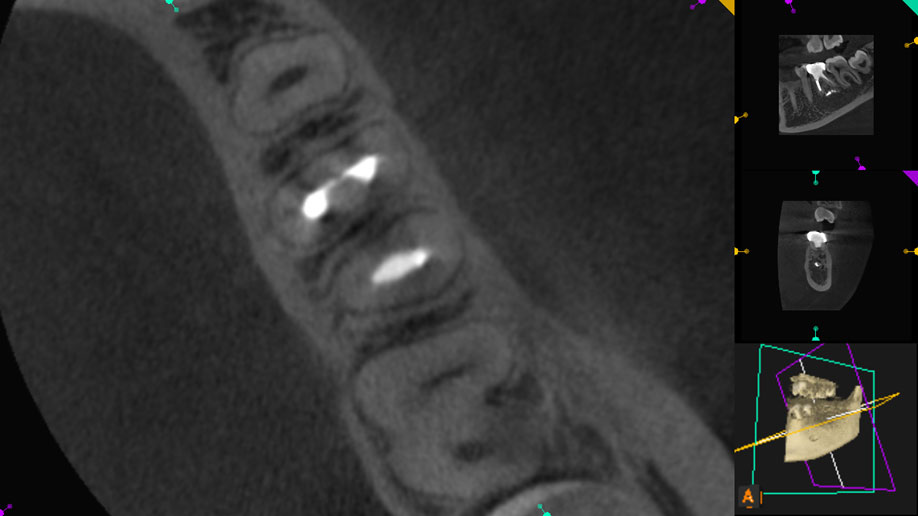
3 year recall CBCT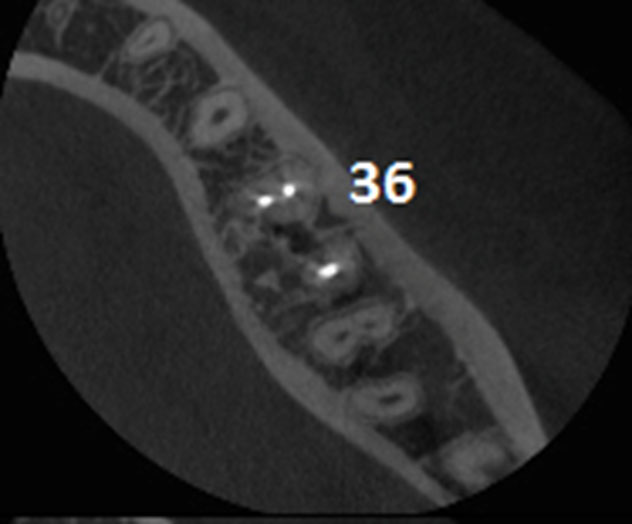
Pre-op & 3 year recall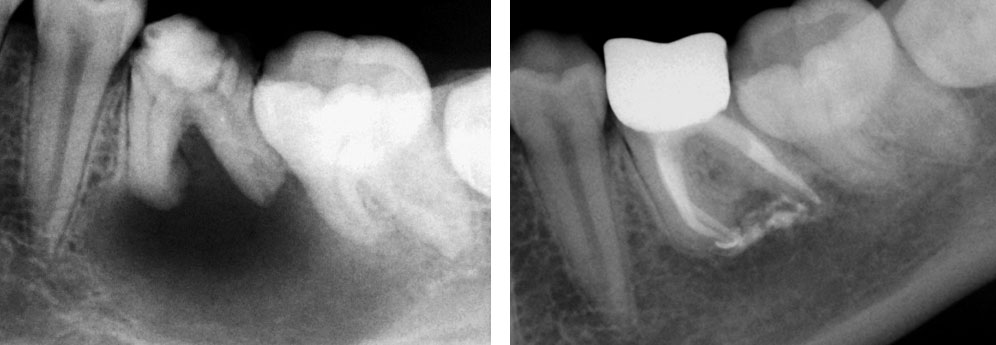
Pre-op & 3 year recall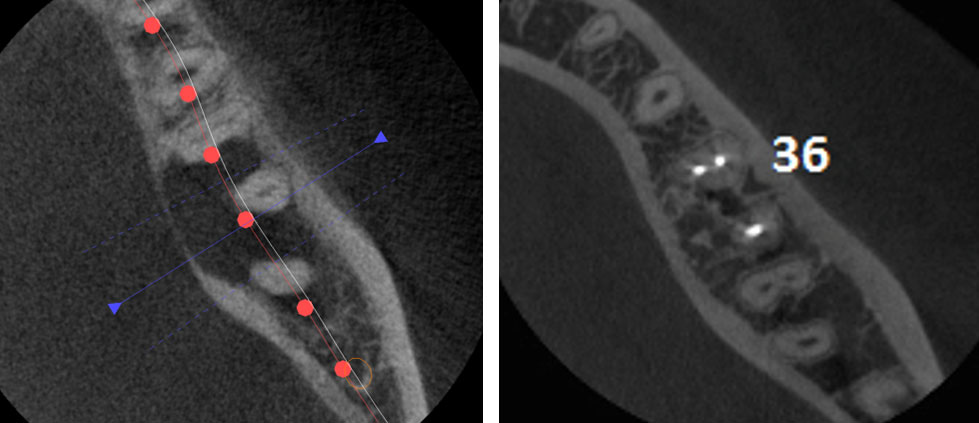
Clinical Case
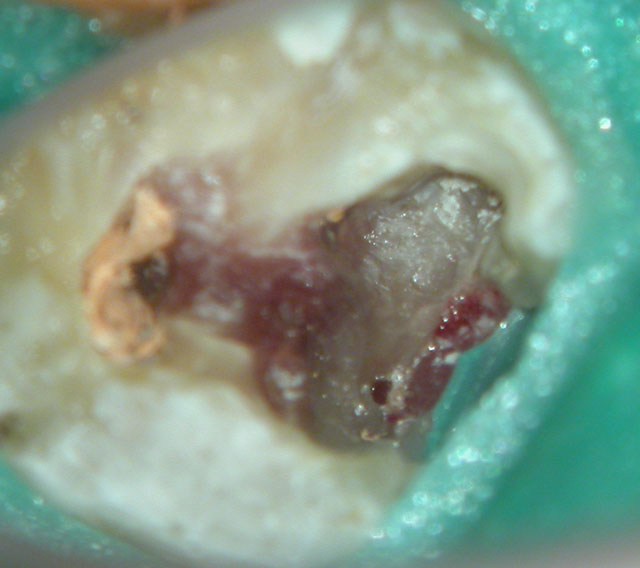
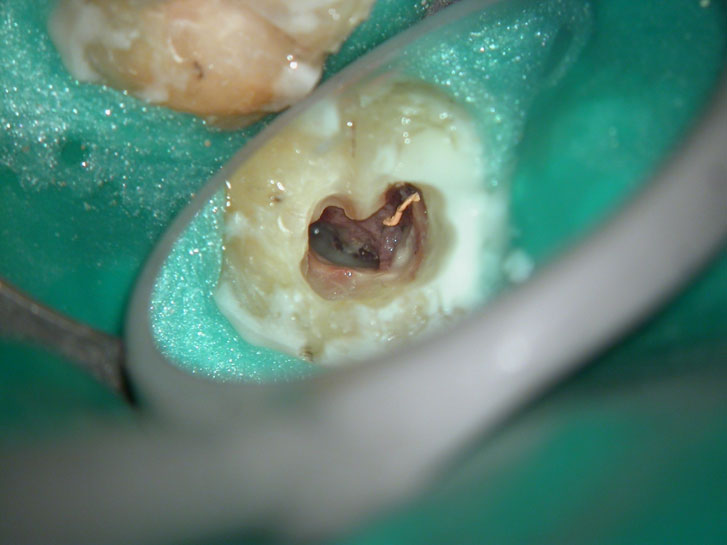
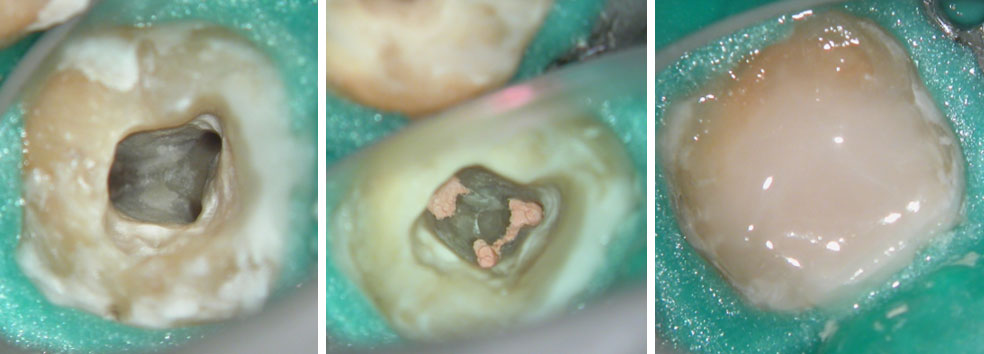
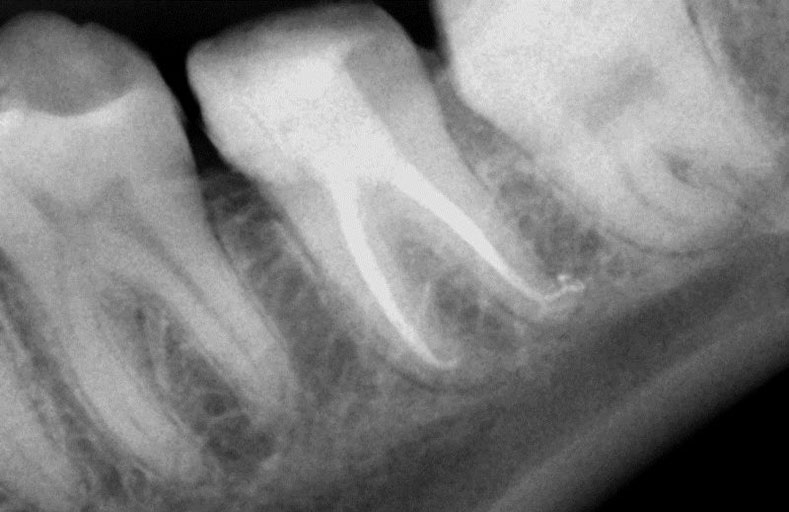
Clinical Case
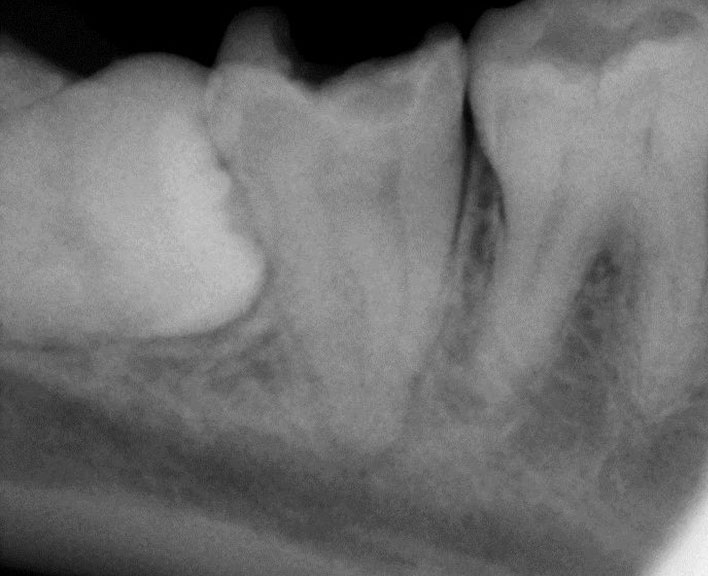
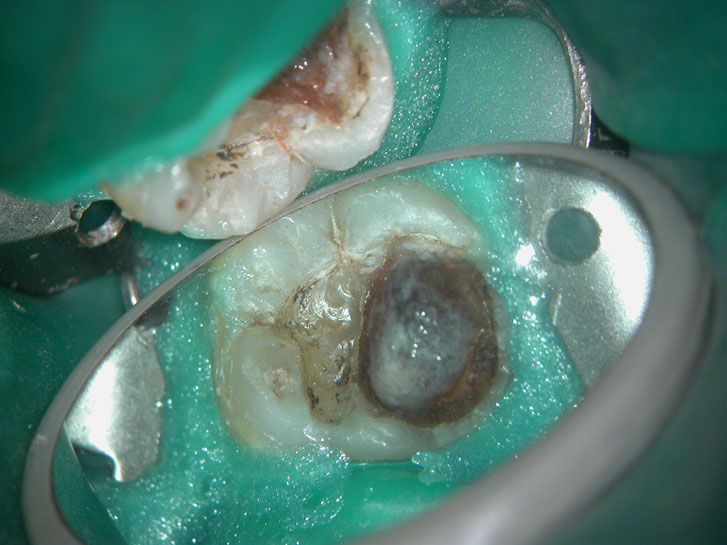
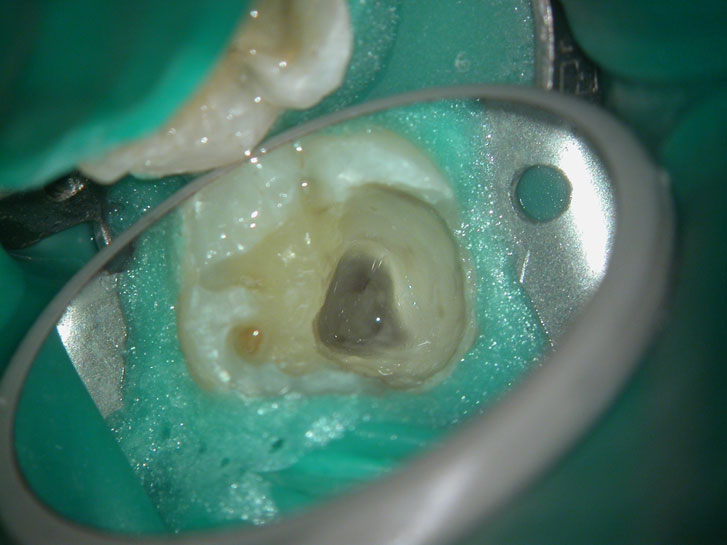
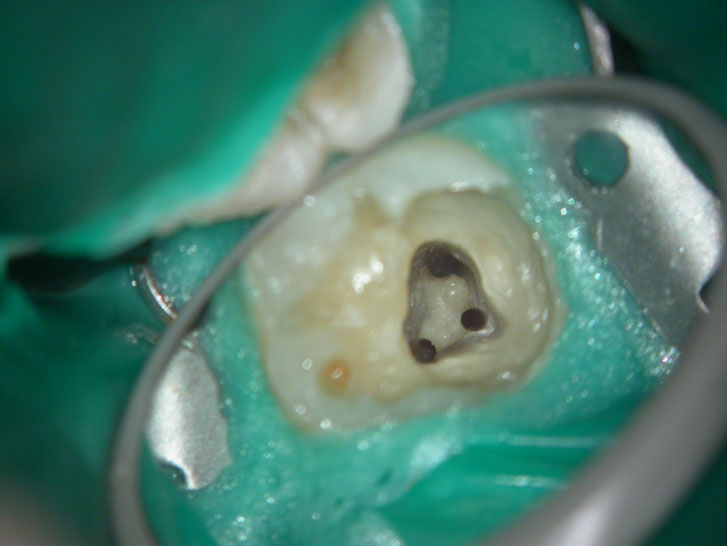
Clinical Case
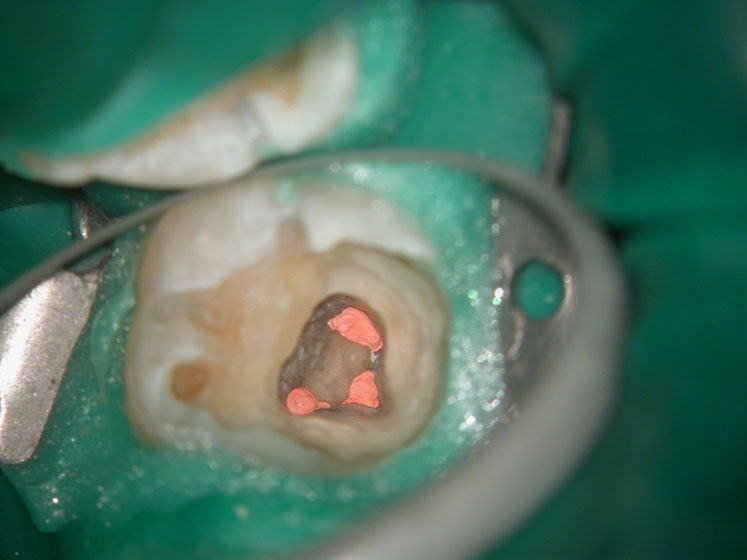
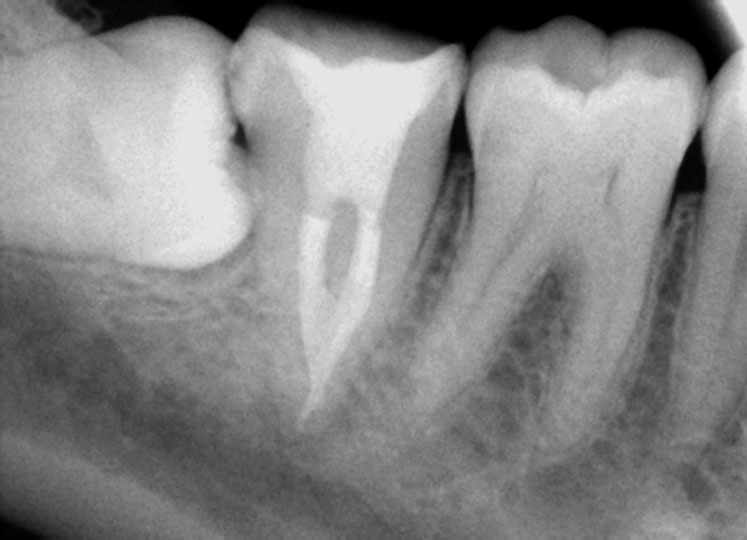
PRE-OP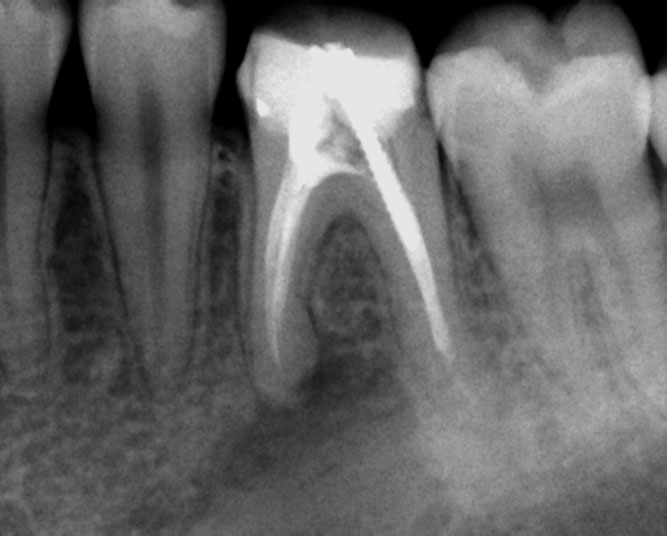
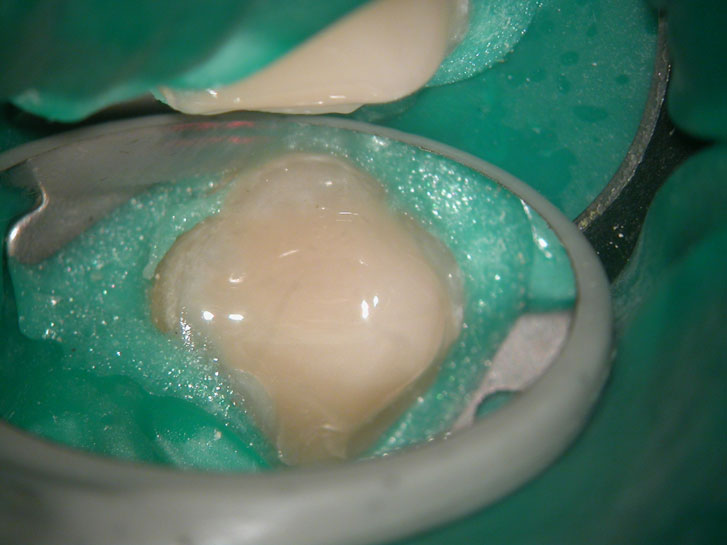
POST-OP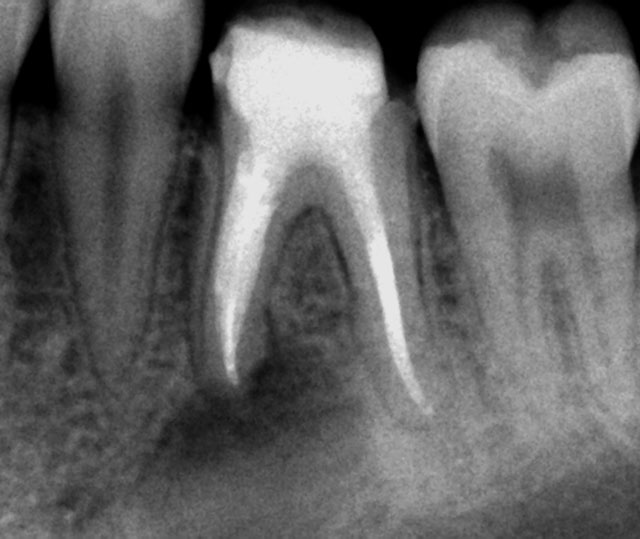
1 YEAR RECALL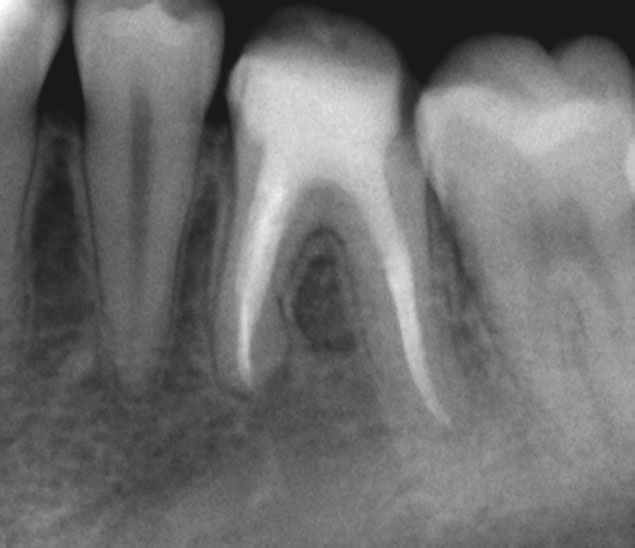
Pre-op, Post-op & One-year recall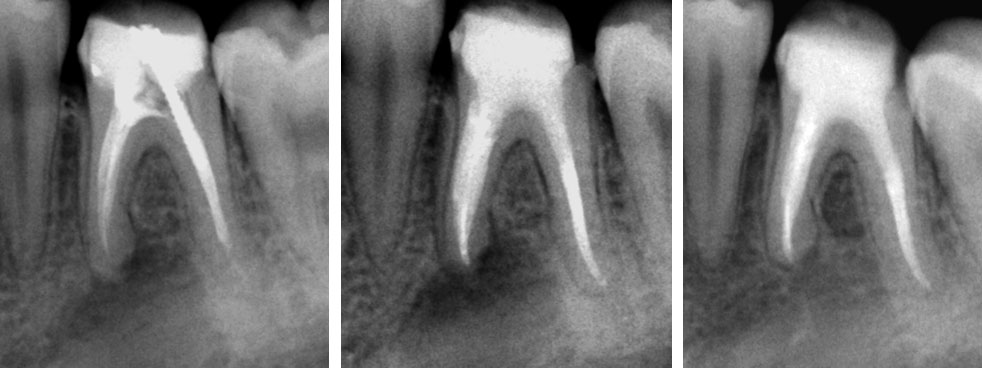
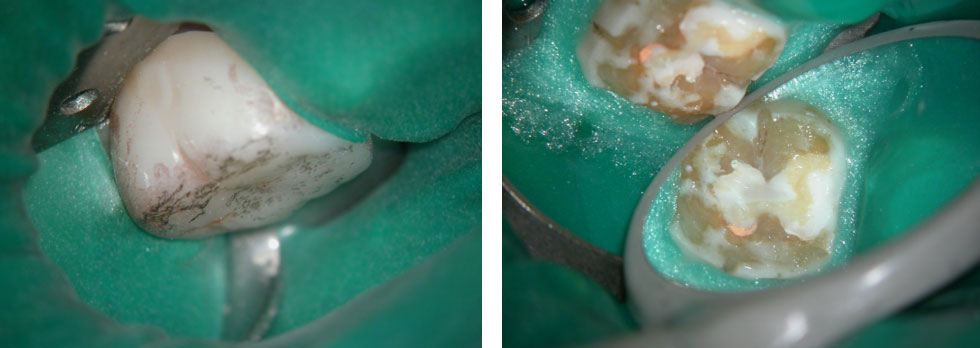
Clinical Case
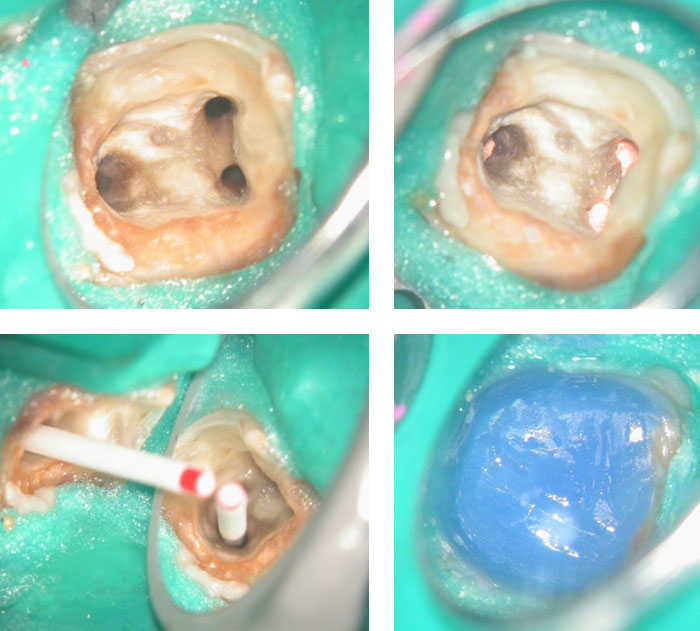
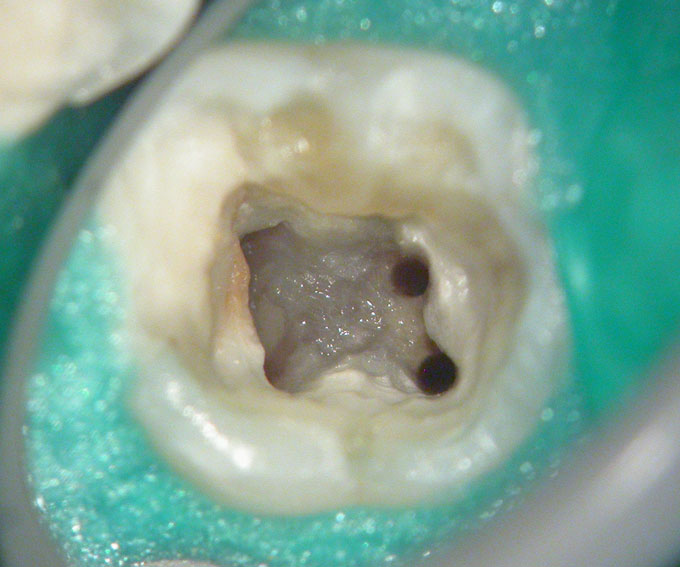
PRE-OP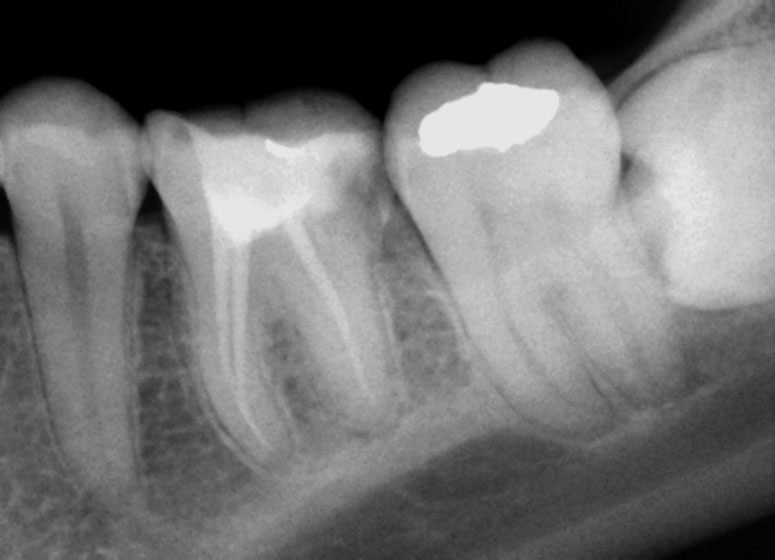
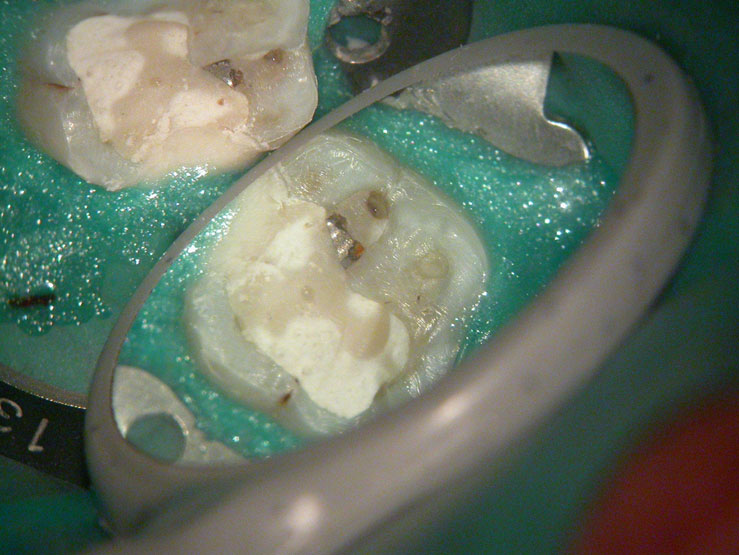
Distal sub-gingival caries 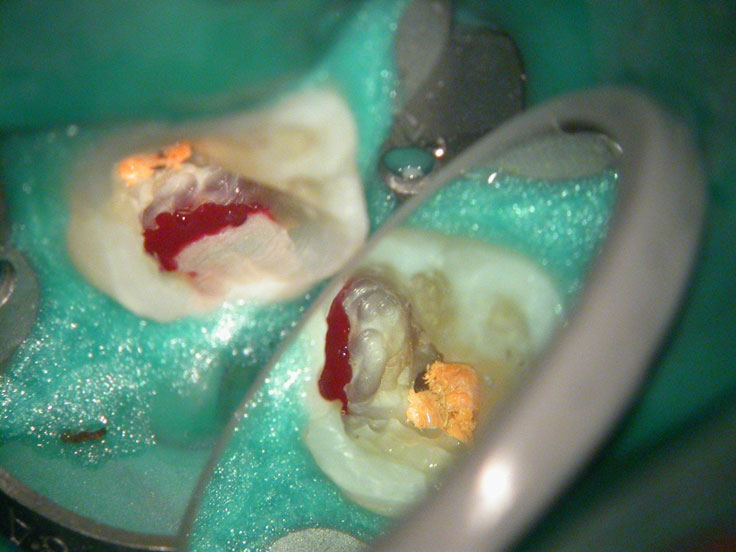
Distal wall built-up temporarily with glass Ionomer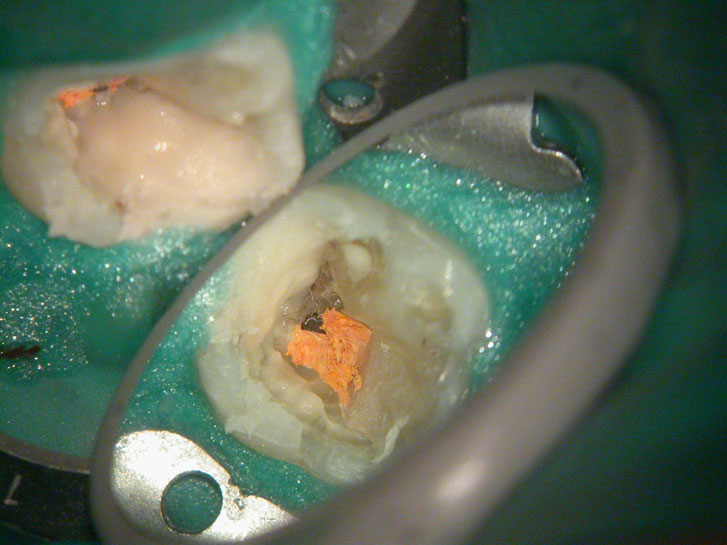
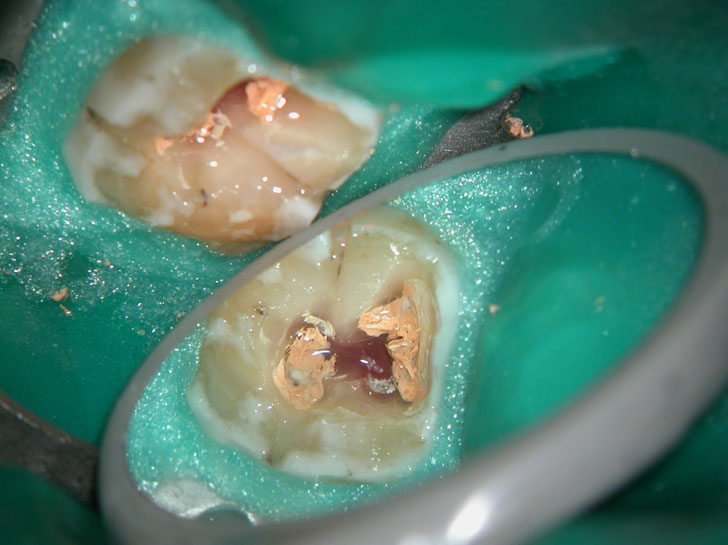
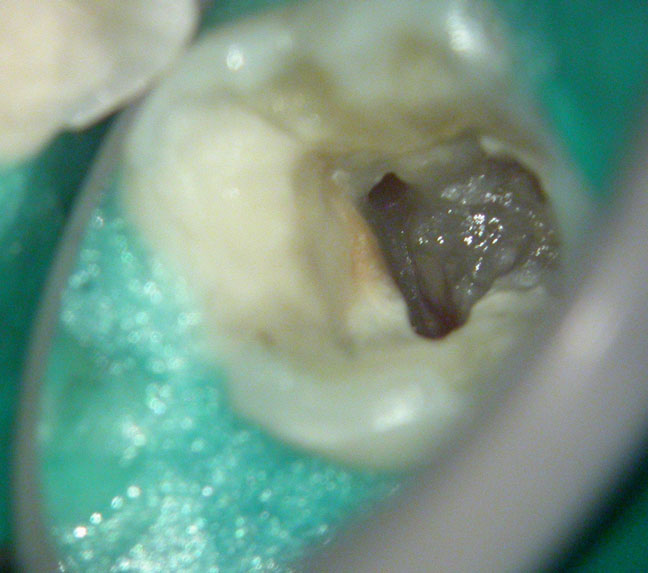
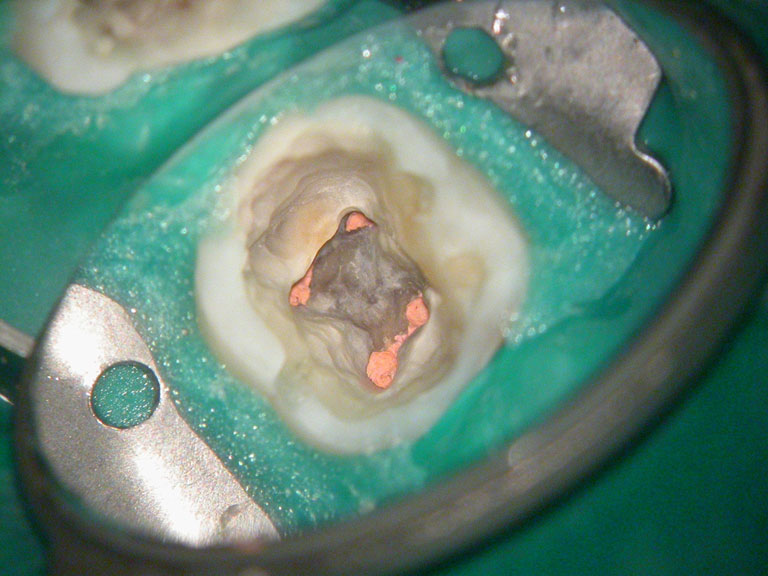
Large pulp stone (red arrows) seen 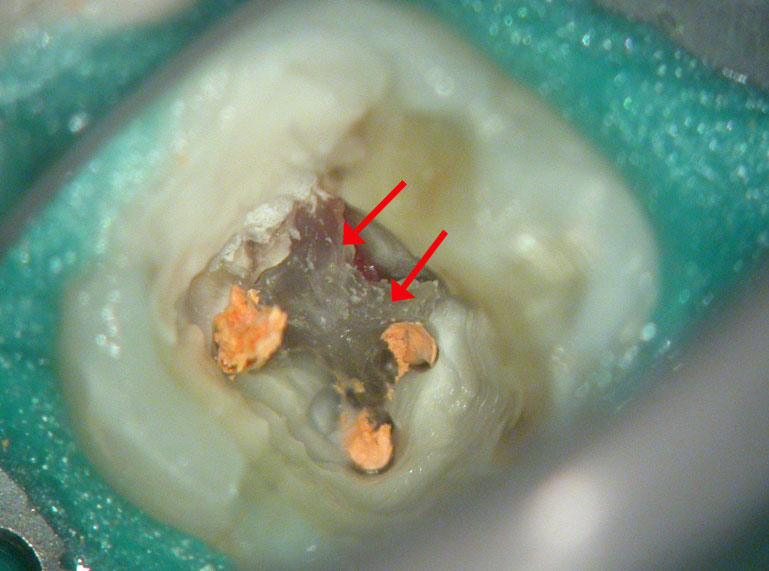
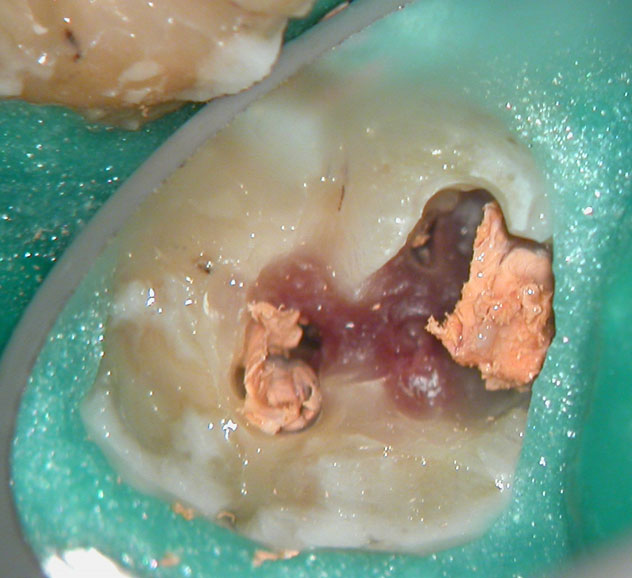
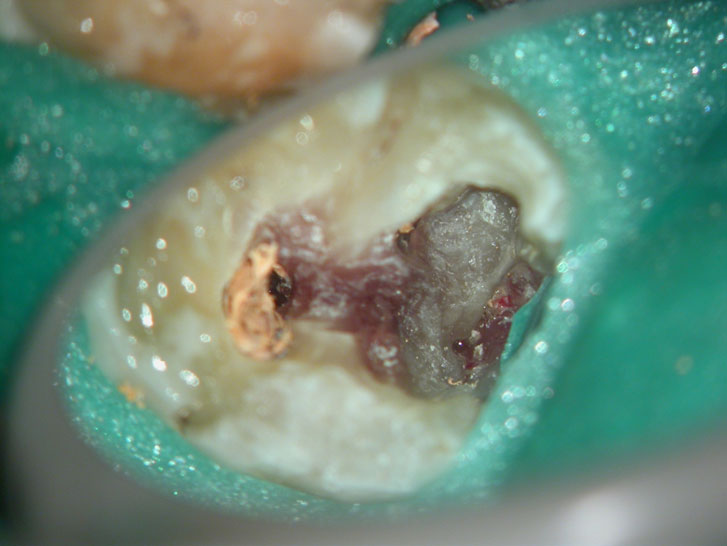
Removal of pulp stone reveals an untreated distal canal which was (surprisingly) vital and hyperaemic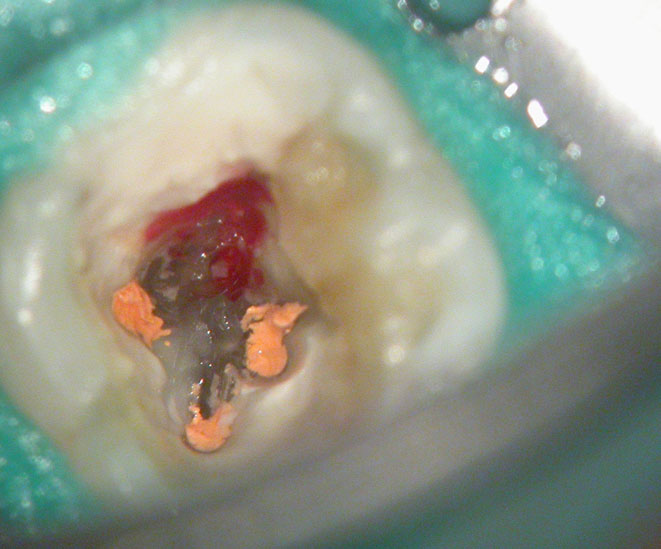
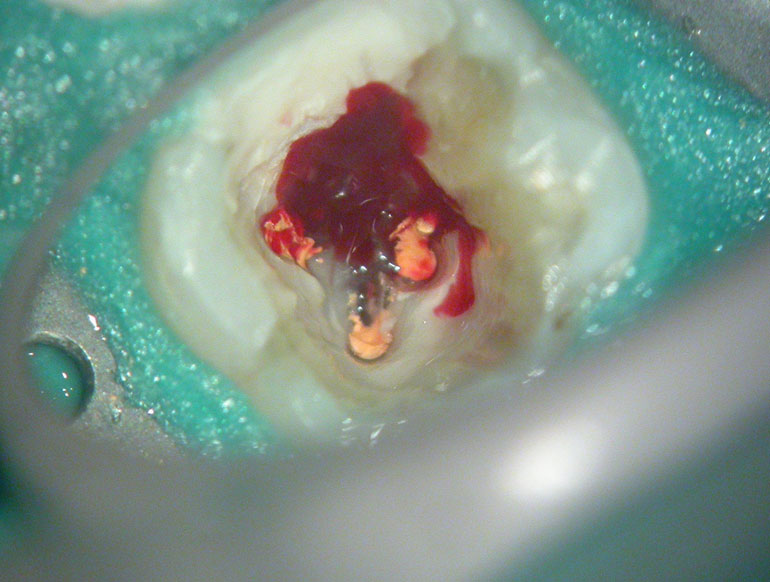
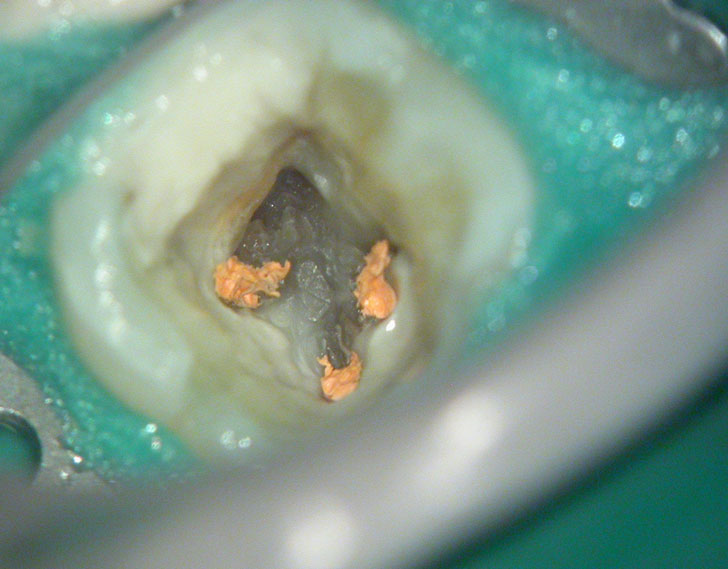
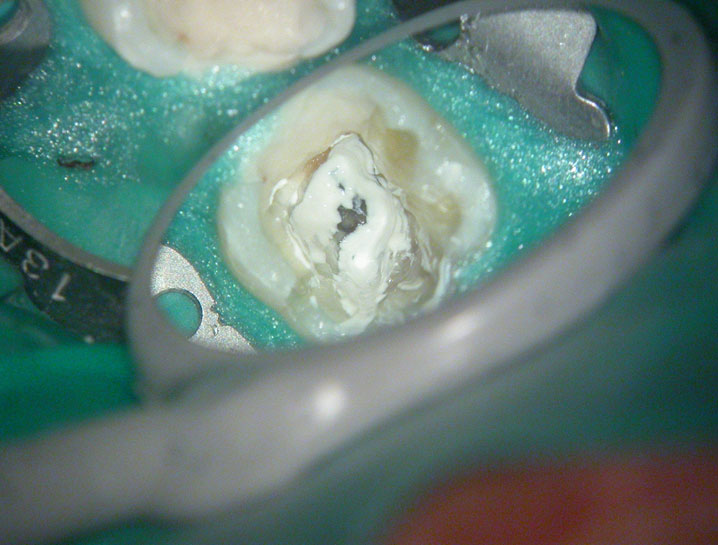

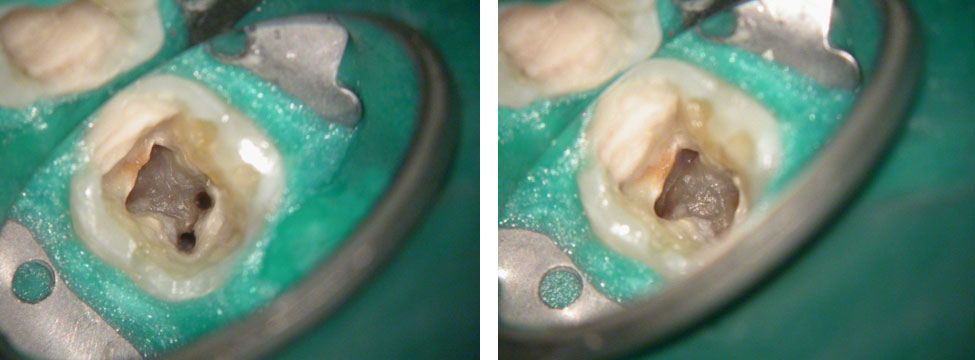
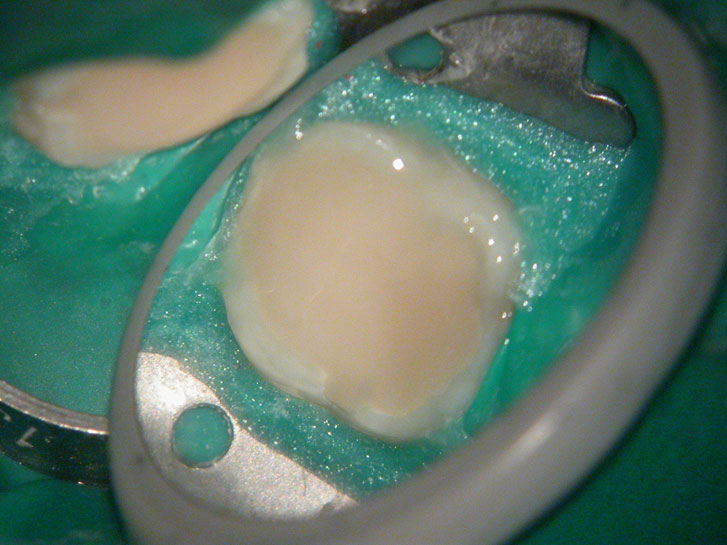
POST-OP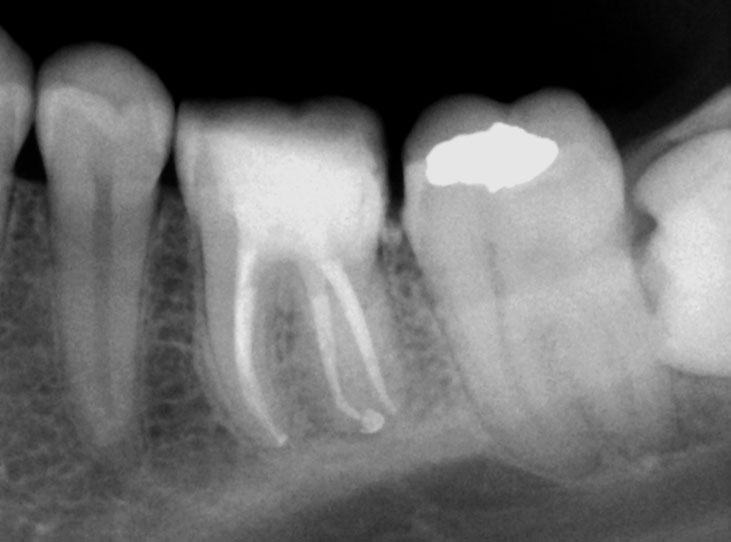
PRE-OP & POST-OP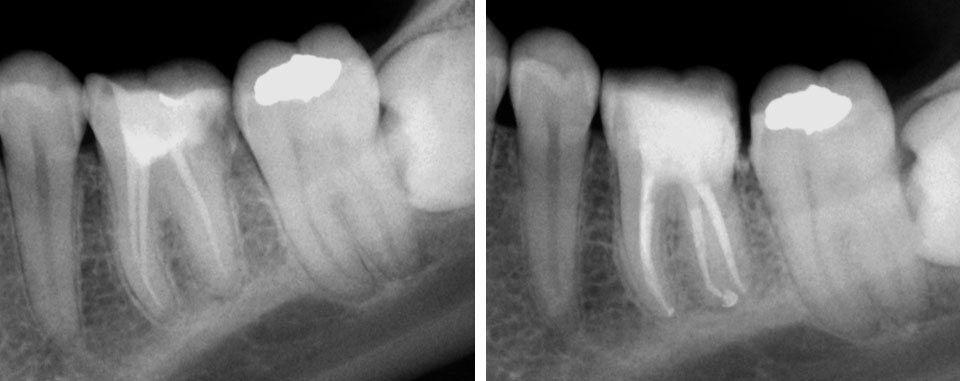
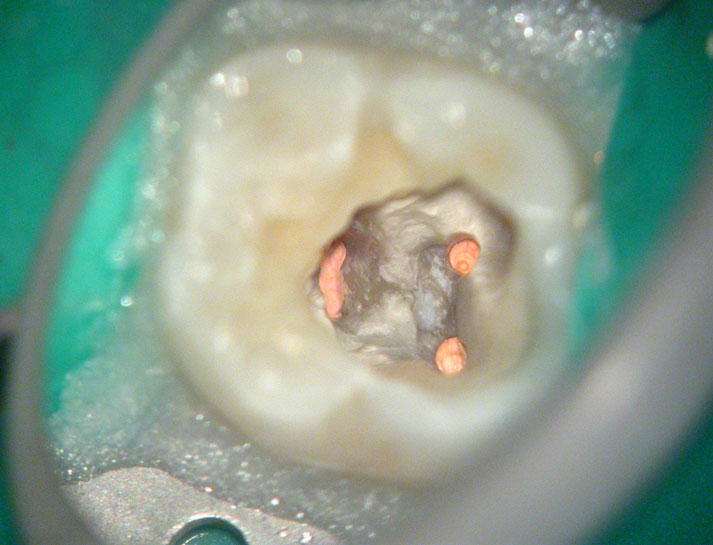
Clinical Case
Pre-op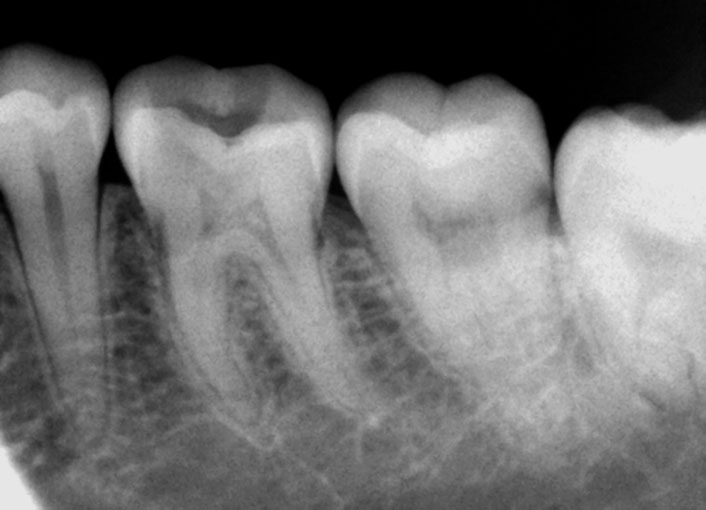
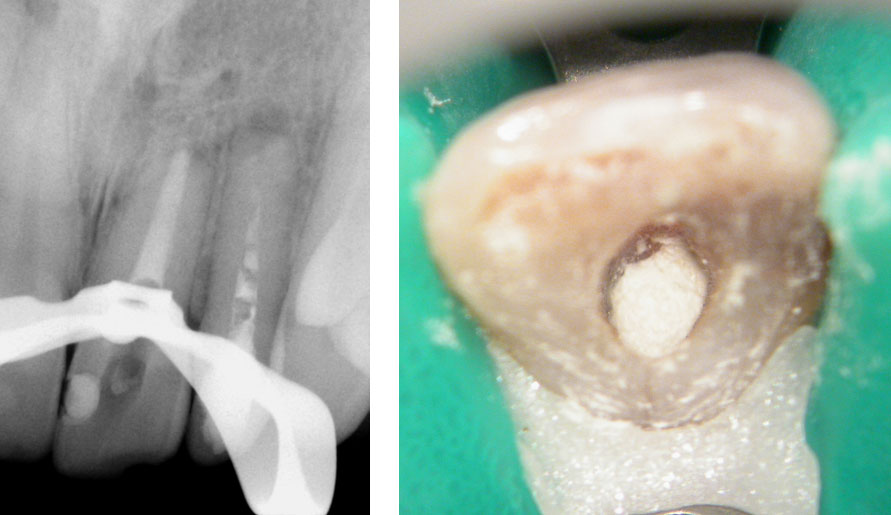
Perforation (red arrow)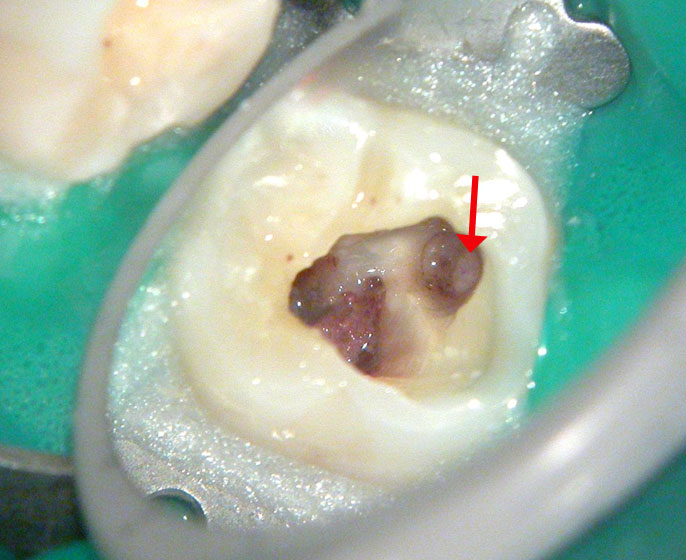
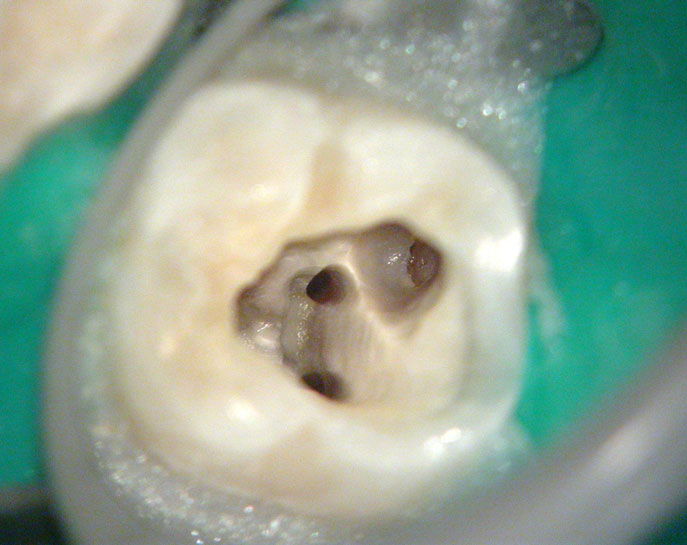
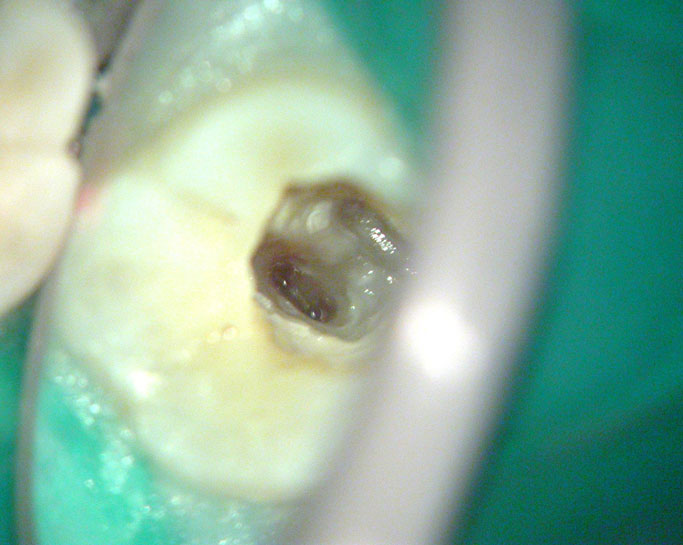
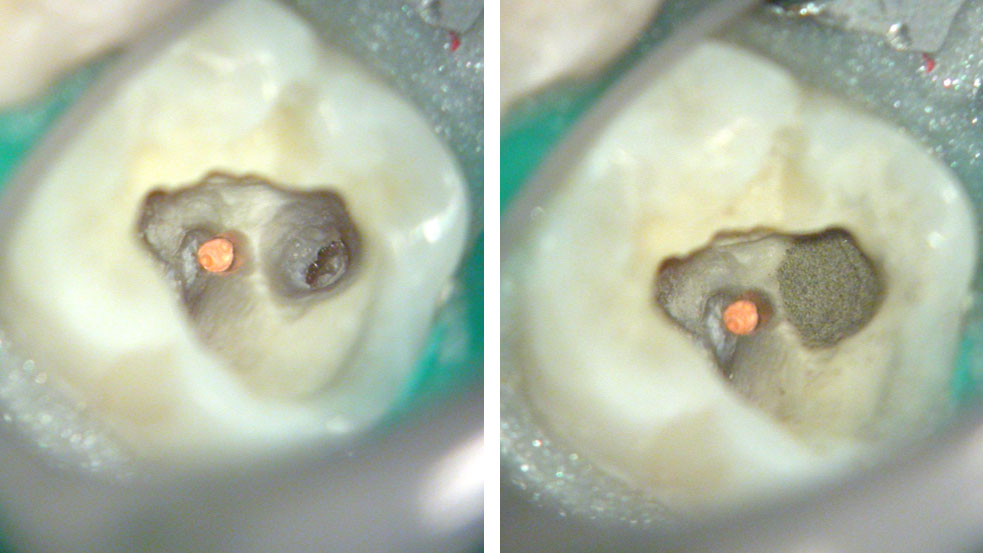
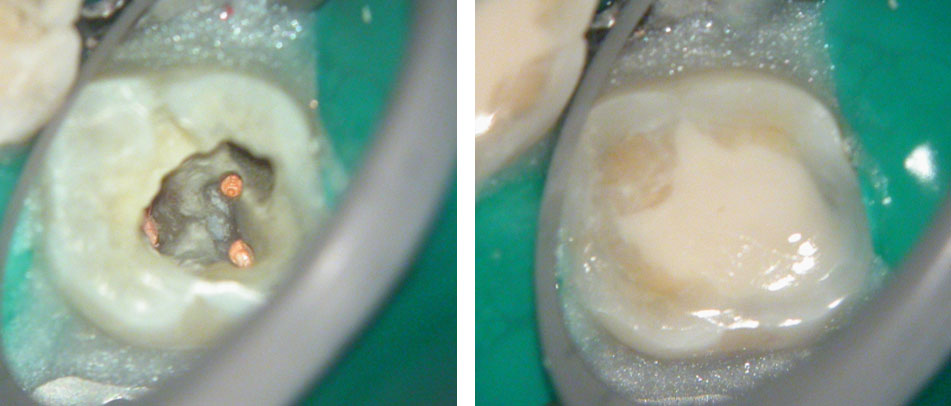
Post-op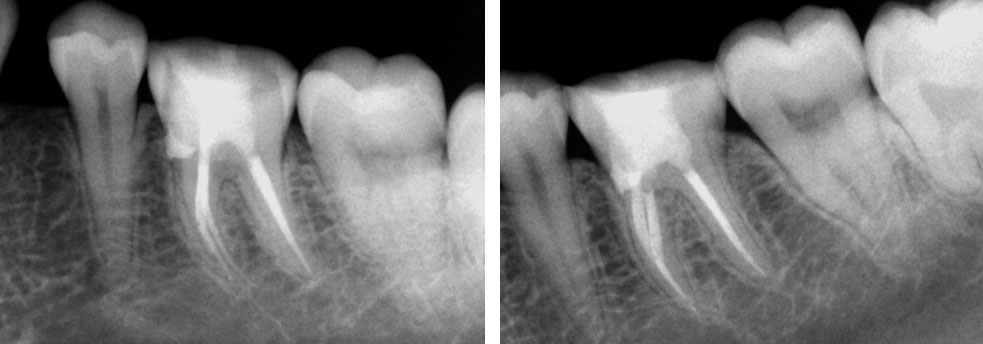
Clinical Case
Pre-op
Maxillary central and lateral incisor with history of previous Endodontic therapy and root-end resection
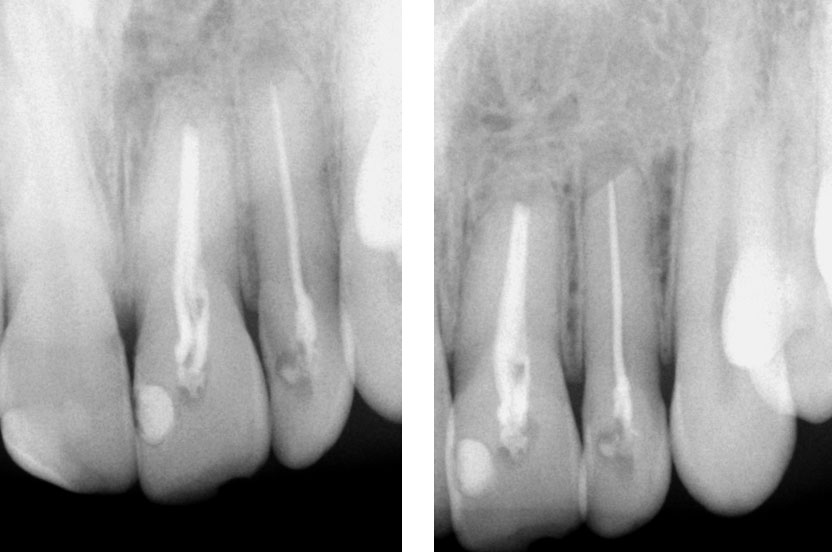
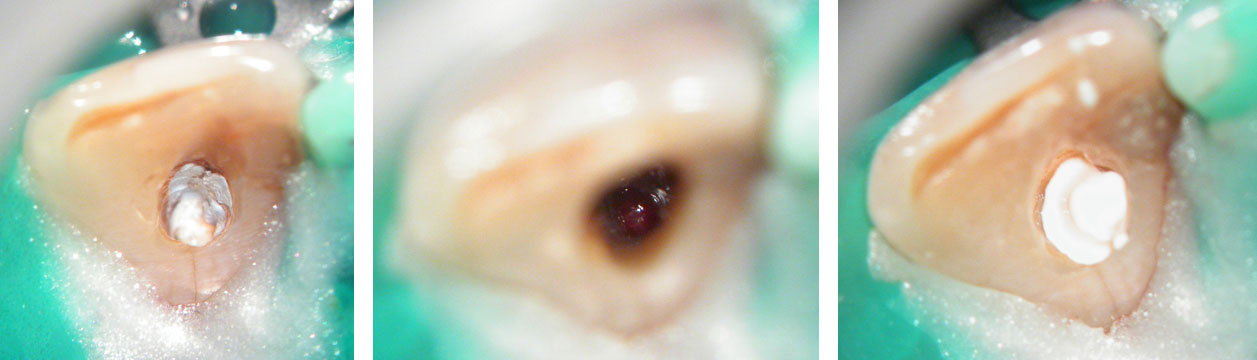
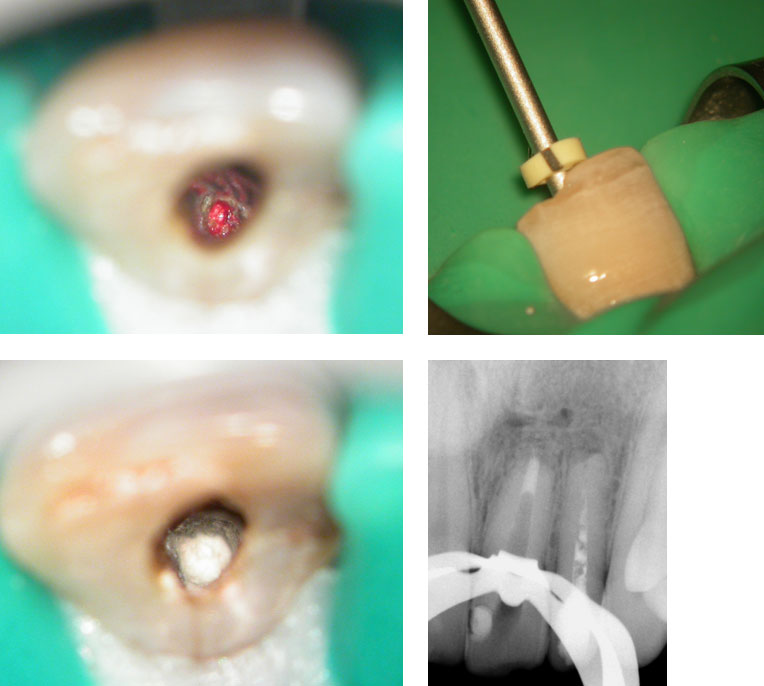
Central incisor: old root canal filling removed. Profuse bleeding from the apex seen. Apex is wide open. Canal cleaned and calcium hydroxide medicament placed.
MTA Placement with Dovgan carrier
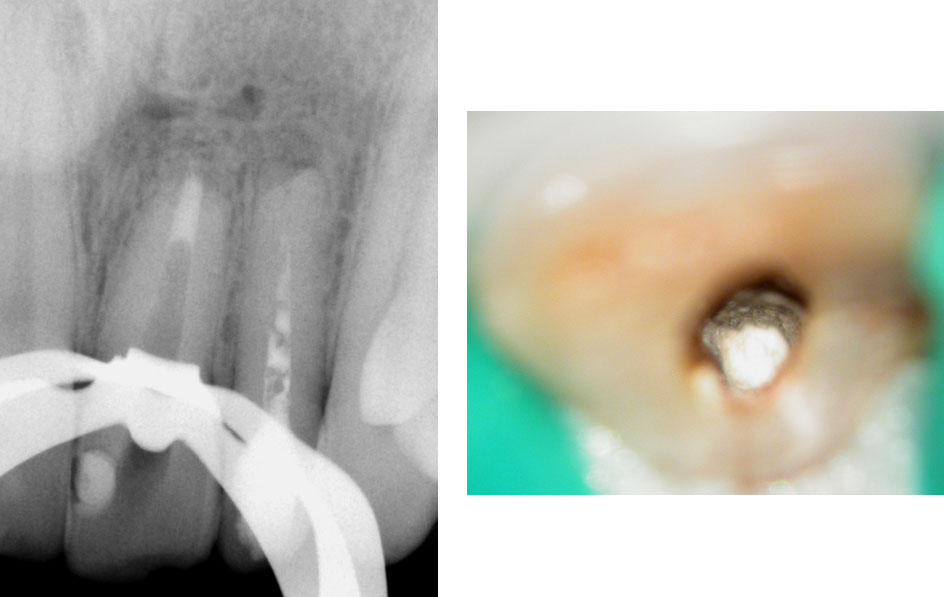
Pre-op & Post-op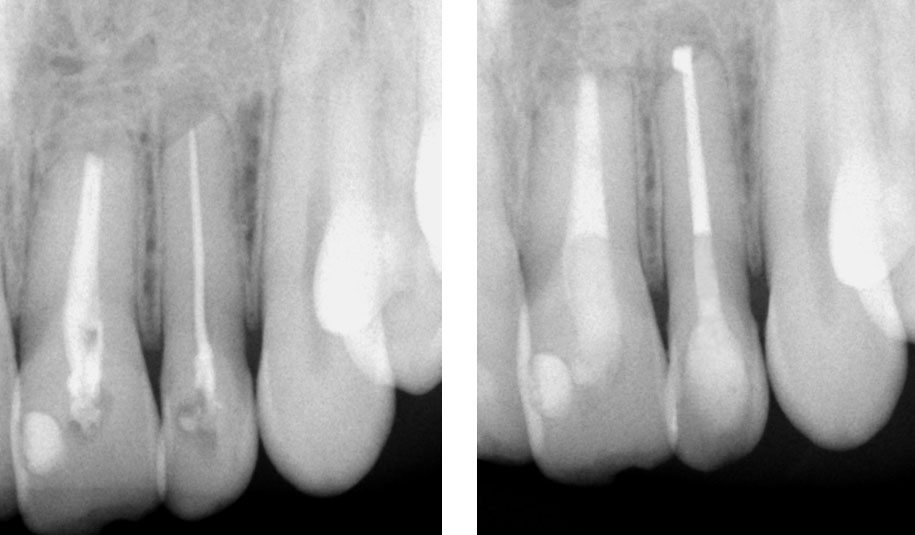
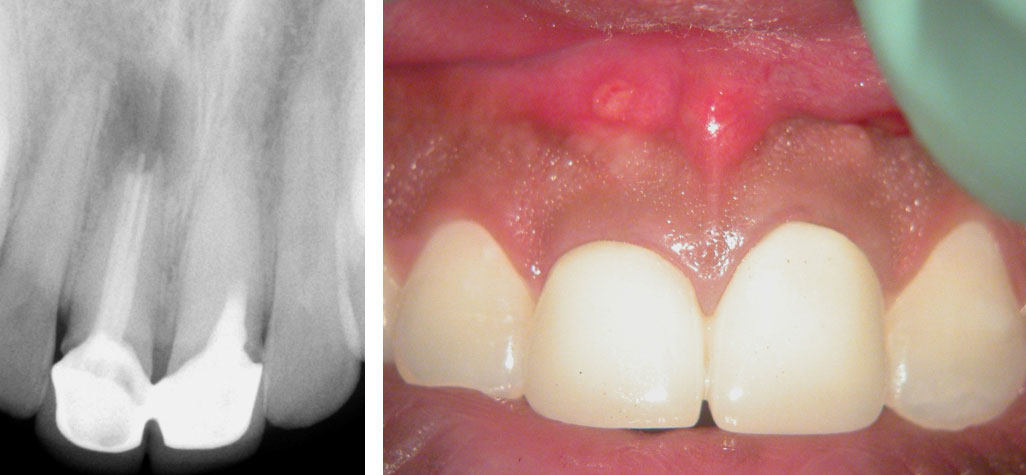
Clinical Case
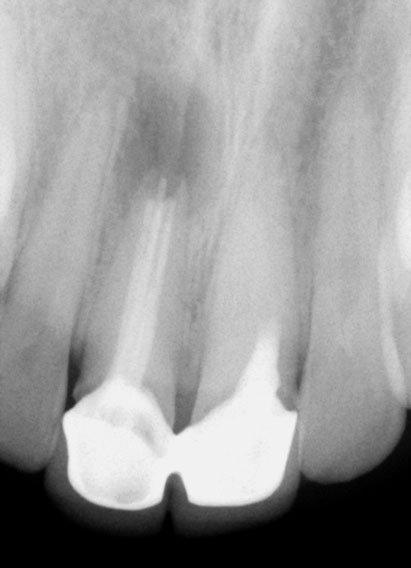
Pre-op
Persistent pain and swelling over the right central Incisor. Pain on palpation over the left central incisor. History of previous root canals and surgery done 3 years ago.
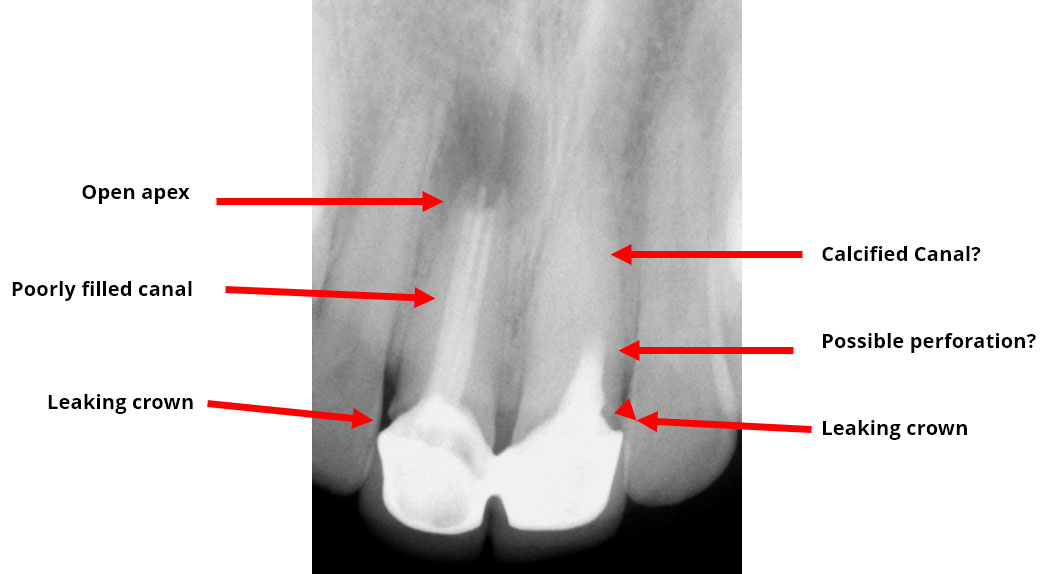
Treatment Plan:
(Patient in town for only 9 days)
• Putty impression. Remove crowns.
• Left Central incisor: Remove old filling. Locate calcified canal. Repair perforation if present. Do obturation and core build-up
• Right Central Incisor: Remove old filling. Fill entire canal with MTA. Core build-up with Composite.
• Refer to Prosthodontist to prep and take impressions for new crowns. Cement temporaries.
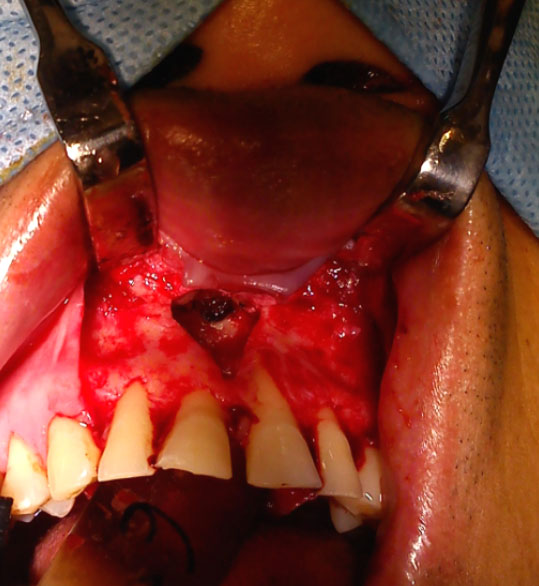
• Surgical Curettage of lesion and Apicoectomy of right central incisor.
6 days later, Suture removal and Cement Permanent crowns.
Left Maxillary central Incisor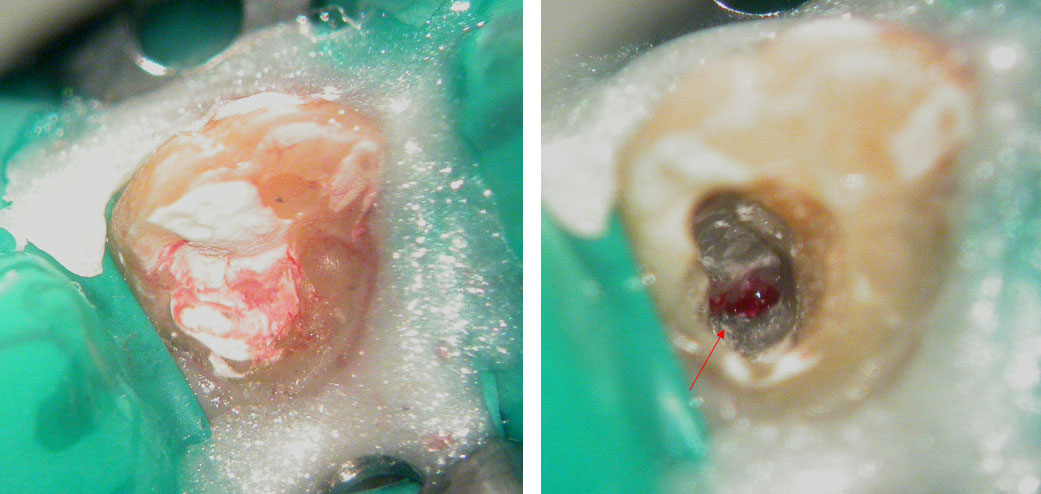
Canal located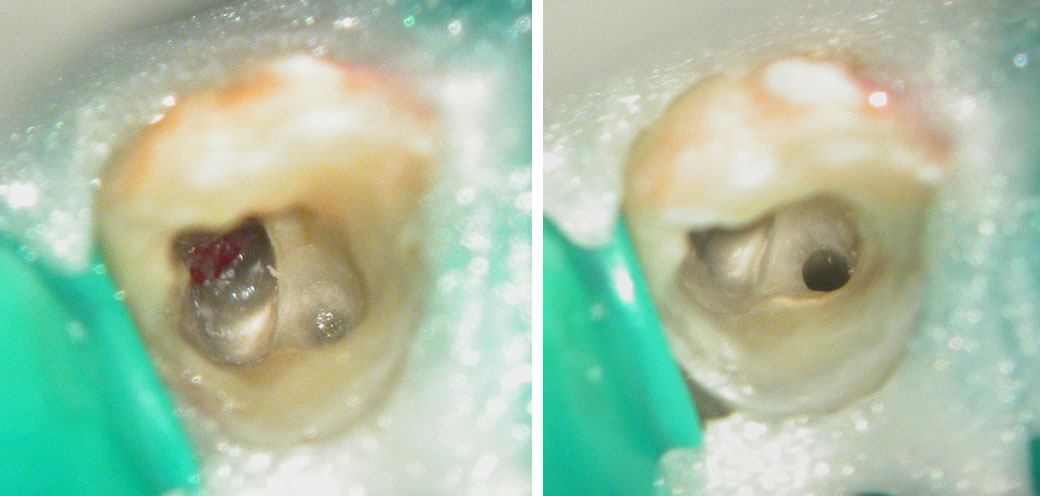
Perforation repaired with MTA 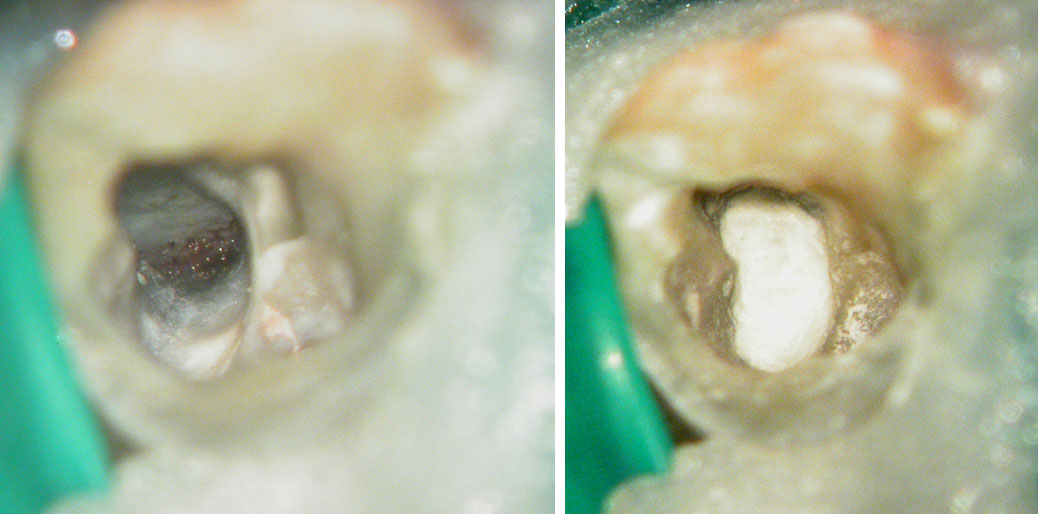
Obturation and core build-up done. 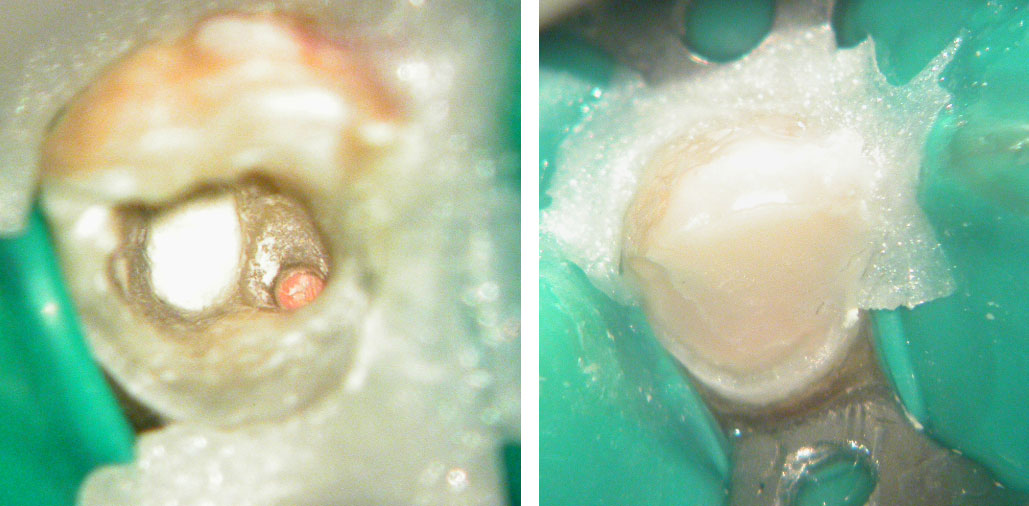
Pre-op, Canal location & Post-op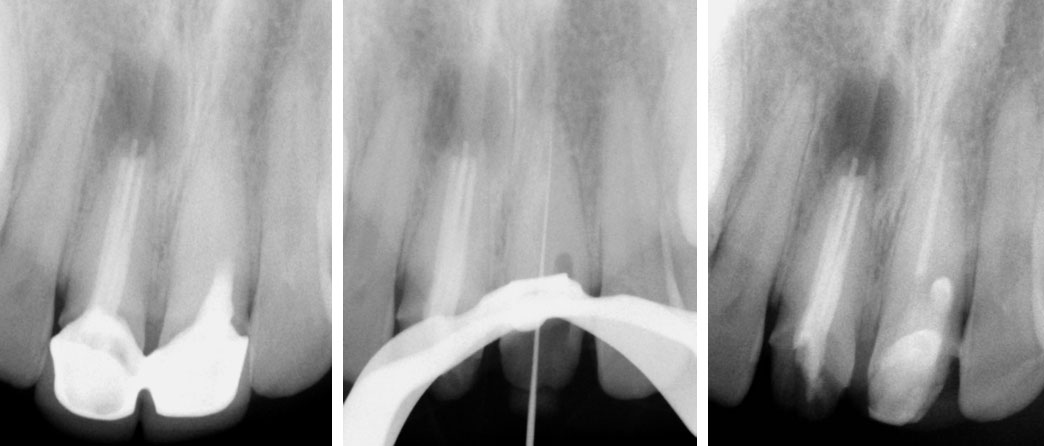
Right Maxillary Incisor
Old filling removed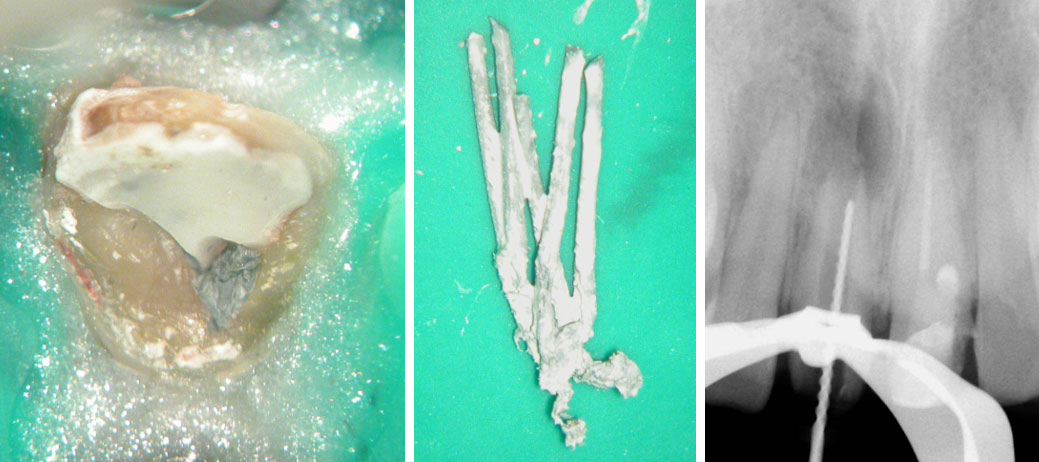
Canal filled with MTA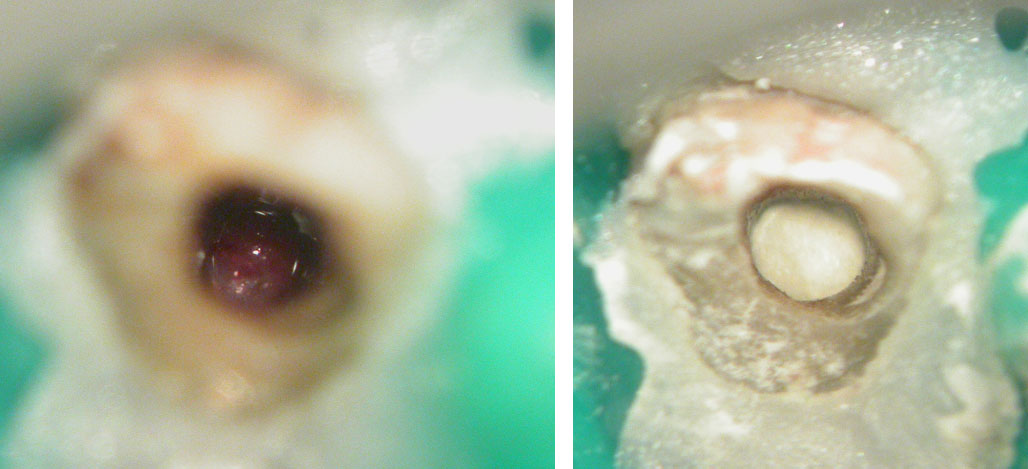
Canal filled with MTA. Core build-up done with composite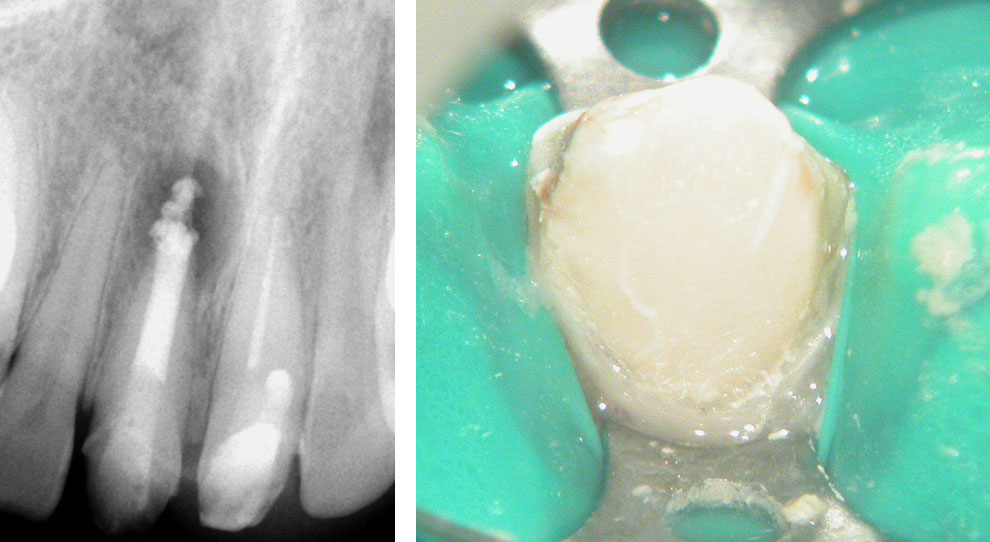
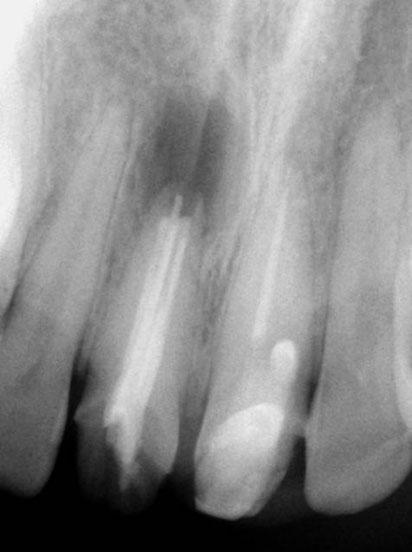
Surgical Curettage of apical lesion and Apicoectomy in right central incisor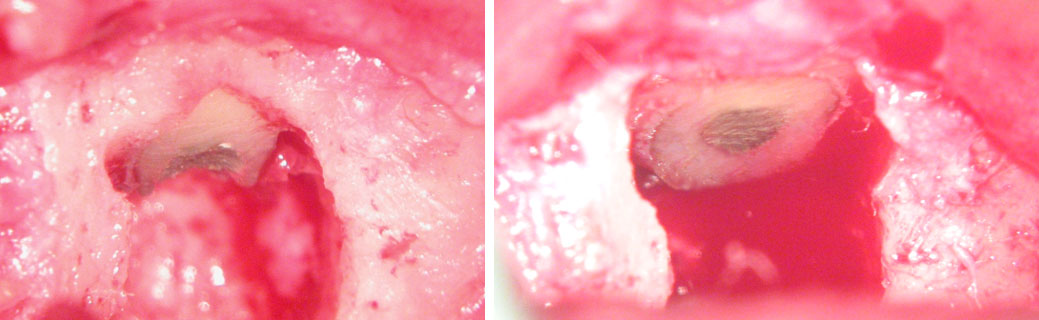
Pre-op, After MTA obturation & After surgery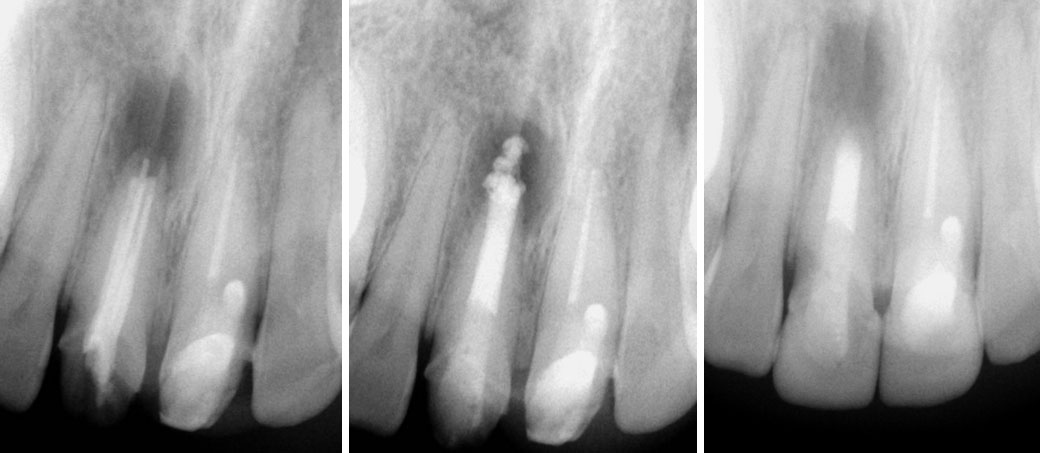
After suture removal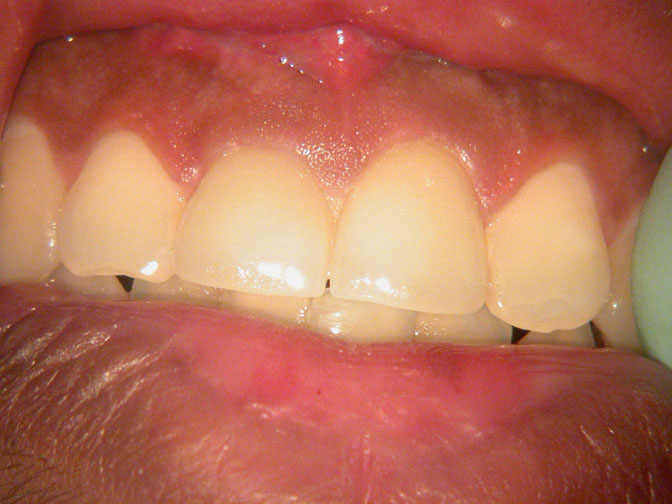
2-YEAR RECALL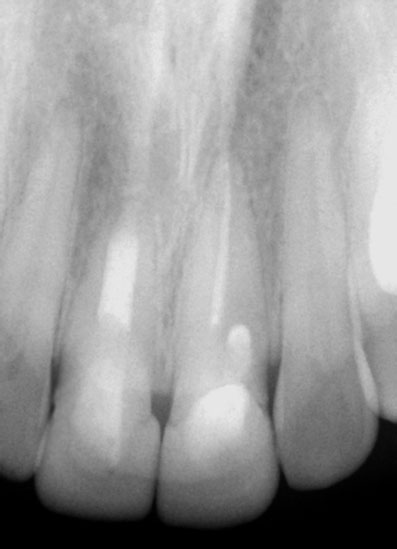
Pre-op, Post-op & 2-Year Recall 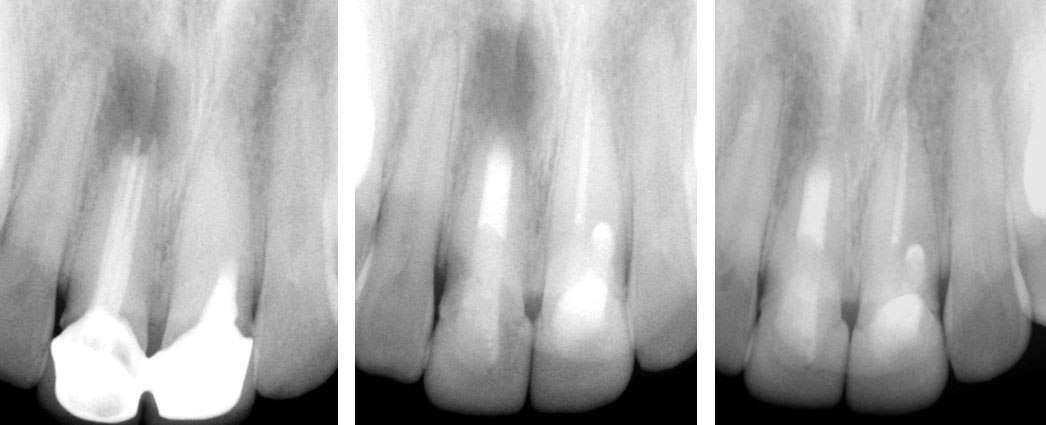
Clinical Case
Pre-op
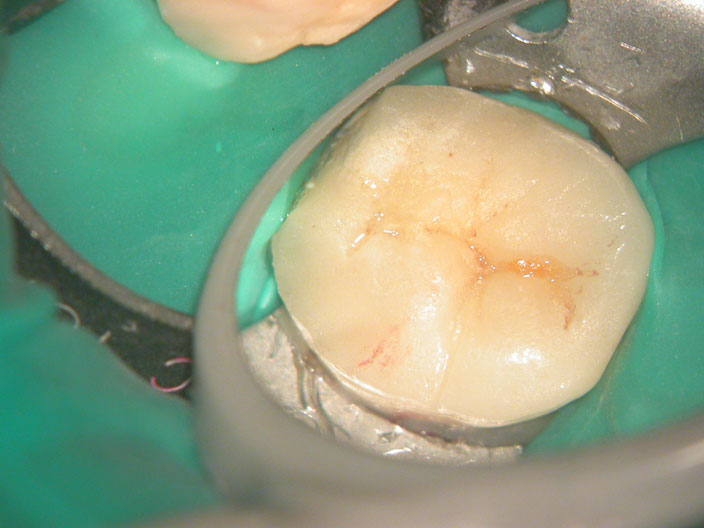
Crown sliced and removed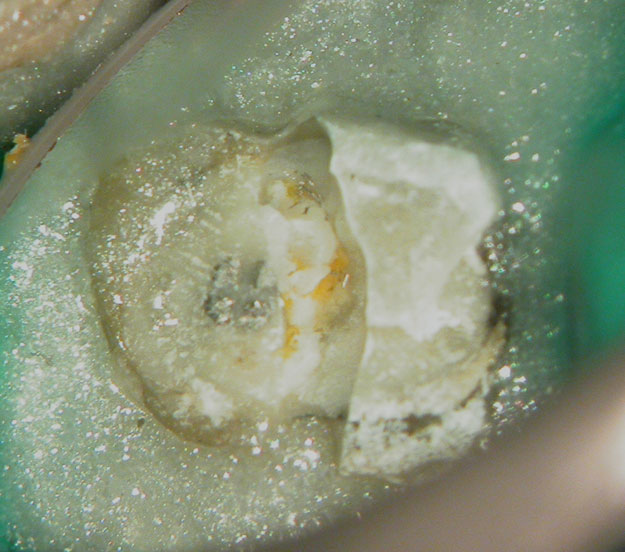
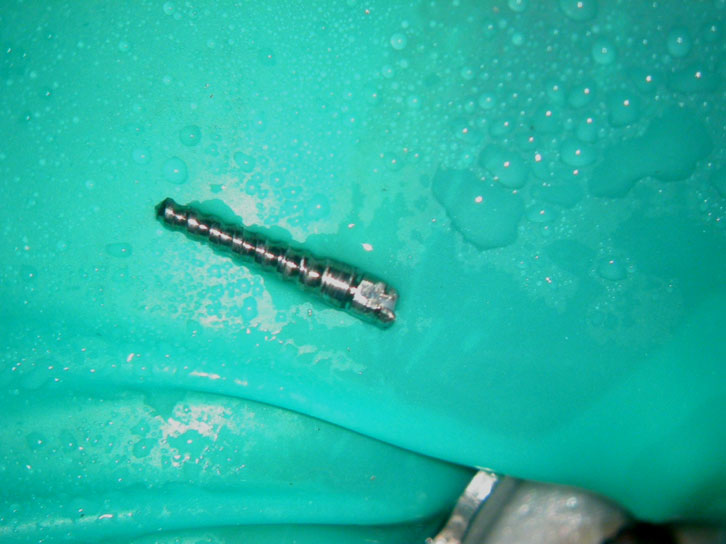
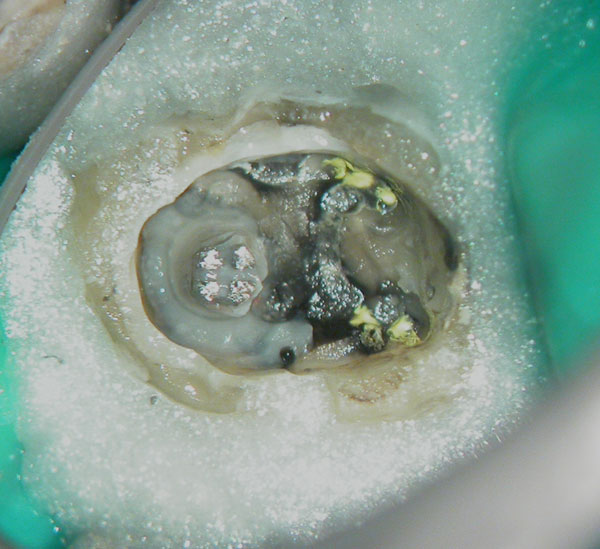

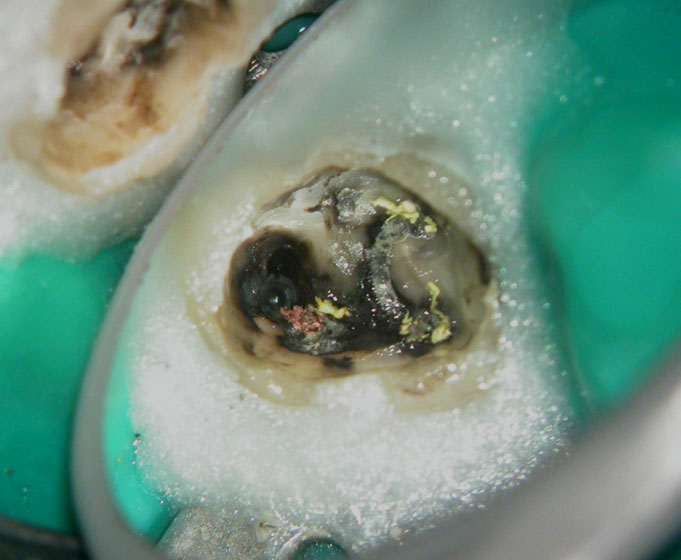
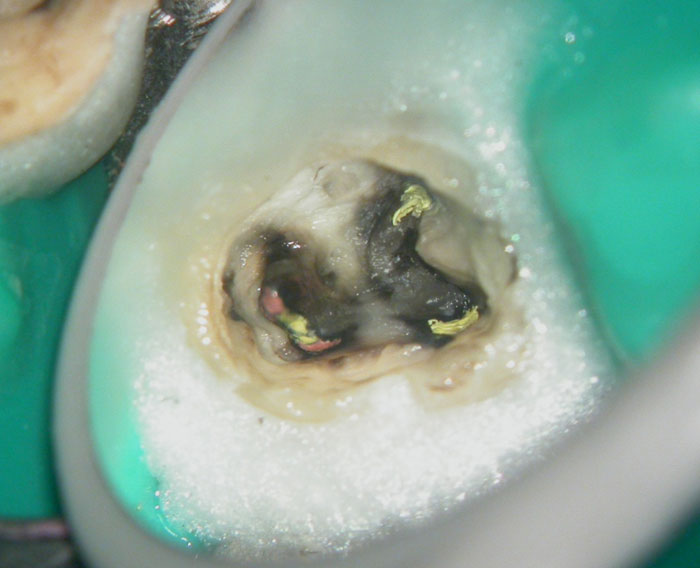
Pus discharge from distal canal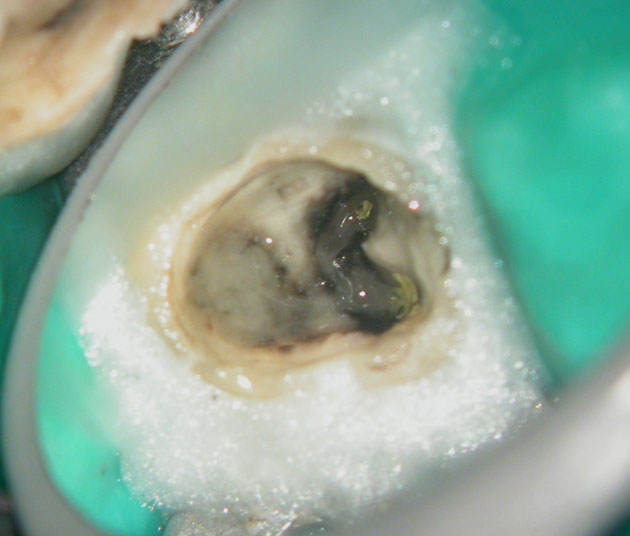
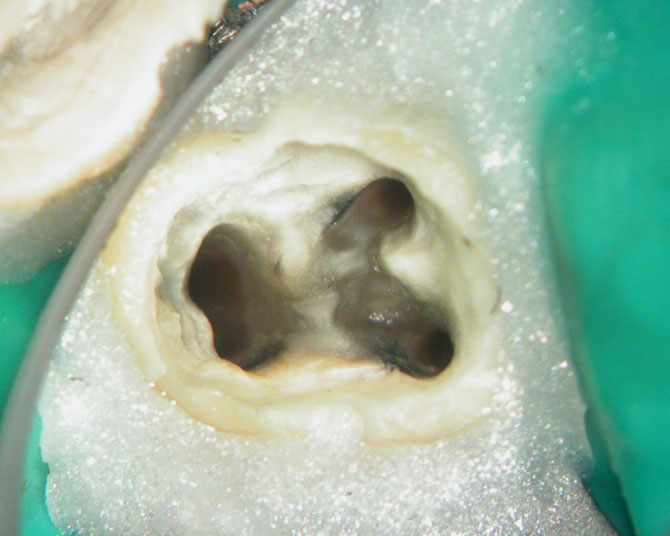
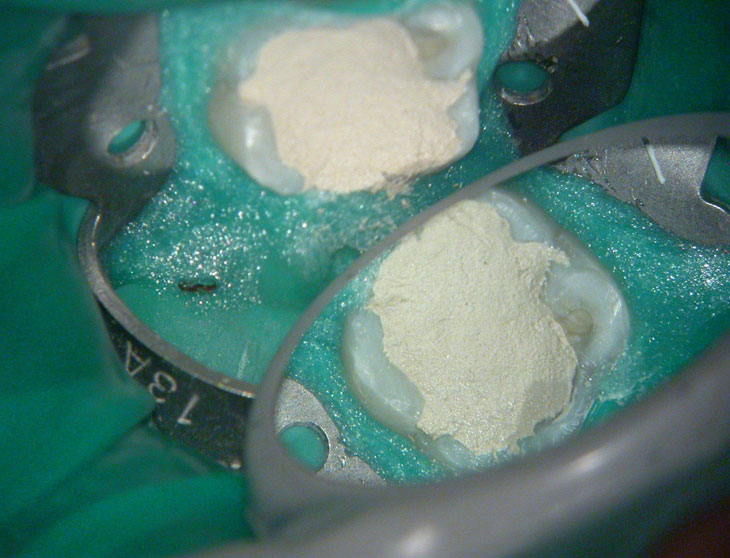
Calcium hydroxide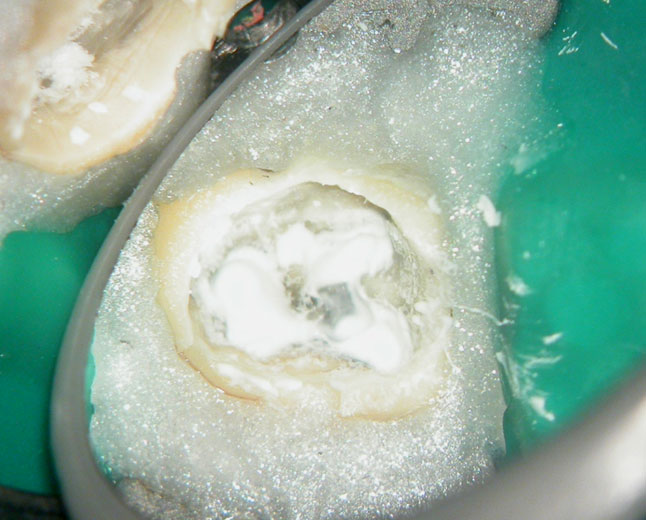
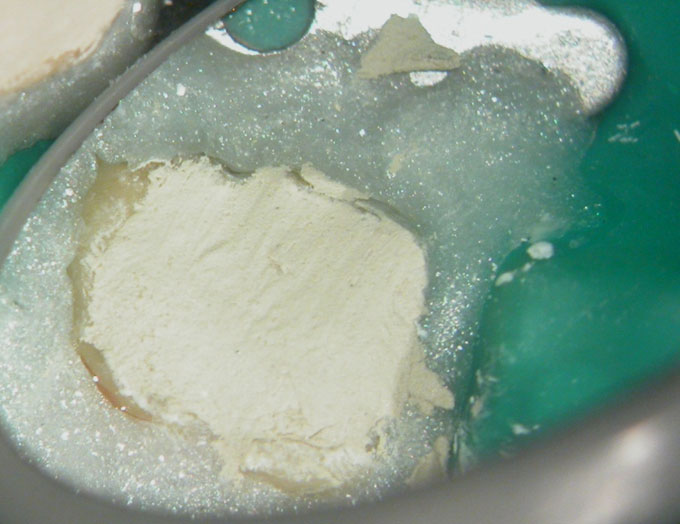

Calcium hydroxide placed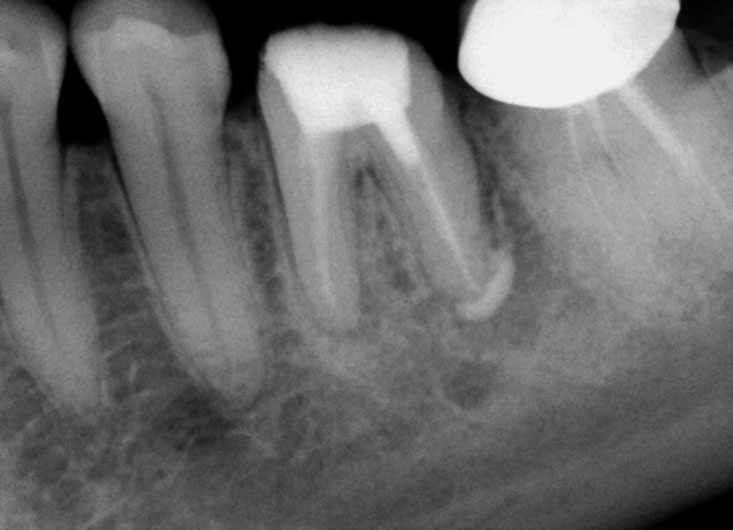
After 3 months of Calcium Hydroxide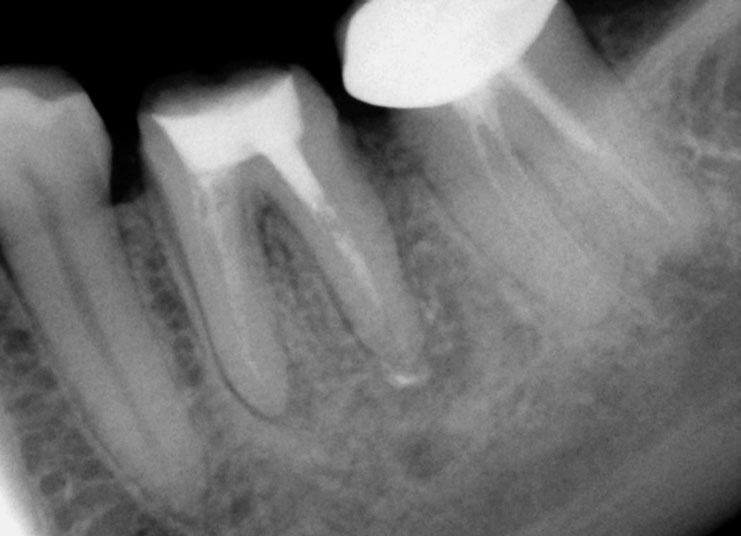
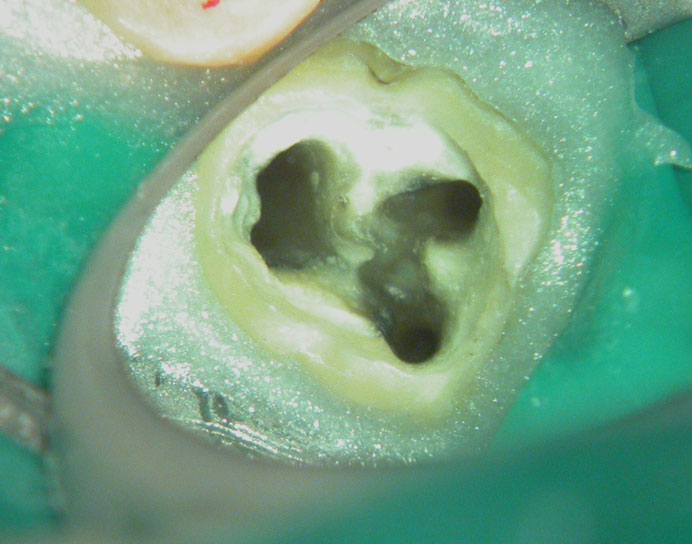
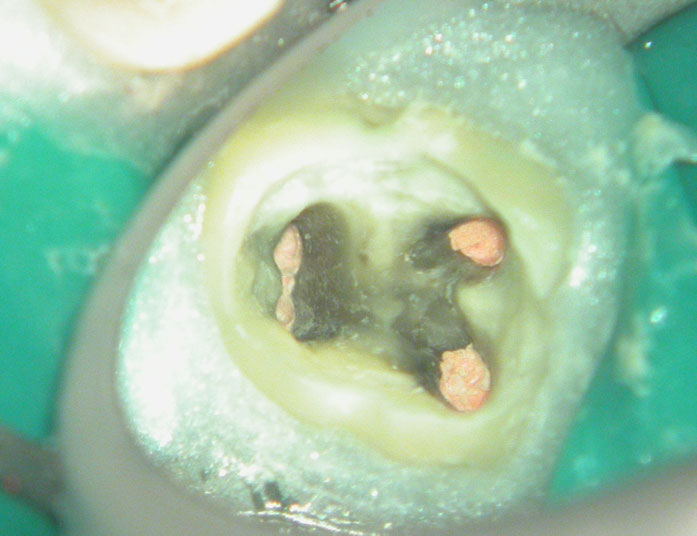
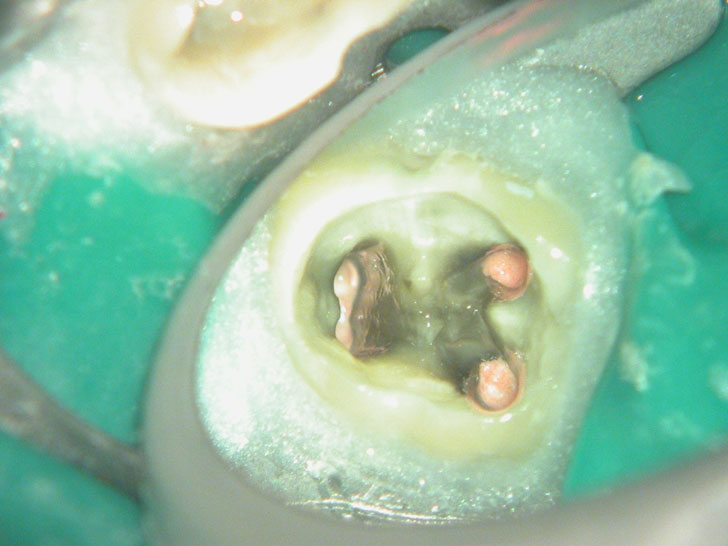
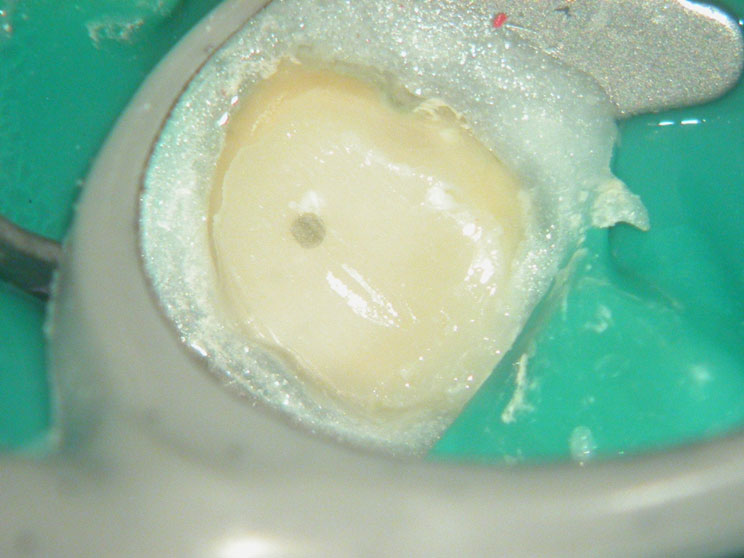
POST-OP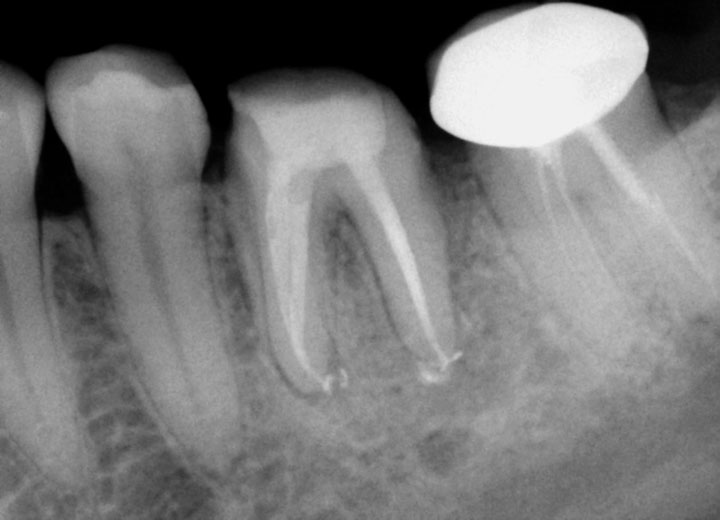
ONE-YEAR RECALL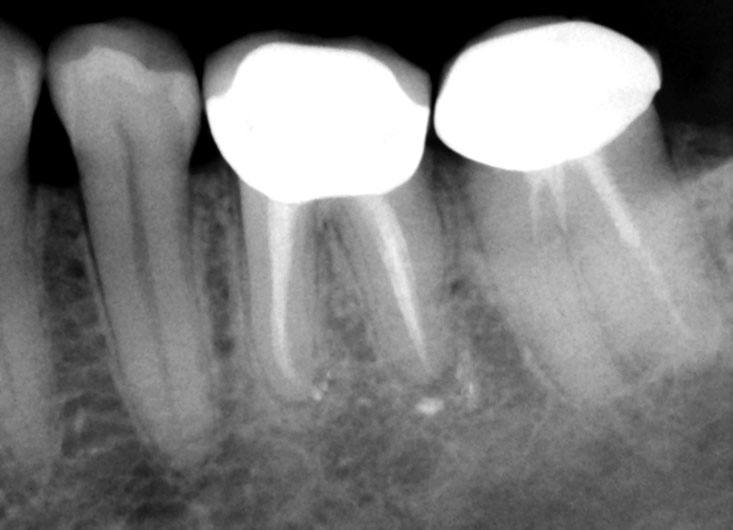
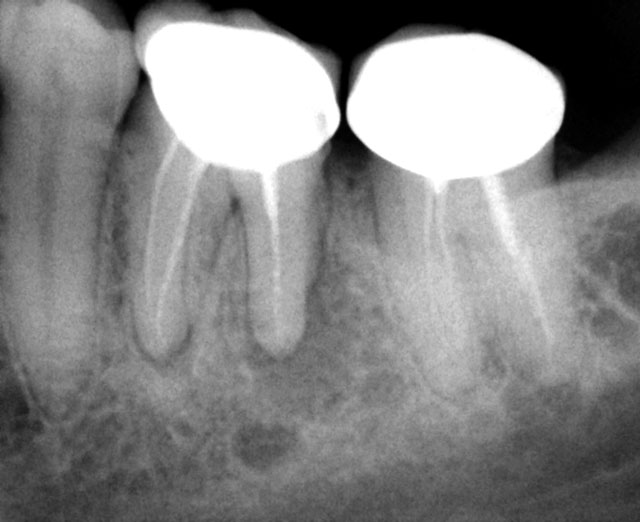
PRE-OP & ONE-YEAR RECALL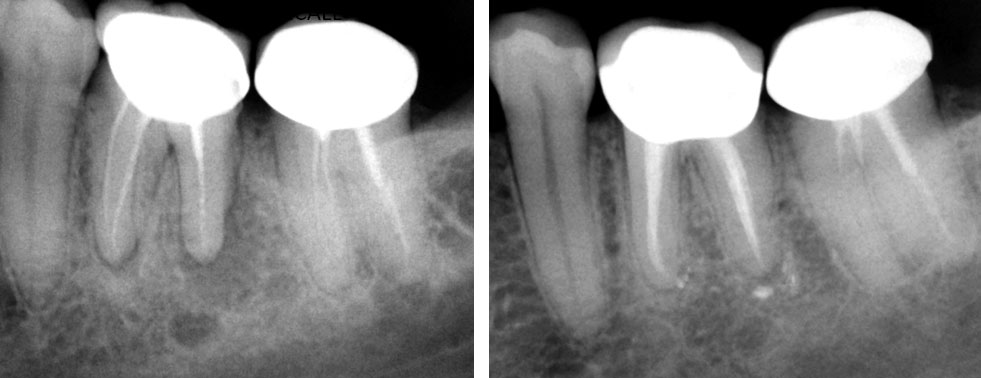
Clinical Case
Pre-op
Contact of file with metal gives a false“beyond the apex” reading on the apex locator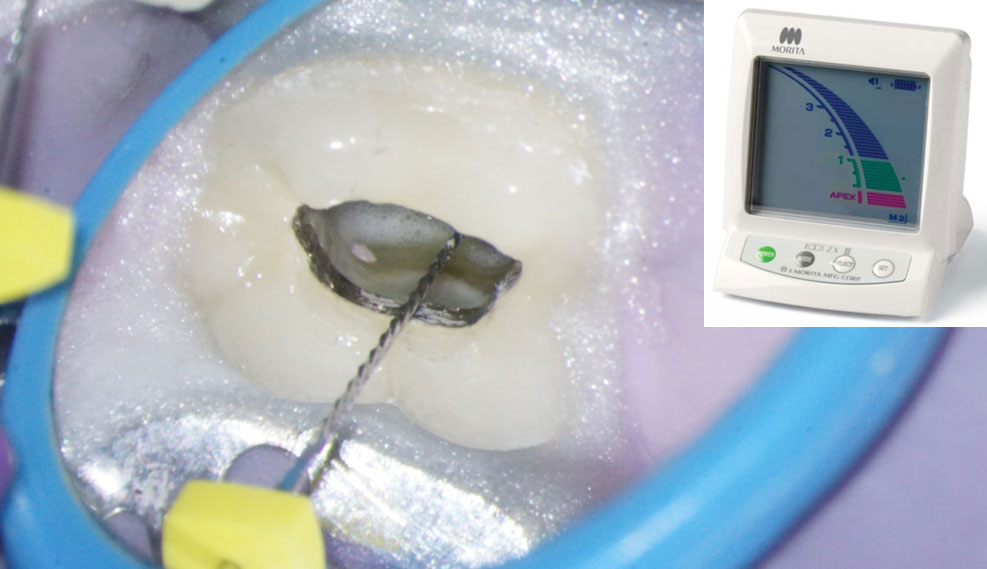
Opal dam to cover metal surface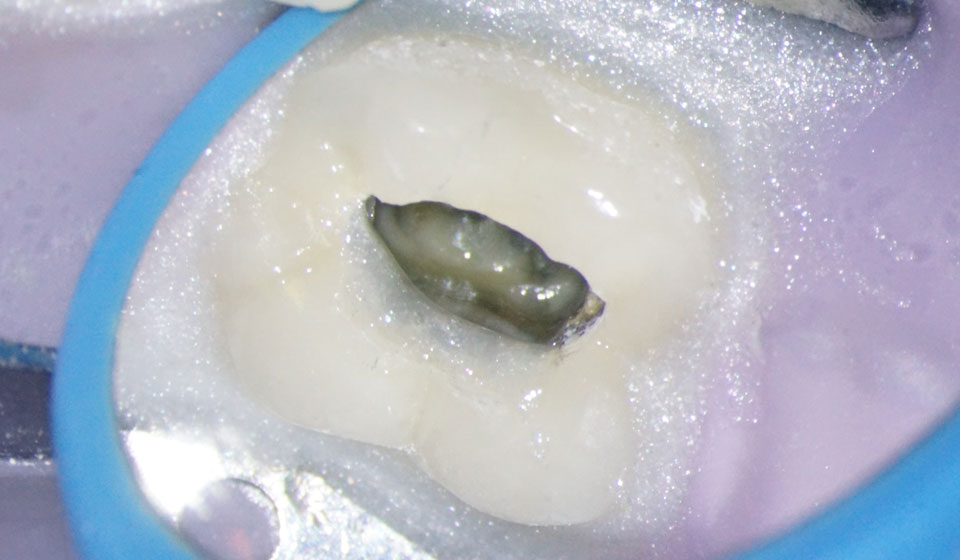
Opal Dam prevents contact with metal. 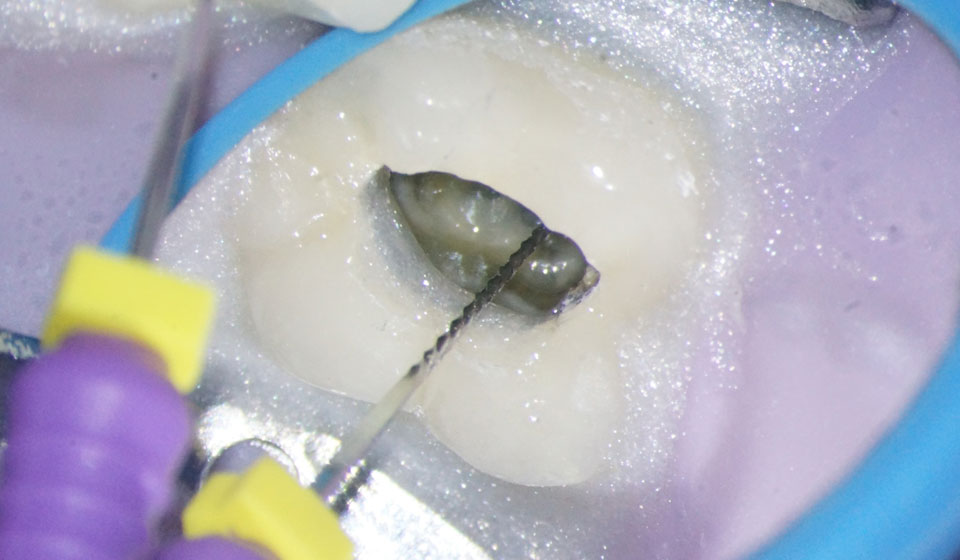
Clinical Case
REFERRAL RADIOGRAPH & PRE-OP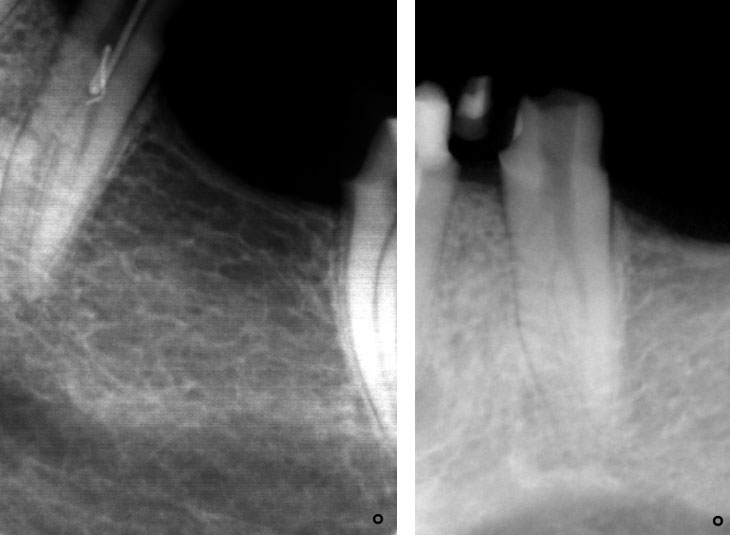
Master cone radiograph 1, Master cone radiograph 2 & Post-op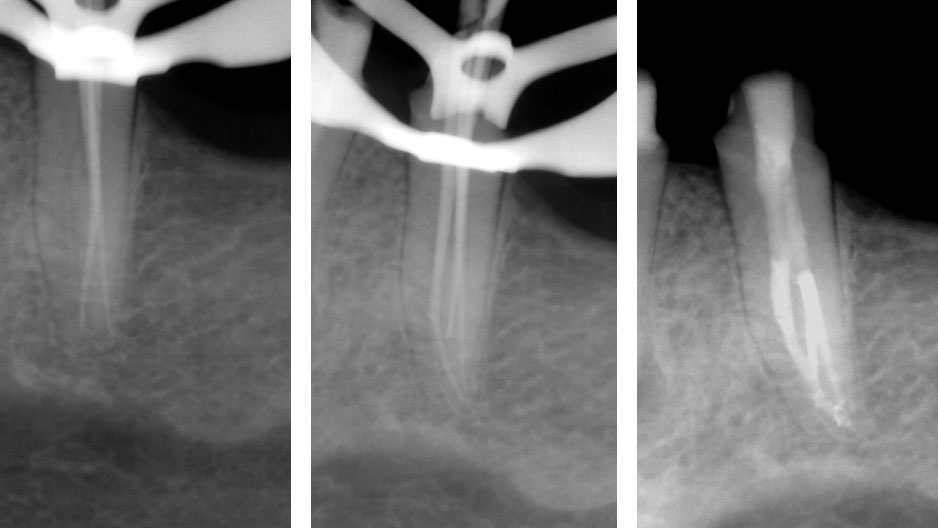
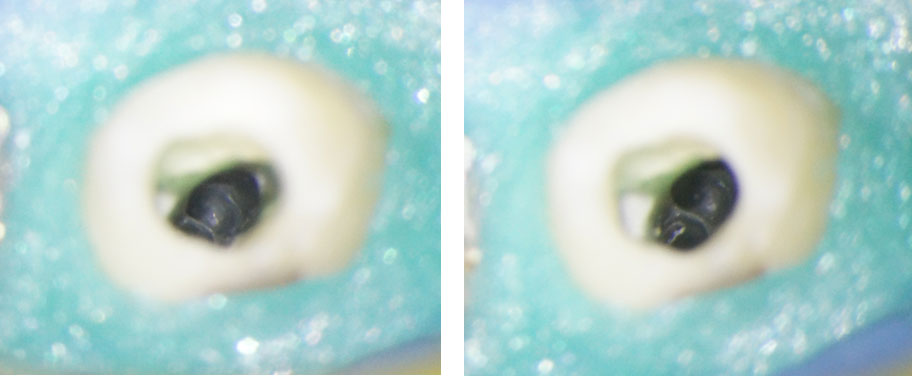
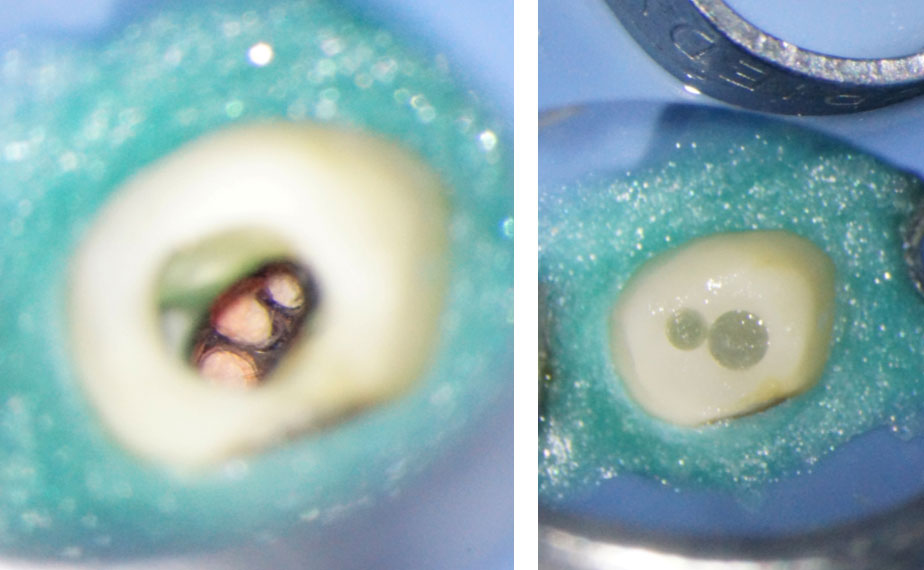
PRE-OP & POST-OP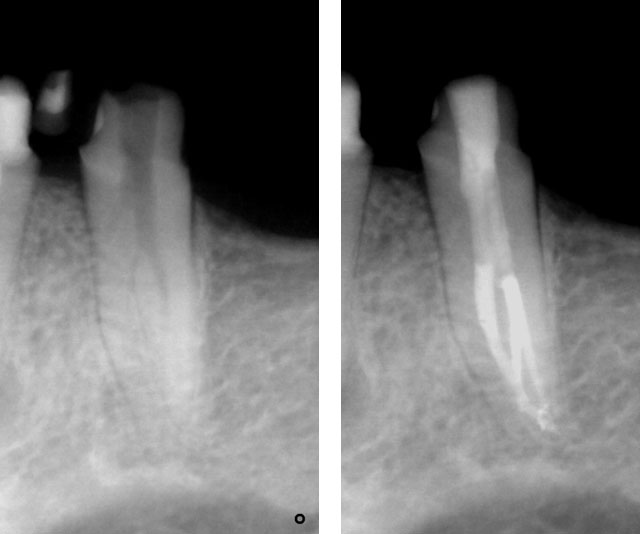
Clinical Case